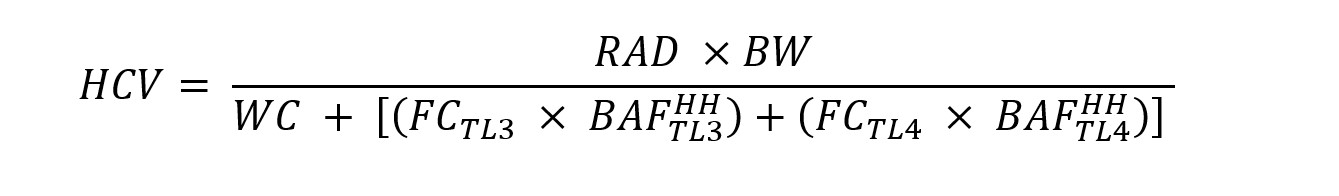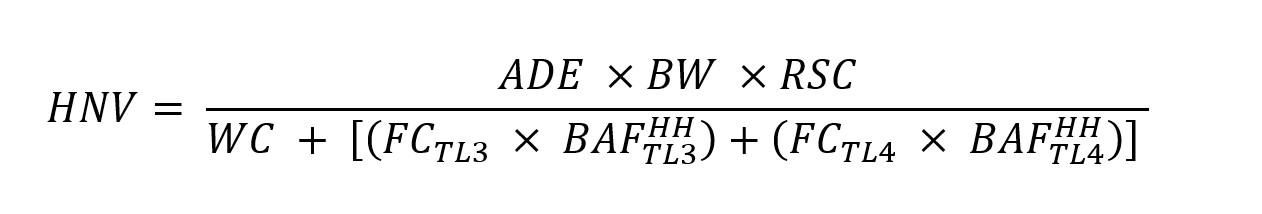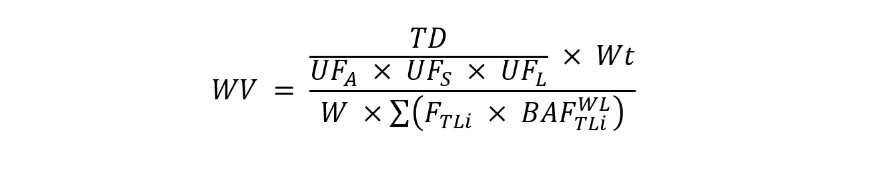This website publishes administrative rules on their effective dates, as designated by the adopting state agencies, colleges, and
universities.
| Rule |
Rule 3745-1-01 | Purpose and applicability.
Effective:
March 20, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government
publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations,
federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see
rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) The purpose of these water quality
standards, in this chapter, is to establish minimum water quality requirements
for all surface waters of the state, thereby protecting public health and
welfare; and to enhance, improve and maintain water quality as provided under
the laws of the state of Ohio, section 6111.041 of the Revised Code, the
federal Clean Water Act, and rules adopted thereunder. (B) Whenever two or more use designations
apply to the same surface water, the more stringent criteria of each use
designation applies. (C) These water quality standards apply
to all surface waters of the state except as provided in paragraph (D), (E), or
(F) of this rule. Compliance schedules may be granted pursuant to rule
3745-33-05 of the Administrative Code. (D) These water quality standards do not
apply to water bodies when the flow is less than the critical low-flow values
determined in rule 3745-2-05 of the Administrative Code. (E) General exceptions. The following
exceptions apply only to the specific water quality criteria involved in each
case for a reasonable period of time as determined by the
director: (1) Pesticide chemicals
applied for control of aquatic plants or animals in the intended application
area, if the following conditions are met: (a) The pesticide is applied in accordance with label
instructions. (b) The pesticide is applied consistent with a national pollutant
discharge elimination system (NPDES) permit, if an NPDES permit for the
activity is in force. (c) If an NPDES permit for the activity is not in force, notice
must be given to the director if the proposed application is for any of the
following: (i) Algae, weed, or
nuisance animal control in public water supply reservoirs. (ii) Nuisance fish
control. (iii) Algae, weed, or
nuisance animal control in waters classified in rule 3745-1-05 of the
Administrative Code as outstanding national resource waters, outstanding state
waters, or superior high quality waters other than lake Erie. (iv) Algae or weed
control in lake Erie done by aircraft. (v) Forest pest
control. The director, upon receiving such notice, may
order that the chemicals not be applied if the director concludes that the
proposed application would pose an unreasonable danger to human or aquatic
life. (2) Exceptions for water
quality disturbance caused by construction activities. Temporary exceptions may
apply whenever construction occurs on or near water bodies or during the period
of time when the aftereffects of construction activities degrade water quality
and such activities have been authorized by any of the following: (a) The United States army corps of engineers or by a section 401
water quality certification. (b) A state isolated wetland permit issued by the Ohio
environmental protection agency. (c) A construction storm water permit for earth disturbing
activities greater than one acre issued by the Ohio environmental protection
agency. (3) Whenever coal
remining permits are issued pursuant to section 301(p) of the act. This
exception applies to pH, iron and manganese for the duration of the remining
activity. This exception applies only if: there is a demonstrated potential for
improved water quality from the remining operation and no degradation of
existing instream conditions occurs. (F) Criteria and exceptions for dredging
and depositing of dredged material. The following criteria and exceptions apply
only to the specific water quality criteria involved in each case for a
reasonable period of time as determined by the director: (1) Criteria applied in
lake Erie. The following criteria apply to dredging work associated with the
regular maintenance of federal navigation channels and ports on lake
Erie: (a) No modeled increase in "bioaccumulation" of a
"bioaccumulative chemical of concern" as those terms are defined in
rule 3745-1-02 of the Administrative Code as a result of the deposit of dredged
material. (b) No deposit of dredged material unless the director authorizes
the deposit of dredged material pursuant to division (C) of section 6111.32 of
the Revised Code or makes a determination pursuant to division (E) of section
6111.32 of the Revised Code. (2) Exceptions from other
criteria. Temporary exceptions from criteria other than those found in
paragraph (F)(1) of this rule may apply whenever dredging and depositing of
dredged material occurs on or near water bodies or during the period of time
when the aftereffects of dredging activities degrade water quality and such
activities have been authorized by the United States army corps of engineers
and by a section 401 water quality certification or state isolated wetland
permit issued by the Ohio environmental protection agency. (G) Temporary variances. The director may
grant temporary variances from compliance with water quality criteria
applicable by this chapter pursuant to rule 3745-1-38 of the Administrative
Code.
Last updated June 25, 2025 at 6:59 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-02 | Definitions.
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) Acronyms and abbreviations used in this chapter are defined as follows: | AAC | Acute aquatic criterion | | AAV | Acute aquatic value | | ACR | Acute-chronic ratio | | ADE | Acceptable daily exposure | | AIM | Area of initial mixing | | BAF | Bioaccumulation factor | | BCC | Bioaccumulative chemical of concern | | BCF | Bioconcentration factor | | BSAF | Biota-sediment accumulation factor | | BW | Body weight | | CAC | Chronic aquatic criterion | | CAV | Chronic aquatic value | | CBOD5 | Five-day carbonaceous biochemical oxygen demand | | C.F.R. | Code of federal regulations | | DOC | Dissolved organic carbon | | ECBP | Eastern corn belt plains ecoregion | | EC50 | Median effective concentration | | EOLP | Erie/Ontario lake plain ecoregion | | EPA | Environmental protection agency | | FACR | Final acute-chronic ratio | | FAV | Final acute value | | FCM | Food-chain multiplier | | FCV | Final chronic value | | FPV | Final plant value | | GMAV | Genus mean acute value | | GMCV | Genus mean chronic value | | HCC | Human cancer criterion | | HCV | Human cancer value | | HELP | Huron/Erie lake plain ecoregion | | HNC | Human noncancer criterion | | HNV | Human noncancer value | | IMZM | Inside mixing zone maximum | | IP | Interior plateau ecoregion | | IRIS | Integrated risk information system | | KOW | Octanol-water partition coefficient | | LC50 | Median lethal concentration | | ln | Natural logarithm | | LOAEL | Lowest observed adverse effect level | | log10 | Base ten logarithm | | MDL | Method detection limit | | NOAEL | No observed adverse effect level | | NPDES | National pollutant discharge elimination system | | OMZA | Outside mixing zone average | | OMZM | Outside mixing zone maximum | | POC | Particulate organic carbon | | POTW | Publicly owned treatment works | | q1* | Cancer slope factor | | QHEI | Qualitative habitat evaluation index | | RAD | Risk associated dose | | RSC | Relative source contribution | | S | Soluble | | SACR | Secondary acute-chronic ratio | | SAF | Secondary acute factor | | SAR | Structure-activity relationship | | SAV | Secondary acute value | | SMAV | Species mean acute value | | SMCV | Species mean chronic value | | T | Total | | TD | Test dose | | temp | Temperature | | TL | Trophic level | | TMDL | Total maximum daily load | | TR | Total recoverable | | UF | Uncertainty factor | | U.S.C. | United States Code | | WAP | Western Allegheny plateau ecoregion | | WET | Whole effluent toxicity | | WLA | Wasteload allocation | | WV | Wildlife value |
(B) Technical terms used in this chapter are defined as follows: (1) "Acceptable daily exposure" or "ADE" means an estimate of the maximum daily dose of a substance which is not expected to result in adverse noncancer effects to the general human population, including sensitive subgroups. (2) "Act" means the federal Water Pollution Control Act, 33 U.S.C. sections 1251 to 1387. (3) "Acute aquatic criterion" or "AAC" means the Ohio EPA estimate of the highest concentration of a material in the water column to which an aquatic community can be exposed briefly without resulting in an unacceptable effect including but not limited to mortality. (4) "Acute-chronic ratio" or "ACR" means a standard measure of the acute toxicity of a material divided by an appropriate measure of the chronic toxicity of the same material under comparable conditions. (5) "Acute mixing zone" means the mixture of receiving water and effluent adjacent to a treated or untreated discharge within which the acute aquatic life criteria may be exceeded but the inside mixing zone maximum criteria are not to be exceeded. The acute aquatic life criteria are to be met on the downstream perimeter of the acute mixing zone. (6) "Acute toxicity" means concurrent and delayed adverse effects that result from an acute exposure and occur within any short observation period which begins when the exposure begins, may extend beyond the exposure period, and usually does not constitute a substantial portion of the life span of the organism. (7) "Adverse effect" means any deleterious effect to organisms due to exposure to a substance. This includes effects which are or may become debilitating, harmful or toxic to the normal functions of the organism, but does not include non-harmful effects such as tissue discoloration alone or the induction of enzymes involved in the metabolism of the substance. (8) "Ambient water temperature" means the spatial (longitudinal, lateral and vertical) and temporal water temperature measured in the receiving body of water prior to a specific waste heat discharge, and is outside the influence of any thermal mixing zone. (9) "Area of initial mixing" or "AIM" means the limited zone where discharge-induced mixing causes the effluent to rapidly mix with the receiving water such that the area is not physically inhabitable to aquatic life. The inside mixing zone maximum criteria may be exceeded within the AIM but is to be met on the perimeter of the AIM. (10) "Average temperature" represents the arithmetic mean of multiple daily average temperatures over a consecutive fifteen-day or thirty-day period or as otherwise specified in rule. (11) "Baseline BAF" means: (a) For organic chemicals, a BAF that is based on the concentration of freely dissolved chemical in the ambient water and takes into account the partitioning of the chemical within the organism. (b) For inorganic chemicals, a BAF that is based on the wet weight of the tissue. (12) "Baseline BCF" means: (a) For organic chemicals, a BCF that is based on the concentration of freely dissolved chemical in the ambient water and takes into account the partitioning of the chemical within the organism. (b) For inorganic chemicals, a BCF that is based on the wet weight of the tissue. (13) "Beneficial uses" means potential uses of a water body by humans or other organisms, including uses for public water supply, propagation of aquatic life, recreation in and on the water, agricultural, industrial, or other purposes. (14) "Bioaccumulation" means the net accumulation of a substance by an organism as a result of uptake from all environmental sources. (15) "Bioaccumulation factor" or "BAF" means the ratio (in l/kg) of a substance's concentration in the tissue of an aquatic organism to its concentration in the ambient water, in situations where both the organism and its food are exposed and the ratio does not change substantially over time. (16) "Bioaccumulative chemical of concern" or "BCC" is any chemical that has the potential to cause adverse effects which, upon entering the surface waters, by itself or as its toxic transformation product, accumulates in aquatic organisms by a human health bioaccumulation factor greater than one thousand, after considering metabolism and other physicochemical properties that might enhance or inhibit bioaccumulation, calculated in accordance with the methodology in rule 3745-1-41 of the Administrative Code. Chemicals with half-lives of less than eight weeks in the water column, sediment, and biota are not BCCs. The minimum BAF information needed to define an organic chemical as a BCC is either a field-measured BAF or a BAF derived using the BSAF methodology. The minimum BAF information needed to define an inorganic chemical, including an organometal, as a BCC is either a field-measured BAF or a laboratory-measured BCF. Bioaccumulative chemicals of concern include, but are not limited to, chlordane, 4,4'-DDD (p,p'-DDD, 4,4'-TDE, p,p'-TDE), 4,4'-DDE (p,p'-DDE), 4,4'-DDT (p,p'-DDT), dieldrin, hexachlorobenzene, hexachlorobutadiene (hexachloro-1,3-butadiene), hexachlorocyclohexanes (BHCs), alpha-hexachlorocyclohexane (alpha-BHC), beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (beta-BHC), delta-hexachlorocyclohexane (delta-BHC), lindane (gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane, gamma-BHC), mercury, mirex, octachlorostyrene, PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls), pentachlorobenzene, photomirex, 2,3,7,8-TCDD (dioxin), 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorobenzene, 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene, and toxaphene. (17) "Bioconcentration" means the net accumulation of a substance by an aquatic organism as a result of uptake directly from the ambient water through gill membranes or other external body surfaces. (18) "Bioconcentration factor" or "BCF" means the ratio (in l/kg) of a substance's concentration in the tissue of an aquatic organism to its concentration in the ambient water, in situations where the organism is exposed through the water only and the ratio does not change substantially over time. (19) "Biota-sediment accumulation factor" or "BSAF" means the ratio (in kg of organic carbon/kg of lipid) of a substance's lipid-normalized concentration in the tissue of an aquatic organism to its organic carbon-normalized concentration in surface sediment, in situations where the ratio does not change substantially over time, both the organism and its food are exposed, and the surface sediment is representative of average surface sediment in the vicinity of the organism. (20) "°C" means degree Celsius. (21) "Carcinogen" means a substance which causes an increased incidence of benign or malignant neoplasms, or substantially decreases the time to develop neoplasms, in animals or humans. The classification of carcinogens is discussed in rule 3745-1-42 of the Administrative Code. (22) "Chronic aquatic criterion" or "CAC" means an estimate of the highest concentration of a material in the water column (ambient water) to which an aquatic community can be exposed indefinitely without resulting in an unacceptable adverse effect, including but not limited to effects on growth or reproduction. This is the chronic criterion. (23) "Chronic mixing zone" means the mixture of receiving water and effluent adjacent to a treated or untreated discharge within which the chronic aquatic life, human health, wildlife and agricultural water supply criteria may be exceeded. The chronic aquatic life, human health, wildlife and agricultural water supply criteria are met on the downstream perimeter of the chronic mixing zone. (24) "Chronic toxicity" means concurrent and delayed adverse effects that occur only as a result of a chronic exposure. Chronic exposure is exposure of an organism for any long period or for a substantial portion of its life span. (25) "Coldwater fauna" means the species of aquatic animal life adapted to waters having temperatures moderated by contributions from deep or perched aquifers or springs. Water temperatures in such streams typically average less than twenty-one degrees Celsius and rarely exceed twenty-four degrees Celsius. (26) "Confluence" means the point where two or more bodies of water flow together. (27) "Criteria" mean elements of water quality standards, expressed as constituent concentrations, levels, or narrative statements, representing a quality of water that supports a particular designated use. (28) "Criterion continuous concentration" or "CCC" means an estimate of the highest concentration of a material in the water column (ambient water) to which an aquatic community can be exposed indefinitely without resulting in an unacceptable adverse effect, including but not limited to effects on growth or reproduction. This is the chronic criterion. (29) "Daily average temperature" means the arithmetic mean of multiple temperature measurements to be taken at least once per hour during a twenty-four-hour day. (30) "Daily maximum temperature" means the highest temperature observed in a twenty-four-hour day. (31) "Degradation" means a lowering of the existing water quality in the surface waters of the state. (32) "Depuration" means the loss of a substance from an organism as a result of any active or passive process. (33) "Designated use" means a beneficial use assigned in this chapter for a water body or segment, whether or not that use is being attained. Specific designated uses are defined in rule 3745-1-07 of the Administrative Code. (34) "Director" means the director of the Ohio environmental protection agency or the director's duly authorized representative. (35) "Discharge" means the addition of any pollutant to the waters of the state from a point source. (36) "Discharge induced mixing" means the state of mixing between the receiving water and effluent where the processes causing the mixing are induced primarily by the momentum of the effluent as it enters the receiving water. (37) "E. coli" means Escherichia coli, a specific bacterial species included in the fecal coliform bacteria group, the presence of which in surface waters has been correlated with gastrointestinal illness in swimmers. (38) "EC50" means the median effective concentration and is a statistically or graphically estimated concentration that is expected to cause one or more specified effects in fifty per cent of a group of organisms under specified conditions. (39) "Endangered species" means any of the following: (a) A native Ohio plant species listed or designated by the Ohio department of natural resources as endangered pursuant to section 1518.01 of the Revised Code. (b) An animal species listed or designated as endangered by the Ohio department of natural resources pursuant to section 1531.25 of the Revised Code. (c) Any plant or animal species that is native to Ohio or that migrates or is otherwise reasonably likely to occur within the state and which has been listed as endangered pursuant to Section 4 of the Endangered Species Act, 16 U.S.C. section 1533. (40) "Ephemeral feature" means surface water flowing or pooling only in direct response to precipitation, such as rain or snow. "Ephemeral feature" does not include a wetland as defined in section 6111.02 of the Revised Code. (41) "Existing uses" means those uses actually attained in the water body on or after November 28, 1975. (42) "°F" means degree Fahrenheit. (43) "Fecal coliform" means the portion of the coliform group of bacteria which is present in the intestinal tract of warmblooded animals, and is evidence of the presence of human or animal wastes. (44) "Final acute value" or "FAV" means either of the following: (a) A calculated estimate of the concentration of a test material such that ninety-five per cent of the genera (with which acceptable acute toxicity tests have been conducted on the material) have higher GMAVs. (b) The SMAV of an important or critical species, if the SMAV is lower then the calculated estimate. (45) "Final chronic value" or "FCV" means any one of the following: (a) A calculated estimate of the concentration of a test material such that ninety-five per cent of the genera (with which acceptable chronic toxicity tests have been conducted on the material) have higher GMCVs. (b) The quotient of an FAV divided by an appropriate acute-chronic ratio. (c) The SMCV of an important and/or critical species, if the SMCV is lower than the calculated estimate or the quotient, whichever is applicable. (46) "Final plant value" or "FPV" means the lowest plant value obtained with an important aquatic plant species in an acceptable toxicity test for which the concentrations of the test material were measured and the adverse effect was biologically important. (47) "Food-chain multiplier" or "FCM" means the ratio of a BAF to an appropriate BCF. A food-chain multiplier is meant to account for accumulation of a chemical up the food chain attributable to predation (i.e., between successive trophic levels). (48) "Genus mean acute value" or "GMAV" means the geometric mean of the SMAVs for the genus. (49) "Genus mean chronic value" or "GMCV" means the geometric mean of the SMCVs for the genus. (50) "Geometric mean" means the Nth root of the product of N quantities. (51) "Great Lakes system" means all the streams, rivers, lakes and other bodies of water within the drainage basin of the Great Lakes within the United States. (52) "Human cancer criterion" or "HCC" is a human cancer value for a pollutant that meets the minimum data requirements for tier I as specified in rule 3745-1-42 of the Administrative Code. (53) "Human cancer value" or "HCV" is the maximum ambient water concentration of a substance at which a lifetime of exposure from either: drinking the water, consuming fish from the water, and water-related recreation activities; or consuming fish from the water, and water-related recreation activities, will represent a plausible upper-bound risk of contracting cancer of one in one hundred thousand using the exposure assumptions specified in the methodologies for the development of human health criteria and values in rule 3745-1-42 of the Administrative Code. (54) "Human noncancer criterion" or "HNC" is a human noncancer value for a pollutant that meets the minimum data requirements for tier I as specified in rule 3745-1-42 of the Administrative Code. (55) "Human noncancer value" or "HNV" is the maximum ambient water concentration of a substance at which adverse noncancer effects are not likely to occur in the human population from lifetime exposure from either: drinking the water, consuming fish from the water, and water-related recreation activities; or consuming fish from the water and water-related recreation activities, using the methodologies for the development of human health criteria and values in rule 3745-1-42 of the Administrative Code. (56) "Lacustuary" is a reach of a given tributary where stream habitat and flow dynamics are affected by lake Erie water levels. In addition to direct lake Erie tributaries, all inland streams and rivers that are tributary to a lake Erie lacustuary are considered a lacustuary in reaches affected by the lake Erie water level. [Comment: Although "lacustuary" is the preferred terminology, the term "estuary" is occasionally used and should be considered interchangeable with "lacustuary" when used consistent with this definition.] (57) "Lake" means a standing body of open water that is present year round, occurs in a natural depression or is created by artificially blocking or restricting the flow of a stream or by diking or excavating dry land where the resulting water body serves as a public water supply or is on public property with public access. (58) "Lake Erie drainage basin" means all the streams, rivers, lakes and other bodies of water within the drainage basin of lake Erie and within the United States. (59) "LC50" means the median lethal concentration and is a statistically or graphically estimated concentration that is expected to be lethal to fifty per cent of a group of organisms under specified conditions. (60) "Linearized multistage model" means a conservative mathematical model for cancer risk assessment. This model fits linear dose-response curves to low doses. It is consistent with a no-threshold model of carcinogenesis, i.e., exposure to even a very small amount of the substance is assumed to produce a finite increased risk of cancer. (61) "Lowest observed adverse effect level" or "LOAEL" means the lowest tested dose or concentration of a substance which results in an observed adverse effect in exposed test organisms when all higher doses or concentrations result in the same or more severe effects. (62) "Method detection limit" or "MDL" means the minimum measured concentration of a substance that can be reported with ninety-nine per cent confidence that the measured concentration is distinguishable from method blank results. (63) "Micrograms per liter (ug/l)" means the micrograms of substance per liter of solution, and is equivalent to 10-9 kilograms per liter or parts per billion, assuming unit density. (64) "Milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg)" means the milligrams of substance per kilogram of weight. (65) "Milligrams per liter (mg/l)" means the milligrams of substance per liter of solution, and is equivalent to 10-6 kilograms per liter or parts per million, assuming unit density. (66) "Mine drainage" means surface or groundwater flowing through or from mines and mine sites. It is usually characterized by concentrations of acidity or alkalinity, various heavy metals, sulfates, and dissolved solids. (67) "Mixing zone" means an area of a water body contiguous to a treated or untreated wastewater discharge. This discharge is in transit and progressively diluted from the source concentration to the receiving system concentration. The mixing zone is considered a place where wastewater and receiving water mix, not a place where wastes are treated. (68) "Nanograms per liter (ng/l)" means the nanograms of substance per liter of solution, and is equivalent to 10-12 kilograms per liter or parts per trillion, assuming unit density. (69) "Natural conditions" mean those conditions that are measured outside the influence of human activities. (70) "New discharge", for the purposes of implementing the bioaccumulative chemical of concern provisions in Chapter 3745-2 of the Administrative Code, means any of the following: (a) A discharge of pollutants to a water body from a building, structure, facility or installation, the construction of which commences after December 30, 2002. (b) A new discharge from an existing discharger that commences after December 30, 2002. (c) An expanded discharge from an existing discharger that commences after December 30, 2002, except for those expanded discharges resulting from changes in loadings of any BCC within the existing capacity and processes (e.g., normal operational variability, changes in intake water pollutants, increasing the production hours of the facility or adding additional shifts, or increasing the rate of production), and that are covered by the existing Ohio national pollutant discharge elimination system permit. Not included within the definition of "new discharge" are new or expanded discharges of BCCs from a publicly owned treatment works when such discharges are necessary to prevent a public health threat to the community (e.g., a situation where a community with failing septic systems is connected to a POTW to avert a potential public health threat from these failing systems). These and all other discharges of BCCs are defined as existing discharges. (71) "No observed adverse effect level" or "NOAEL" means the highest tested dose or concentration of a substance which results in no observed adverse effect in exposed test organisms where higher doses or concentrations result in an adverse effect. (72) "Nonpoint source" means any source of pollutants other than those defined or designated as point sources. (73) "Octanol-water partition coefficient" or "Kow" means the ratio of the concentration of a substance in the N-octanol phase to its concentration in the aqueous phase in an equilibrated two-phase octanol-water system. For log Kow, the log of the octanol-water partition coefficient is a base ten logarithm. (74) "Ohio river drainage basin" means all the streams, rivers, lakes and other bodies of water within the drainage basin of the Ohio river. (75) "pH" means the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion activity concentrations when expressed as moles per liter or pH = -log (H+). (76) "Picograms per liter (pg/l)" means the picograms of substance per liter of solution, and is equivalent to 10-15 kilograms per liter or parts per quadrillion, assuming unit density. (77) "Point source" means any discernible, confined or discrete conveyance from which a pollutant is or may be discharged to the surface waters of the state. (78) "Pollutant" means sewage, industrial waste or other waste as defined by divisions (B) to (D) of section 6111.01 of the Revised Code. (79) "Pollution prevention alternatives assessment" means an analysis that identifies any cost-effective pollution prevention alternatives and techniques that are available to the discharger, and that would reduce the extent to which the increased loading results in a lowering of water quality. A pollution prevention alternatives analysis demonstrates a good faith effort by the discharger to review equipment or technology modifications, process or procedure modifications, reformulation or redesign of products, substitution of raw materials and improvements to housekeeping. The discharger will not need to implement a pollution prevention alternative if it is not technically or economically feasible. (80) "Public water system" means the same as the definition in rule 3745-81-01 of the Administrative Code. (81) "Publicly owned treatment works" or "POTW" means any device or system used in the treatment (including recycling and reclamation) of domestic sewage or industrial waste of a liquid nature that is owned by a municipality, county, or state entity or any public body created under state law that has authority over disposal of sewage. (82) "Qualitative habitat evaluation index" or "QHEI" means an assessment methodology of the principal physical and riparian stream habitat features that affect fish communities and other aquatic life. (83) "Receiving waters" mean the surface waters of the state into which point and nonpoint sources flow. (84) "Relative source contribution" or "RSC" means the factor (percentage) used in calculating a HNV or HNC to account for all sources of exposure to a contaminant. The RSC reflects the per cent of total exposure which can be attributed to surface water through water intake and fish consumption. (85) "Representative aquatic species" mean those organisms, either natural or introduced, which presently exist or have existed in the surface waters of the state prior to July 1, 1977, with the exception of those banned species outlined in rule 1501:31-19-01 of the Administrative Code. In addition, it may include any species that are legally introduced into the surface waters of the state. Aquatic species designated as representative satisfy one or more of the following: (a) Species that are particularly vulnerable to the existing or proposed environmental impact in question. (b) Species that are commercially or recreationally valuable. (c) Species that are threatened, rare, or endangered. (d) Species that are critical to the structure and function of the aquatic community. (e) Species whose presence is causally related to the existing or proposed environmental impact under examination. (f) Species that are potentially capable of becoming localized nuisance species. (g) Species that are representative of the ecological, behavioral, and physiological requirements and characteristics of species determined in paragraphs (B)(77)(a) to (B)(77)(f) of this rule, but which themselves might not be representative. (86) "Risk associated dose" or "RAD" means a dose of a known or presumed carcinogenic substance in (mg/kg) /day which, over a lifetime of exposure, is estimated to be associated with a plausible upper bound incremental cancer risk equal to one in one hundred thousand. (87) "Slope factor" or "Q1*" means the incremental rate of cancer development calculated through use of a linearized multistage model or other appropriate model. It is expressed in (mg/kg/day) of exposure to the chemical in question. (88) "Species mean acute value" or "SMAV" means the geometric mean of the results of all acceptable flow-through acute toxicity tests (for which the concentrations of the test material were measured) with the most sensitive tested life stage of the species. For a species for which no such result is available for the most sensitive tested life stage, the SMAV is the geometric mean of the results of all acceptable acute toxicity tests with the most sensitive tested life stage. (89) "Species mean chronic value" or "SMCV" means the geometric mean of the results of all acceptable life-cycle and partial life-cycle toxicity tests with the species; for a species of fish for which no such result is available, the SMCV is the geometric mean of all acceptable early life-stage tests. (90) "Structure-activity relationship" or "SAR" means a mathematical relationship between a property (i.e., biological activity or response) of a chemical and a number of descriptors of the chemical. These descriptors are chemical or physical characteristics obtained experimentally or predicted from the structure of the chemical. (91) "Surface waters of the state" or "water bodies" mean all streams, lakes, reservoirs, ponds, marshes, wetlands or other waterways which are situated wholly or partially within the boundaries of the state, except those private waters which do not combine or effect a junction with natural surface or underground waters. Waters defined as sewerage system, treatment works or disposal system in section 6111.01 of the Revised Code are not included. (92) "Thermal mixing zone" means that portion of a water body into which waste heat is discharged and assimilated, and within which the average and maximum daily average temperatures do not apply, except as prescribed by this chapter. (93) "Threatened species" means any of the following: (a) A native Ohio plant species listed or designated by the Ohio department of natural resources as threatened with extirpation pursuant to section 1518.01 of the Revised Code. (b) An animal species listed or designated as threatened with statewide extinction by the Ohio department of natural resources pursuant to section 1531.25 of the Revised Code. (c) Any plant or animal species that is native to Ohio or that migrates or is otherwise reasonably likely to occur within the state and which has been listed as threatened pursuant to Section 4 of the Endangered Species Act, 16 U.S.C. section 1533. (94) "Threshold effect" means an effect of a substance for which there is a theoretical or empirically established dose or concentration below which the effect does not occur. (95) "Tier I criteria" mean numeric values derived by use of the tier I methodologies specified in rules 3745-1-40, 3745-1-42 and 3745-1-43 of the Administrative Code, that either have been adopted as numeric criteria into a water quality standard or are used to implement narrative water quality criteria. (96) "Tier II values" means numeric values derived by use of the tier II methodologies specified in rules 3745-1-40 and 3745-1-42 of the Administrative Code that are used to implement narrative water quality criteria. (97) "Total maximum daily load" or "TMDL" means the sum of the existing or projected point source, nonpoint source, and background loads for a pollutant to a specified watershed, water body, or water body segment. A TMDL sets and allocates the maximum amount of a pollutant that may be introduced into the water and still ensures attainment and maintenance of water quality standards. (98) "Toxic substances" mean any substances which can cause death, disease, behavioral abnormalities, cancer, genetic mutations, physiological or reproductive malfunction or physical deformities in any organism or its offspring, or which can become poisonous after concentration in the food chain or in combination with other substances. (99) "Tributary" means a stream flowing into a larger body of water. (100) "Uncertainty factor" or "UF" means one of several numeric factors used in operationally deriving criteria from experimental data to account for the quality or quantity of the available data. (101) "Uptake" means acquisition of a substance from the environment by an organism as a result of any active or passive process. (102) "Use attainability analysis" means a structured scientific assessment of the factors affecting the attainment of the use which may include physical, chemical, biological, and economic factors. (103) "Warmwater fauna" means the species of aquatic animal life that occur where water temperature is primarily influenced by ambient air temperature; habitat and other characteristics also influence their range and propagation. (104) "Wasteload allocation" or "WLA" means the portion of a receiving water's loading capacity that is allocated to one of its existing or future point sources of pollution. In the absence of a TMDL or TMDL assessment and remediation plan, a WLA is the allocation for an individual point source that ensures that the level of water quality to be achieved by the point source is derived from and complies with all applicable water quality standards. (105) "Water bodies" or "waters of the state" mean all streams, lakes, ponds, marshes, watercourses, waterways, wells, springs, irrigation systems, drainage systems, and all other bodies or accumulations of water, surface and underground, natural or artificial, that are situated wholly or partly within, or border upon, this state, or are within its jurisdiction, except those private waters that do not combine or effect a junction with natural surface or underground waters. "Waters of the state" does not include an ephemeral feature for which the United States army corps of engineers lacks the authority to issue a permit under 33 U.S.C. section 1344. (106) "Water quality standards" means the rules set forth in this chapter establishing stream use designations and water quality criteria protective of such uses for the surface waters of the state. (107) "Wetlands" means those areas that are inundated or saturated by surface or ground water at a frequency and duration that are sufficient to support, and that under normal circumstances do support, a prevalence of vegetation typically adapted for life in saturated soil conditions. "Wetlands" includes swamps, marshes, bogs, and similar areas that are delineated in accordance with the 1987 United States army corps of engineers wetland delineation manual and any other procedures and requirements adopted by the United States army corps of engineers for delineating wetlands. (108) "Whole effluent toxicity" or "WET" means the aggregate toxic effect of an effluent measured directly by a toxicity test where the test results are based on acute (lethal) or chronic (lethal and sublethal) endpoints.
Last updated June 25, 2025 at 6:16 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-03 | Analytical methods and availability of documents.
Effective:
October 10, 2024
(A) Analytical methods. (1) All methods of
analysis used in applying any of the chemical-specific and bacteriological
criteria in this chapter shall be in accordance with those prescribed in 40
C.F.R. 136 and 405-471, except for chlorophyll a and pheophytin a, which shall
be in accordance with EPA method 445.0 as cited in paragraph (B) of this
rule. (2) All methods of sample
collection and preservation used in applying any of the chemical-specific and
bacteriological criteria in this chapter shall be in accordance with
"Surface Water Field Sampling Manual for water quality parameters and
flows" as cited in paragraph (B) of this rule. (3) Methods for
conducting whole-effluent toxicity tests shall be in accordance with those
prescribed in 40 C.F.R. 136, as cited in paragraph (B) of this
rule. (4) Mixing zones for
thermal discharges will be determined in accordance with "Guidelines for
the Submittal of Demonstrations Pursuant to Sections 316(a) and 316(b) of the
Clean Water Act and Chapter 3745-1 of the Administrative Code," as cited
in paragraph (B) of this rule. (5) Methods, data
collection, and data analysis requirements for applying the biological criteria
in rule 3745-1-07 of the Administrative Code shall be in accordance with
"Biological Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life" as cited in
paragraph (B) of this rule. (B) Availability of documents. The
following documents are cited in this chapter or used to administer
requirements of this chapter. (1) Code of Federal
Regulations (C.F.R.) references. The Code of Federal Regulations can generally
be found in public libraries, and can be viewed electronically online at
http://govinfo.gov and purchased by writing to: "Superintendent of
Documents. Attn: New Orders, PO Box 371954, Pittsburgh, PA 15250-7954."
The regulations listed in this paragraph are those effective July 1, 2022,
except for 50 C.F.R. 17, which is effective October 1, 2021. (a) 40 C.F.R. 124.8, "Procedures for Decisionmaking, Subpart
A - General Program Requirements - Fact sheet." (b) 40 C.F.R. 124.56, "Procedures for Decisionmaking,
Subpart D - Specific Procedures Applicable to NPDES Permits - Fact
Sheets." (c) 40 C.F.R. 131, "Water Quality
Standards." (d) 40 C.F.R. 132, "Water Quality Guidance for the Great
Lakes System." (e) 40 C.F.R. 136, "Guidelines Establishing Test Procedures
for the Analysis of Pollutants." (f) 40 C.F.R. 230.10, "Section 404(b)(1) Guidelines for
Specification of Disposal Sites for Dredged or Fill Material - Restrictions on
discharge." (g) 40 C.F.R. 400 to 471, "Subchapter N - Effluent
Guidelines and Standards." (h) 50 C.F.R. 17, "Endangered and Threatened Wildlife and
Plants." (2) Federal statute
references. These laws can generally be found in public libraries, and can be
viewed electronically online at http://govinfo.gov and purchased by writing to:
"Superintendent of Documents. Attn: New Orders, PO Box 371954, Pittsburgh,
PA 15250-7954." The laws listed in this paragraph are those as amended
through July 1, 2022. (a) "Federal Water Pollution Control Act (commonly referred
to as the Clean Water Act)," 33 U.S.C. sections 1251 to 1387. (b) "Endangered Species Act," 16 U.S.C. sections 1531
to 1544. (c) "Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide
Act," 7 U.S.C. 136. (d) "Safe Drinking Water Act," 42 U.S.C. sections 300f
to 300j-26. (3) Other references. The
availability of these documents is provided with each paragraph. (a) Ohio EPA references. These documents are available on the
internet at
http://epa.ohio.gov/divisions-and-offices/surface-water/reports-data/biological-criteria-for-the-protection-of-aquatic-life
unless otherwise noted. (i) "Biological
Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Volume I: The Role of Biological
Data in Water Quality Assessment, Ohio EPA, Ecological Assessment Section,
Division of Water Quality Planning & Assessment, July 24, 1987, updated
February 15, 1988." (ii) "Biological
Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Volume II: Users Manual for
Biological Field Assessment of Ohio Surface Waters, Ohio EPA, Ecological
Assessment Section, Division of Water Quality Planning & Assessment,
October 30, 1987, updated January 1, 1988, amended September 30, 1989, updated
November 8, 2006." (iii) "Biological
Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Volume III: Standardized
Biological Field Sampling and Laboratory Methods for Assessing Fish and
Macroinvertebrate Communities, Ohio EPA, Ecological Assessment Section,
Division of Surface Water, June 26, 2015." (iv) "The
Qualitative Habitat Evaluation Index [QHEI]: Rationale, Methods, and
Application, Ohio EPA, Ecological Assessment Section, Division of Water Quality
Planning & Assessment, November 6, 1989." (v) "Methods for
Assessing Habitat in Flowing Waters: Using the Qualitative Habitat Evaluation
Index (QHEI), Ohio EPA Technical Bulletin EAS/2006-06-1, Ohio EPA, Division of
Surface Water, June 2006." (vi) "Methods for
Assessing Habitat in Lake Erie Shoreline Waters Using the Qualitative Habitat
Evaluation Index (QHEI) Approach (Version 2.1), Ohio EPA, Division of Surface
Water, June 2010." (vii) "Field Methods
for Evaluating Primary Headwater Streams in Ohio 2020, Version 4.1, Ohio EPA
Division of Surface Water, Columbus, Ohio. 129 pp." This document is
available on the internet at
http://epa.ohio.gov/static/Portals/35/wqs/headwaters/PHWHManual_2020_Ver_4_1_May_2020_Final.pdf (viii) "Surface
Water Field Sampling Manual, Ohio EPA, Division of Surface Water, May 19,
2021." This document is available on the internet at
http://epa.ohio.gov/static/Portals/35/bioassess/2021-DSW-FieldSamplingManual-Main.pdf (ix) "Surface Water
Field Sampling Manual - Appendix I Inland Lakes Sampling Procedure Manual, Ohio
EPA, Division of Surface Water, April 22, 2019." This document is
available on the internet at
http://epa.ohio.gov/static/Portals/35/bioassess/Inland_Lake_Sampling_Manual_2019_Update_web.pdf. (b) "Ambient Water Quality Criteria to Address
Nutrient Pollution in Lakes and Reservoirs, U.S. EPA Office of Water,
EPA-822-R-21-005, August 2021." This document is available on the internet
at
http://epa.gov/system/files/documents/2021-08/nutrient-lakes-reservoirs-report-final.pdf (c) "Corps of Engineers Wetlands Delineation Manual,
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Wetlands Research Program Technical Report
Y-87-1, January 1987." This document is available on the internet at
http://nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/16/nrcs143_020653.pdf. (d) "Development of a Multimetric Index for Assessing
the Biological Condition of the Ohio River, Emery et. al., Transactions of the
American Fisheries Society 132:791-808, 2003." This document is available
on the internet at
http://orsanco.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Development-of-a-Multimetric-Index-for-Assessing-the-Biological-Conditon-of-the-Ohio-River.pdf. (e) "Guidance for Water Quality-based Decisions: The
TMDL Process, U.S. EPA Office of Water, EPA 440/4-91-001, April 1991."
This document is available on the internet at
http://epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-10/documents/guidance-water-tmdl-process.pdf. (f) "Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment, Risk
Assessment Forum, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC,
EPA/630/P-03/001F, March 2005." This document is available on the internet
at http://epa.gov/risk/guidelines-carcinogen-risk-assessment. (g) "Guidelines for the Submittal of Demonstrations
Pursuant to Sections 316(a) and 316(b) of the Clean Water Act and Chapter
3745-1 of the Administrative Code, Ohio Environmental Protection Agency,
Division of Industrial Wastewater, September 30, 1978." This document is
available on the internet at
http://epa.ohio.gov/static/Portals/35/guidance/316guidelines.pdf. (h) "Methodology for Deriving Ambient Water Quality
Criteria for the Protection of Human Health (2000), Office of Science and
Technology, Office of Water, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington,
DC, EPA-822-B-00-004, October 2000." This document is available on the
internet at
http://epa.gov/waterscience/criteria/humanhealth/method/index.html. (i) "Methods for Determination of Chemical Substances
in Marine and Estuarine Matrices - 2nd Edition. Method 445.0, Revision 1.6,
September 1997, In Vitro Determination of Chlorophyll a and Pheophytin a in
Marine and Freshwater Algae by Fluorescence, Microbiological and Chemical
Exposure Assessment Research Division, National Exposure Research Laboratory,
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, Ohio, EPA-600-R-97-072,
Revision 1.6, September 1997." This document is available on the internet
at https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPURL.cgi?Dockey=30003K0S.txt. (j) "ORSANCO 2021 Ohio River Pool Assessments:
Dashields, Hannibal, Markland, and McAlpine Pools. ORSANCO, 2022." This
document is available on the internet at
http://orsanco.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/2021PoolReportUpdated0622.pdf. (k) "Recommendations for and Documentation of
Biological Values for Use in Risk Assessment (U.S. EPA, 1988),
EPA/600/6-87/008." This document is available on the internet at
https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPURL.cgi?Dockey=500022JL.txt. (l) "Recommended Human Health Recreational Ambient
Water Quality Criteria or Swimming Advisories for Microcystins and
Cylindrospermopsin, U.S. EPA Office of Water, EPA-822-R-19-001, May 2019."
This document is available on the internet at
http://epa.gov/wqc/recreational-water-quality-criteria-and-methods#rec1. (m) "Recreational Water Quality Criteria. U.S. EPA
Office of Water, EPA-820-F-12-058, 2012." This document is available on
the internet at
http://epa.gov/wqc/recreational-water-quality-criteria-and-methods#rec1 (n) "Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances
(RTECS) (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati,
Ohio, July 1997)." This document is available on the internet
athttp://cdc.gov/niosh/docs/97-119/. (o) "Standard Guide for Conducting Bioconcentration
Tests with Fishes and Saltwater Bivalve Mollusks. Standard E 1022. Molluscs.
Designation E1022-94. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2013."
This document is available by contacting "Ohio EPA, Division of Surface
Water, 50 W. Town Street, Suite 700, Columbus, OH 43215." (p) "Water Quality Standards Handbook, U.S. EPA Office
of Water, EPA-823-B-17-001, January 2017." This document is available on
the internet at
http://water.epa.gov/scitech/swguidance/standards/handbook/index.cfm. (q) "The Wildlife Exposure Factors Handbook (U.S. EPA,
1993), EPA/600/R-93/187." This document is available on the internet at
http://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/cfm/recordisplay.cfm?deid=2799.
Last updated June 26, 2025 at 2:49 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-04 | Criteria applicable to all waters.
Effective:
March 20, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government
publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations,
federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see
rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] The following general water quality criteria apply
to all surface waters of the state including mixing zones. To every extent
practical and possible as determined by the director, these waters shall be as
follows: (A) Free from suspended solids or other
substances that enter the waters as a result of human activity and that will
settle to form putrescent or otherwise objectionable sludge deposits, or that
will adversely affect aquatic life. (B) Free from floating debris, oil, scum
and other floating materials entering the waters as a result of human activity
in amounts sufficient to be unsightly or cause degradation. (C) Free from materials entering the
waters as a result of human activity producing color, odor or other conditions
in such a degree as to create a nuisance. (D) Free from substances entering the
waters as a result of human activity in concentrations that are toxic or
harmful to human, animal or aquatic life or are rapidly lethal in the mixing
zone. (E) Free from nutrients entering the
waters as a result of human activity in concentrations that create nuisance
growths of aquatic weeds and algae. (F) Free from public health nuisances
associated with raw or poorly treated sewage reaching surface waters of the
state. A public heath nuisance exists when the conditions set forth in
paragraph (F)(1) of this rule are demonstrated. (1) An inspection
conducted by, or under the supervision of, Ohio EPA or a sanitarian registered
under Chapter 4736. of the Revised Code documents both of the
following: (a) Odor, color or other visual manifestations of raw or poorly
treated sewage. (b) Water samples exceed one thousand thirty E. coli counts per
one hundred milliliters in two or more samples when five or fewer samples are
collected, or in more than twenty per cent of the samples when more than five
samples are taken. (2) Paragraph (F)(1) of
this rule may be used by the appropriate authorities to document the existence
of unsanitary conditions as described in section 6117.34 of the Revised Code,
but does not preclude the use of other evidence of unsanitary conditions for
the purposes described in section 6117.34 of the Revised Code. (G) For the purposes of applying
paragraph (F) of this rule the water samples shall be collected as
follows: (1) When flow is
representative of steady state dry weather conditions, i.e., base flow or
delayed flow. (2) At least two hours
apart. (3) Over a time period
not to exceed thirty days. (H) Nothing in paragraph (F) or (G) of
this rule limits or otherwise changes the applicability of paragraphs (A) to
(E) of this rule.
Last updated June 26, 2025 at 4:38 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-05 | Antidegradation.
Effective:
February 6, 2017
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) Definitions. [Comment: The following definitions are in addition to the definitions contained in rule 3745-1-02 of the Administrative Code.] (1) "Available pollutant assimilative capacity" means the water body pollutant assimilative capacity for a substance, as determined in paragraph (A)(28)(a) of this rule, minus the background pollutant load, or the quantity for a substance as calculated in paragraph (A)(28)(b) of this rule. (2) "Background pollutant load" means the sum of all upstream pollutant loads of a regulated pollutant and has the same meaning as the background water quality as determined in accordance with paragraph (A)(3) of rule 3745-2-05 of the Administrative Code. (3) "Best available demonstrated control technology" means a wastewater treatment capable of meeting the following effluent limitations or design criteria: (a) For the discharge of sanitary wastewater from facilities using conventional treatment technologies, the effluent limitations in table 5-1 of this rule. (b) For the discharge of sanitary wastewater from alternative treatment technologies such as lagoon systems, land application and controlled discharge systems, constructed wetland systems or combined sewer overflow control systems effluent limitations shall be developed on a case-by-case basis. (c) For industrial direct discharges subject to federal effluent guidelines, the facility shall be designed to meet the most stringent of the new source performance standards, best conventional pollutant control technology, best available technology economically achievable and best practicable control technology currently available for the appropriate categorical guidelines of 40 C.F.R. 400 to 40 C.F.R. 471. (d) For categorical industrial indirect dischargers, the facility shall be designed to meet categorical pretreatment standards for existing sources or categorical pretreatment standards for new sources as contained in Chapter 3745-3 of the Administrative Code. (e) For non-categorical industrial direct or indirect discharges, effluent limitations will be developed based upon best engineering or professional judgment. (f) For wastewater discharges resulting from clean-up of response action sites contaminated with volatile organic compounds, the facility shall include air-stripping, carbon columns, both, or equivalent treatment capable of achieving final thirty-day average effluent limits of five micrograms per liter or less for each individually regulated volatile organic compound. (4) "Control document" means any authorization issued by a state or federal agency to any source of pollutants to waters under its jurisdiction that specifies conditions under which the source is allowed to operate. (5) "Declining fish species" mean those species listed in table 5-2 of this rule. Declining fish species are native species that have declined in distribution across Ohio based on collection records since 1978 compared to historical distributions of fish species. (6) "Designated uses" mean those uses assigned in this chapter for a water body or segment whether or not those uses are being attained. Specific designated uses are defined in rule 3745-1-07 of the Administrative Code. (7) "Director" means the director of the Ohio environmental protection agency, or the director of the Ohio department of agriculture for projects or activities governed under Chapter 903. of the Revised Code. (8) "Existing uses" mean those uses actually attained in the water body on or after November 28, 1975. (9) "Existing source" means any treatment works or disposal system, and its associated treatment or production capacity that: (a) Was built, operational and discharging prior to July 1, 1993. (b) Was authorized by a permit to install or national pollutant discharge elimination system permit issued after July 1, 1993. An individual or a collection of several household sewage treatment systems does not constitute an existing source. (10) "High quality waters" mean all surface waters of the state except limited quality waters. Pursuant to division (A)(2) of section 6111.12 of the Revised Code, four categories of high quality waters are hereby recognized and described in this paragraph. Categorizations of specific water bodies shall follow the procedures in paragraph (E) of this rule. (a) "General high quality waters" are wetlands categorized as category 2 or 3 in accordance with rule 3745-1-54 of the Administrative Code and other surface waters that are not specifically categorized limited quality waters, superior high quality waters, outstanding state waters, or outstanding national resource waters. (b) "Superior high quality waters" are surface waters that possess exceptional ecological values and that have been so categorized pursuant to paragraph (E) of this rule. Except as provided in this rule, exceptional ecological values shall be assessed based upon a combination of the presence of threatened or endangered species and a high level of biological integrity. The following factors shall be considered in determining exceptional ecological value: providing habitat for Ohio or federal endangered species; providing habitat for Ohio threatened species; harboring stable populations of a declining fish species that coincide with the presence of suitable habitat for that species, or that coincide with an essential migration path between areas of suitable habitat for that species; and displaying a level of biological integrity equivalent to the exceptional warmwater habitat index of biotic integrity or invertebrate community index criteria values listed in rule 3745-1-07 of the Administrative Code. Water bodies that exhibit a pattern of biological integrity equivalent to index of biotic integrity and, where applicable, invertebrate community index scores of fifty-six or greater at most sites are characteristic of a near-pristine aquatic habitat. Such waters, as well as other ecologically unique water bodies that have essentially undisturbed native faunas, but for which the biological criteria in rule 3745-1-07 of the Administrative Code do not apply, may be considered as possessing exceptional ecological values without the presence of threatened or endangered species. (c) "Outstanding state waters" are waters that have special significance for the state because of their exceptional ecological values or exceptional recreational values, and that have been so categorized pursuant to paragraph (E) of this rule. To qualify on the basis of exceptional ecological values they must meet the qualifications for superior high quality waters and be further distinguished as being demonstratively among the best waters of the state from an ecological perspective. To qualify on the basis of exceptional recreational values they must provide outstanding or unique opportunities for recreational boating, fishing or other personal enjoyment. (d) "Outstanding national resource waters" are surface waters that have a national ecological or recreational significance, and that have been so categorized pursuant to paragraph (E) of this rule. National ecological significance may include providing habitat for populations of federal endangered or threatened species or displaying some unique combination of biological characteristics in addition to those factors listed in paragraph (A)(10)(b) of this rule. National recreational significance may include designation in the national wild and scenic river system. (11) "Land application and controlled discharge system" means an innovative technology for the treatment of sewage that balances land application of treated wastewater with controlled discharges of wastewater under conditions that minimize stress on the aquatic environment. The system shall be designed to allow a discharge during winter months and required land application of the wastewater during summer months. (12) "Limited quality waters" mean wetlands categorized as category 1 in accordance with rule 3745-1-54 of the Administrative Code and other surface waters of the state specifically designated in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-30 of the Administrative Code as limited resource water, nuisance prevention, limited warmwater habitat, or modified warmwater habitat. (13) "Mass discharge limit" means for an existing source: (a) The average thirty-day mass limit specified in the national pollutant discharge elimination system permit. (b) The product of the average concentration limit specified in the permit and the permitted discharge flow, if no average mass limit is specified. (c) The product of an average concentration value derived from the maximum concentration limit specified in the permit using derivation methods established in the total maximum daily load procedures and the permitted discharge flow, if no average concentration or mass limit is specified. (14) "Minimal degradation alternative" means an alternative, other than the applicant's preferred alternative, including pollution prevention alternatives, that would result in a lesser lowering of water quality. (15) "Mitigative technique alternative" means an alternative, other than the applicant's preferred alternative, or other on-site or off-site control measures designed to offset all or part of the lowering of water quality, preferably within the same watershed. (16) "Modification of a facility" means: (a) The addition of new wastewater or sources of pollutants to an existing source, including the addition of new industrial users. (b) Any other physical change at the facility from which the discharge is generated that increases the capacity of that facility to discharge a pollutant or results in the discharge of a pollutant not previously discharged, excluding the following: (i) Routine repair, maintenance and replacement of existing equipment. (ii) Increases in hours or rates of operation and the use of alternative fuels or raw materials that can be implemented without any physical changes to the facility. (iii) Physical changes designed to restore previously existing production or treatment capacity. An expansion of the wastewater treatment system is not considered a modification of the facility. (17) "Net increase" means: (a) For a new source, any level of a regulated pollutant discharged to waters of the state as a result of the activity subject to this rule. (b) For an existing source: (i) The amount by which the sum of the following exceeds zero: (a) The increase in the mass discharge limit attributable to the activity subject to this rule. (b) All other contemporaneous increases or decreases attributable to other pollutant sources affecting the surface water segments under consideration and which are stipulated as a condition of the applicant's permit and which shall occur during the term of the applicant's permit. (ii) For heat, bacteria and any other regulated pollutant which, though not measurable as a mass level is nonetheless susceptible to determinations of net increase, the amount by which the sum of the following exceeds zero: (a) The increase in an authorized discharge level attributable to the activity subject to this rule. (b) All other contemporaneous increases or decreases attributable to other pollutant sources affecting the surface water segments under consideration and which are stipulated as a condition of the applicant's permit and which shall occur during the term of the applicant's permit. (18) "New source" means any treatment works or disposal system other than an existing source, excluding new domestic sewage sources and industrial users tributary to a publicly owned treatment works. A new treatment works built to serve a home or homes with individual systems is considered a new source. (19) "Non-degradation alternative" means an alternative, other than the applicant's preferred alternative, including pollution prevention alternatives, that would result in the elimination of the need to lower water quality. (20) "Permit modification" means an application filed by the permit holder pursuant to paragraph (D) of rule 3745-33-04 of the Administrative Code. (21) "Permitted discharge flow" means the discharge flow specified in the national pollutant discharge elimination system permit, or permit to install application if not specified in a national pollutant discharge elimination system permit, and shall be representative of the typical wastewater flow to be discharged by a facility when the wastewater facility is operating at full capacity, and considering, where applicable, discharge flows during wet weather events. (22) "Pollution prevention alternative" means the use of source reduction techniques in order to reduce risk to public health, safety, welfare and the environment and, as a second preference, the use of environmentally sound recycling to achieve these same goals. Pollution prevention avoids cross-media transfers of waste or pollutants and is multi-media in scope; it addresses all types of waste and environmental releases to the air, water and land. (23) "Regulated pollutant" means any parameter for which water quality criteria have been adopted in, or developed pursuant to, Chapter 3745-1 of the Administrative Code with the exception of biological criteria, and any other parameter that may be limited in a national pollutant discharge elimination system permit as a result of new source performance standards, best conventional pollutant control technology, best available technology economically achievable or best practicable control technology currently available for the appropriate categorical guidelines of 40 C.F.R. 400 to 40 C.F.R. 471. For the purposes of this rule, pH and dissolved oxygen are not considered "regulated pollutants." (24) "Remaining available pollutant assimilative capacity" means the available pollutant assimilative capacity for a substance minus the load already allocated to existing national pollutant discharge elimination system permits for dischargers in the water body segment receiving the allocation. This term is not used in the application of antidegradation for lake Erie. (25) "State resource water" is a designation of high quality waters that is being replaced by the categories of high quality waters described in paragraph (A)(10) of this rule. All water body segments currently designated state resource waters in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-30 of the Administrative Code are categorized in this rule as general high quality waters, unless they are specifically listed in tables 5-4 to 5-7 of this rule. Waters designated state resource waters in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-30 of the Administrative Code are subject to the considerations of paragraph (C)(5)(d) of this rule. (26) "Threatened species" mean those species listed in table 5-3 of this rule. A threatened species is an indigenous species whose survival in Ohio is not in immediate jeopardy, but to which a threat exists. Continued or increased stress will result in its becoming endangered. (27) "Total maximum daily load procedures" mean the procedures for calculating wasteload allocations adopted in Chapter 3745-2 of the Administrative Code. (28) "Water body pollutant assimilative capacity" means the total maximum allowable load of a substance for a specific water body segment and is calculated as: (a) For a stream, the water quality criteria for a substance multiplied by the total applicable flow at the end of the segment being studied. The applicable flow is determined using the total maximum daily load procedures. (b) For a lake, a value equal to the permitted discharge flow times Y, where Y equals eleven times the water quality criteria for a substance minus ten times the background concentration for the substance. Water body pollutant assimilative capacity for a lake can also be determined by any alternative method which the director determines to be appropriate and consistent with the total maximum daily load procedures. (B) Applicability; responsibilities of the applicant. Except as provided in paragraphs (B)(2), (D) and (F) of this rule, projects or activities covered under paragraph (B)(1) of this rule shall be subject to an antidegradation review described in paragraph (C) of this rule. (1) This rule shall apply to the following: (a) For existing sources, any re-issuance or modification of a national pollutant discharge elimination system permit that, if approved, would result in: (i) Any net increase of a regulated pollutant. (ii) If the national pollutant discharge elimination system permit specifies no limit for the pollutant, then the imposition of any effluent limit as a result of a modification of the facility. (iii) Approval of combined sewer overflow long term control plans and incorporation of the appropriate conditions into an NPDES permit. Long term control plans shall address planned sewer connections and development tributary to the collection system. (b) For new sources, any permit to install or national pollutant discharge elimination system permit application that, if approved, would result in a net increase in the discharge of any regulated pollutant. For these sources, if a national pollutant discharge elimination system permit application is submitted and approved under the provisions of this rule, a subsequent permit to install application proposing the selected alternative will not be subject to review under this rule. (c) Any section 401 water quality certification application pursuant to Chapter 3745-32 of the Administrative Code. (d) Any nonpoint source of pollution that results in a net increase in the release of any regulated pollutant, provided the director has separate authority to regulate the activity. (e) Unless authorized by a section 404 permit and section 401 water quality certification or a state isolated wetland permit, any permit to install application reviewed pursuant to Chapter 6111. of the Revised Code that would authorize the placement of fill or the construction of any portion of a sewerage system in or near surface waters of the state, if the director determines that aquatic habitat alterations caused by the activity and associated construction disturbances would result in the loss of an existing or designated use as defined in this chapter. (f) The transfer of all or a portion of the wastewater discharged by a treatment works to a different receiving water body, or to a different treatment works discharging to a different water body, unless the transfer is to a treatment works with capacity to accept the transferred wastewater within the terms of its existing national pollutant discharge elimination system permit. If a discharge is relocated on the same receiving water body within two miles of the original discharge then there is considered to be no net increase in the discharge. (g) The issuance by the director of environmental protection, in accordance with Chapter 3745-38 of the Administrative Code, or by the director of agriculture, in accordance with Chapter 901:10-4 of the Administrative Code, of a general national pollutant discharge elimination system permit that would result in a net increase. (h) Any state isolated wetland permit application submitted under section 6111.024 of the Revised Code. (2) The activities, permits, applications, certifications or other circumstances described in this paragraph are exempt from all provisions of this rule. (a) Any existing source discharging to waters of the state prior to July 1, 1993, or modifications of a facility made after July 1, 1993, that is not discharging under the terms of a national pollutant discharge elimination system permit. Only the portion of the flow that the existing source was capable of discharging as of July 1, 1993 shall not be subject to the rule provisions. (b) Any existing source where the net increase is: (i) The result of allowing a previously authorized or documented production or treatment capacity to be achieved. (ii) The result of allowing a limit up to that authorized by the immediately preceding, effective national pollutant discharge elimination system permit, which is not the result of a modification of a facility. (iii) If no limit was included in the immediately preceding national pollutant discharge elimination system permit and the pollutant was present or believed present in the discharge when the prior permit was issued, the inclusion of a limit for that pollutant provided there is no increase that is the result of a modification of a facility. (c) Any permit to install application for a sanitary sewer line extension or a new or expanding industrial user upstream of combined sewer overflows in a community operating a combined sewer system if: (i) The application conforms to the conditions related to approved long term development or planning documents associated with combined sewer overflow control measures incorporated into a national pollutant discharge elimination system permit as referenced in paragraph (B)(1)(a)(iii) of this rule. (ii) It can be documented that subsequent overflows from the combined sewer system will only occur in situations where the wet weather flows within the sanitary sewers exceed six times the average dry weather flows within the sanitary sewers. (iii) It can be documented that the combined sewers are and will continue to be operating at less than the original design dry weather capacity. (iv) There is an approved and ongoing flow or pollutant offset or infiltration and inflow reduction program for the collection system. (d) Any notice of intent filed with the director of environmental protection requesting coverage under a general national pollutant discharge elimination system permit issued in accordance with Chapter 3745-38 of the Administrative Code or notice of intent filed with the director of agriculture requesting coverage under a general national pollutant discharge elimination system permit issued in accordance with Chapter 901:10-4 of the Administrative Code. (e) Any discharge that, as the result of the addition of heat associated with the process or wastewater treatment system, increases the ambient temperature of the receiving water body by less than one degree Fahrenheit or is otherwise covered by the provisions of a section 316(a) variance. (f) The initial inclusion of whole effluent toxicity limitations in any national pollutant discharge elimination system permit or other control document, if there has been no change in discharge since July 1, 1993. (g) The addition or expansion of an industrial user to a publicly owned treatment works (POTW) collection system that does not trigger a permit limit for the POTW. Local limits shall be established for the POTW pretreatment program, or equivalent, utilizing a ten per cent safety factor when performing the evaluation related to effluent limitations to protect water quality standards. (h) The addition of domestic sewage sources to the POTW within the design capacity of the POTW. (i) A national pollutant discharge elimination system permit associated with a coal remining site where no individual section 401 water quality certification is required for the remining operation and where the director determines that the proposed discharge meets the criteria for modified effluent limits for a pollution abatement area as that term is defined under 40 C.F.R. 434.70. (3) Except as provided in paragraphs (B)(2), (B)(4), (D) and (F) of this rule, the applicant covered by paragraph (B)(1) of this rule must submit documentation of the following: (a) Identification of the substances to be discharged, including the amount of regulated pollutants to be discharged in terms of mass and concentration, and, if paragraph (B)(1)(c) of this rule applies, the amount of dredged and fill material to be discharged. (b) A description of any construction work, fill or other structures to occur or be placed in or near the stream bed. (c) A description and schematic of the applicant's preferred alternative for design and operation, including appropriate cost estimates, of the activity. (d) Description and analyses, including availability, cost effectiveness and technical feasibility, of the utilization of central or regional treatment facilities rather than creating a new point source discharge. This analysis shall include an evaluation of long-range plans outlined in state or local water quality management planning documents and applicable facility planning documents. (e) Descriptions, schematics and analyses of non-degradation alternatives, minimal degradation alternatives and mitigative technique alternatives for the design and operation, including appropriate cost estimates, of the activity that the applicant has considered. (f) An estimate of the important social, economic and environmental benefits to be realized through the project or activity if the water quality is lowered, including, as appropriate, the number and types of jobs created and the tax revenues generated. (g) An estimate of important social, economic and environmental benefits to be lost if water quality is lowered, such as lost or lowered recreational opportunities. (h) To the extent that such information is known to those in the local community or is otherwise public, a listing and description of all government or privately sponsored conservation projects that have specifically targeted improved water quality or enhanced recreational opportunities on the water body affected by the activity. (4) Applications for section 401 water quality certifications are exempt from paragraph (B)(3) of this rule. Required submissions shall be determined in accordance with section 6111.30 of the Revised Code, Chapter 3745-32 of the Administrative Code and rules 3745-1-50 to 3745-1-54 of the Administrative Code. (C) Antidegradation review requirements. (1) Protection of water body uses. Existing uses, which are determined using the use designations defined in rule 3745-1-07 of the Administrative Code, and the level of water quality necessary to protect existing uses, shall be maintained and protected. There may be no degradation of water quality that results in either a violation of the applicable water quality criteria for the designated uses, unless authorized by a water quality standard variance issued in accordance with rule 3745-1-38 of the Administrative Code, or the elimination or substantial impairment of existing uses. The director shall, pursuant to paragraph (C) of rule 3745-1-07 of the Administrative Code, prohibit increased concentrations of specific regulated pollutants that are incompatible with the attainment or restoration of the designated use. Existing wetland uses, as defined in rule 3745-1-53 of the Administrative Code, shall be maintained and protected in accordance with rules 3745-1-50 to 3745-1-54 of the Administrative Code. (2) Required treatment technology, nonpoint source controls. Except as provided in paragraph (D)(2) of this rule, any net increase in the discharge of a specific regulated pollutant resulting from a modification or new source shall, as a minimum, be controlled through best available demonstrated control technology relative to the specific regulated pollutant. More stringent treatment may be required pursuant to paragraph (C)(8) of this rule, or if needed to meet water quality standards. Feasible management or regulatory programs pursuant to sections 208, 303 and 319 of the act shall be applied to nonpoint sources. (3) Public involvement. Except as provided in paragraphs (B)(2) and (D) of this rule, the director shall provide for public participation and intergovernmental coordination prior to taking action on all activities covered by paragraph (B)(1) of this rule using the provisions of this paragraph. (a) In accordance with Chapter 3745-49 of the Administrative Code, the director shall publish a public notice within thirty days regarding receipt of any permit application or state isolated wetland permit application covered by paragraph (B)(1) of this rule. The purpose of such notice shall be to allow for inspection and review of the application, to indicate that the project is subject to the provisions of this rule and whether any of the exclusions or waivers described in paragraph (D) of this rule apply, to instruct people to contact the director within thirty days if they want to be on the interested parties mailing list for that application, and, on general high quality waters and limited quality waters, to determine whether there is interest in having a public hearing. Public notice for section 401 water quality certification applications shall be published pursuant to the requirements in section 6111.30 of the Revised Code. Notices shall be sent by first class mail to all persons on the mailing list created pursuant to paragraph (C)(3)(d) of this rule. (b) The director shall develop an informational fact sheet for each permit or activity for which a public notice is issued in accordance with paragraph (C)(3)(a) of this rule, excluding section 401 water quality certification and state isolated wetland permit activities, within thirty days of receipt of the application. The purpose of such fact sheet shall be to: provide information to potentially affected parties; provide a description of the project; outline the review process and schedule; specify where the application or permits can be viewed; identify the water bodies potentially affected; instruct individuals how to request to be on the interested parties mailing list; provide an opportunity to request a public hearing pursuant to paragraph (C)(3)(f) of this rule; and advertise the date, time and location of a public hearing if one is scheduled pursuant to paragraph (C)(3)(e) of this rule. These fact sheets shall be sent by first class mail, or alternative means as requested, to all persons on the mailing list created pursuant to paragraph (C)(3)(d) of this rule. (c) All notices of public hearings required by paragraphs (C)(3)(e) and (C)(3)(f) of this rule shall be published once in a newspaper having general circulation in the county where the source, activity or facility is located. The notice shall be published at least forty-five days before the hearing. Notices of hearings shall also be sent by first class mail, or by alternative means as requested, to all persons on the mailing list created pursuant to paragraph (C)(3)(d) of this rule. (d) The director shall develop and maintain a list of persons and organizations who have expressed an interest in or may, by the nature of their purposes, activities or members, be affected by or have an interest in antidegradation reviews. These persons and organizations may request that all fact sheets or public hearing public notices identified by this rule be forwarded to them by means other than first class mail (e.g., by electronic transmission). (e) Within ninety days of receipt of the application, the director shall hold a public hearing for any permit application, section 401 water quality certification application or state isolated wetland permit application covered by paragraph (B)(1) of this rule whenever a water body categorized outstanding national resource water, outstanding state water, superior high quality water or category 3 wetland is affected. This public hearing shall be for the purpose of evaluating issues related to lower water quality and shall be prior to and separate from a public hearing on the proposed or draft action on the application. Section 401 water quality certifications impacting lake Erie or its shoreline are exempt from this requirement. Public hearings for section 401 water quality certifications impacting lake Erie or its shoreline will be held at the discretion of the director and according to the timelines contained in section 6111.30 of the Revised Code. (f) For general high quality waters other than category 3 wetlands and for limited quality waters, the director shall hold a public hearing for any permit to install application, national pollutant discharge elimination system permit application, section 401 water quality certification application or state isolated wetland permit application covered by paragraph (B)(1) of this rule whenever the director determines there is significant public interest. A public hearing shall be held for the issuance of any draft general national pollutant discharge elimination system permit. The director shall hold public hearings relative to issues of lower water quality as a concurrent hearing at the time of the draft or proposed action. However, if the application is not covered by paragraph (D) of this rule, the director may choose to hold a public hearing preceding the draft or proposed action if, at the director's discretion, the project is considered to be controversial or complex. For section 401 water quality certification applications and state isolated wetland permit applications, the public hearing shall precede any action of the director. (g) A public notice of the director's proposed or draft action regarding the activity and its potential to lower water quality shall be published following the procedures in Chapter 3745-49 of the Administrative Code. The director shall provide notification by first class mail, or alternative means as requested, to all interested parties identified through the procedures in paragraph (C)(3) of this rule. Additional procedures are described in paragraph (C)(8) of this rule. (h) The director shall notify the Ohio department of natural resources, the United States fish and wildlife service, the United States environmental protection agency and any affected local areawide planning agencies of all proposed activities that may lower water quality. In addition, for activities covered under paragraph (B)(1)(a), (B)(1)(b) or (B)(1)(f) of this rule, the director shall notify the Ohio department of development and any affected local governmental units. The director or the other agencies may initiate additional intergovernmental coordination. (4) Outstanding national resource waters: The director shall impose the following requirements on all activities covered by paragraph (B)(1) of this rule that discharge to outstanding national resource waters, or that discharge upstream of outstanding national resource waters. (a) Present ambient water quality in outstanding national resource waters shall not be degraded for any substance. (b) The director may re-issue permits for any source discharging to an outstanding national resource water if the source had a national pollutant discharge elimination system permit at the time the water body was categorized an outstanding national resource water as described in paragraph (E) of this rule, provided there is no increase in the permitted discharge concentrations or loads. (c) New sources may not discharge directly to outstanding national resource waters, and may not discharge at points located upstream from outstanding national resource waters unless it can be demonstrated by the applicant that the chemical and biological quality of the outstanding national resource water will not be adversely affected. (d) Notwithstanding the provisions stated in paragraphs (C)(4)(a) and (C)(4)(e) of this rule, activities that result in short-term changes in water quality in outstanding national resource waters may be allowed if the director determines there will be no long-term detrimental impact. Activities resulting in short-term impacts on outstanding national resource waters will be subject to a review of non-degradation alternatives, minimal degradation alternatives, mitigative technique alternatives, economic and social benefits, public participation and intergovernmental coordination. For section 401 water quality certifications for outstanding national resource waters, demonstration of avoidance, minimization and mitigation of impacts shall serve as the applicant's non-degradation, minimal degradation and mitigative technique alternatives analysis as required in paragraph (B) of rule 3745-32-03 of the Administrative Code. (e) Notwithstanding the provisions stated in paragraphs (C)(4)(a) and (C)(4)(d) of this rule discharges of dredged and fill material to outstanding national resource waters that are wetlands, and are owned and managed solely for natural area preservation, public recreation, education or scientific purposes, may be authorized provided the discharges and associated activities result in only a short-term disturbance to water quality and will not adversely affect the ecological quality of the wetland or other surface waters. Authorized discharges and associated activities include boardwalk construction, repair and maintenance of dikes and other hydrological controls, and removal of non-native and invasive plant species. For these discharges and associated activities the director may waive the need for the review outlined in paragraph (C)(4)(d) of this rule. (5) Other waters. For waters other than outstanding national resource waters and limited quality waters, the director shall impose the following requirements on all activities covered by paragraph (B)(1) of this rule, except that for section 401 water quality certifications and state isolated wetland permits pursuant to section 6111.024 of the Revised Code for high quality waters that are wetlands, the director shall impose the requirements specified in rules 3745-1-50 to 3745-1-54 of the Administrative Code in lieu of paragraphs (C)(5) and (C)(8) of this rule. In addition, the director may apply the items in paragraphs (C)(5)(a) to (C)(5)(f) and (C)(5)(k) to (C)(5)(m) of this rule, may consider cumulative impacts as defined in paragraph (I) of rule 3745-1-50 of the Administrative Code, and shall consider whether the wetland is scarce regionally or statewide and the feasibility of replacing that wetland type, in making a decision whether to allow the lowering of water quality. For section 401 water quality certifications for high quality waters, other than wetlands, demonstration of avoidance, minimization and mitigation of impacts shall serve as the applicant's non-degradation, minimal degradation and mitigative technique alternatives analysis as required in paragraph (B) of rule 3745-32-03 of the Administrative Code. The director may approve activities that lower water quality only if there has been an examination of non-degradation, minimal degradation and mitigative technique alternatives, a review of the social and economic issues related to the activity, a public participation process and appropriate intergovernmental coordination, and the director determines that the lower water quality is necessary to accommodate important social or economic development in the area in which the water body is located. The director may require the applicant to implement a non-degradation alternative, a minimal degradation alternative or a mitigative technique alternative to offset all or part of the proposed lowering of water quality, if the director determines that the alternative is technically feasible and economically justifiable. Any lowering of water quality shall not exceed the limitations specified in paragraph (C)(6) of this rule. When making determinations regarding proposed activities that lower water quality the director shall consider the following: (a) The magnitude of the proposed lowering of water quality. (b) The anticipated impact of the proposed lowering of water quality on aquatic life and wildlife, including threatened and endangered species, important commercial or recreational sport fish species, other individual species and the overall aquatic community structure and function. (c) The anticipated impact of the proposed lowering of water quality on human health and the overall quality and value of the water resource. (d) The degree to which water quality may be lowered in waters located within national, state or local parks, preserves or wildlife areas, waters listed as state resource waters in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-30 of the Administrative Code, or waters categorized outstanding national resource waters, outstanding state waters or superior high quality waters. (e) The effects of lower water quality on the economic value of the water body for recreation, tourism and other commercial activities, aesthetics, or other use and enjoyment by humans. (f) The extent to which the resources or characteristics adversely impacted by the lowered water quality are unique or rare within the locality or state. (g) The cost of the water pollution controls associated with the proposed activity. (h) The cost effectiveness and technical feasibility of the non-degradation alternatives, minimal degradation alternatives or mitigative technique alternatives and the effluent reduction benefits and water quality benefits associated with such alternatives. (i) The availability, cost effectiveness, and technical feasibility of central or regional sewage collection and treatment facilities, including long-range plans outlined in state or local water quality management planning documents and applicable facility planning documents. (j) The availability, reliability and cost effectiveness of any non-degradation alternative, minimal degradation alternative or mitigative technique alternative. (k) The reliability of the preferred alternative including, but not limited to, the possibility of recurring operational and maintenance difficulties that would lead to increased degradation. (l) The condition of the local economy, the number and types of new direct and indirect jobs to be created, state and local tax revenue to be generated, and other economic and social factors as the director deems appropriate. (m) Any other information regarding the proposed activities and the affected water body that the director deems appropriate. (6) Set asides to limit lower water quality. In addition to the other provisions of paragraph (C) of this rule, the director shall not allow water quality to be lowered by more than as specified in this paragraph when acting on applications or activities covered by paragraph (B)(1) of this rule. (a) For outstanding state waters, the director shall reserve seventy per cent of the remaining available pollutant assimilative capacity for all regulated pollutants for which water quality criteria have been adopted in or developed pursuant to this chapter. Except as provided in paragraph (C)(7) of this rule, the reserved portion shall not be allocated to any source unless, and to the extent that, the source demonstrates that a smaller reserve will adequately protect resident or representative species. The requirements of this paragraph shall not apply to any water body categorized as outstanding state water solely because of its exceptional recreational value. (b) For lake Erie, new and existing sources shall be limited to the water body pollutant assimilative capacity as defined in paragraph (A)(28)(b) of this rule. (c) For superior high quality waters, other than lake Erie and those waters covered by paragraph (C)(6)(e) of this rule, the director shall reserve thirty-five per cent of the remaining available pollutant assimilative capacity for all regulated pollutants for which water quality criteria have been established in this chapter. Except as provided in paragraph (C)(7) of this rule, the reserved portion shall not be allocated to any source unless, and to the extent that, the source demonstrates that a smaller reserve will adequately protect resident or representative species. The director may reserve a higher percentage of the remaining available pollutant assimilative capacity if there is scientific evidence that strongly suggests that resident or representative species are more sensitive to a pollutant or class of pollutants and may be inadequately protected using the applicable water quality criteria and the standard set aside provision. The higher set aside shall be established for specific pollutants or classes of pollutants through rule making pursuant to paragraph (E) of this rule. (d) For general high quality waters and limited quality waters, water quality may not be lower than the applicable water quality criteria for the water body, unless authorized by a water quality standard variance issued in accordance with appropriate rules. (e) For outstanding state waters so categorized because of exceptional recreational value the director shall: (i) Evaluate, or cause the applicant to evaluate, the impact of the project on bacteriological contamination for any project covered under paragraph (B)(1) of this rule. No permit shall be granted if the director finds that the project or discharge will result in a significant long term increase in the frequency and duration of bacteriological pollution. (ii) Review all permit actions, covered under paragraph (B)(1) of this rule, to minimize the introduction of pollutants or floating debris and materials which may affect the aesthetic quality of the receiving waters. (7) Credit projects. An applicant for a project covered under paragraph (B)(1) of this rule may request that the director approve a credit project in lieu of the set asides described in paragraphs (C)(6)(a) and (C)(6)(c) of this rule. In order for a credit project to be considered for approval, the proposal must: (a) Occur in the same water body where the proposed lowering of water quality is to take place. (b) Not necessarily offset the proposed pollutant load being pursued, but address an existing or potential threat to the water body. This may include providing for water body enhancement or restoration activities. If the director determines to approve a credit project in lieu of the set asides described in paragraphs (C)(6)(a) and (C)(6)(c) of this rule, the director may include, at the director's discretion, an alternative lower set aside to accompany the credit project. A lower set aside must be established through rule making and incorporated into tables established in paragraph (E) of this rule. (8) Procedures. (a) The director shall assess each proposed activity covered by paragraph (B)(1) or (F) of this rule on a case-by-case basis. For each proposed activity, the director shall weigh the information acquired relative to the proposal, that was submitted by the applicant or otherwise obtained by the director, and all comments presented during the public review period, including intergovernmental comments, and make a determination to: (i) Allow the applicant's preferred alternative with appropriate conditions, if applicable, and the lower water quality as proposed because it has been determined that a discharge or the activity is necessary. (ii) Deny the applicant's preferred alternative as proposed. (iii) Require a cost beneficial, technically feasible or available non-degradation, minimal degradation or mitigative technique alternative that would result in no or a lesser lowering of water quality. (b) Any action of the director issuing a permit to install or a national pollutant discharge elimination system permit covered under paragraph (B)(1) or (F) of this rule shall be preceded by a draft action and shall be issued in accordance with Chapter 3745-49 of the Administrative Code. (c) Any action of the director denying a permit to install or a national pollutant discharge elimination system permit covered under paragraph (B)(1) or (F) of this rule shall be preceded by a proposed action and shall be issued in accordance with Chapter 3745-49 of the Administrative Code. (d) Any action of the director on a section 401 water quality certification covered under paragraph (B)(1) or (F) of this rule shall be taken in accordance with Chapters 3745-32 and 3745-49 of the Administrative Code. (e) Any action of the director on a state isolated wetland permit application submitted pursuant to section 6111.024 of the Revised Code and covered under paragraph (B)(1) or (F) of this rule shall be taken in accordance with Chapter 3745-49 of the Administrative Code. (D) Exclusions and waivers. The exclusions and waivers described in paragraphs (D)(1)(a), (D)(1)(b), (D)(1)(d), (D)(1)(e) and (D)(3) of this rule do not apply to bioaccumulative chemicals of concern within the lake Erie basin. (1) The following situations are excluded from the submittal and review requirements listed in paragraphs (B)(3)(e) to (B)(3)(h) and (C)(5) of this rule. In determining the applicability of any of the following exclusions, the evaluation shall not only consider potential effects or impacts to the receiving waters, but also to any subsequent waters potentially affected by the discharge or activity. (a) Any source discharging to limited quality waters. (b) Any de minimis net increase determined using the following criteria. For the discharge of primarily sanitary wastewaters, only ammonia-nitrogen will be evaluated to determine the applicability of the appropriate exclusion. (i) For general high quality waters, any net increase in the discharge of a regulated pollutant that is less than ten per cent of the wasteload allocation to maintain water quality standards calculated using total maximum daily load procedures, provided the proposed lowering of water quality does not exceed eighty per cent of the wasteload allocation to maintain water quality standards calculated using total maximum daily load procedures. (ii) For superior high quality waters, other than lake Erie, and outstanding state waters any net increase in the discharge of a regulated pollutant that results in less than a five per cent change in the ambient water quality concentration of the receiving water as projected to occur using total maximum daily load procedures, provided the proposed lowering of water quality does not exceed the portion of the remaining available assimilative capacity specified by the director pursuant to paragraphs (C)(6)(a) or (C)(6)(c) and (E) of this rule. (iii) For lake Erie any net increase in the discharge of a regulated pollutant that is less than ten per cent of the water body pollutant assimilative capacity. (c) Combined sewer overflow elimination or reduction projects affecting one or more water bodies where there will be a net decrease in the overall pollutant loadings discharged to surface waters of the state. Treatment byproducts of combined sewer overflow discharges (e.g., chlorine for disinfection) shall be excluded from review. (d) Any disposal system built and operated exclusively for the treatment of contaminated ground water at response action clean-up sites. (e) Any disposal system built and operated as a land application and controlled discharge system as defined in paragraph (A)(11) of this rule. (f) Any net increase in the discharge of a regulated pollutant resulting from a change in fuel used by the discharger, provided the discharger was capable of accommodating the new fuel on the effective date of this rule. (g) Any imposition of mercury effluent limitations in an NPDES permit for an existing source where the mercury limitations are based on a variance pursuant to paragraph (J) of rule 3745-1-38 of the Administrative Code. (h) Any discharge of the following regulated pollutants within the range indicated: (i) Total suspended solids at or below sixty-five mg/l. (ii) Oil and grease at or below ten mg/l. (i) Any discharge that, as the result of the addition of heat associated with the process or wastewater treatment system, increases the ambient temperature of the receiving stream greater than or equal to one degree Fahrenheit, as calculated using total maximum daily load procedures, up to that allowed through water quality standards. (j) Any general permit developed by the director in accordance with the provisions of Chapter 3745-38 of the Administrative Code. (2) The director may waive the requirement to install best available demonstrated control technology for new sources discharging sanitary wastewater if: (a) The modification, new source or national pollutant discharge elimination system application is for a project designed exclusively to restore, maintain or ensure design capacity and associated pollutant discharge levels already authorized in an effective national pollutant discharge elimination system permit. (b) The modification, new source or national pollutant discharge elimination system application is the direct and sole result of a proposed transfer of pollutant loading from an existing direct discharge of pollution to waters of the state, and the director has determined that the transfer will result in overall environmental improvement. The director's determination on this matter shall be based upon the antidegradation review process specified in paragraph (C) of this rule, unless otherwise excluded from such review pursuant to paragraph (D) of this rule. (3) The director may waive the submittal and review requirements listed in paragraphs (B)(3)(f) to (B)(3)(h) and (C)(5) of this rule if it is determined that: (a) The proposed net increase in the discharge of a regulated pollutant does not result in an increase in the ambient water quality concentration of the receiving water after mixing as projected to occur under the total maximum daily load procedures. (b) Any proposed net increase in the discharge of nutrients (such as, but not limited to, phosphorus and nitrogen) or toxic substances complies with all applicable water quality standards and will not threaten environmentally sensitive areas such as downstream lakes, reservoirs, wetlands, exceptional warmwater habitats, coldwater habitats, outstanding national resource waters, outstanding state waters, or superior high quality waters. (c) The requirements of paragraphs (B)(3)(d) and (B)(3)(e) of this rule have been met and the director determines that none of the non-degradation alternatives, minimal degradation alternatives or mitigative technique alternatives for the design and operation of the activity are technically feasible and economically justifiable. (4) Nothing in this rule shall prohibit the director from approving activities that lower water quality on a temporary basis whenever the director determines that an emergency exists requiring immediate action to protect public health and welfare. The director shall issue any such approval in accordance with division (C) of section 6111.06 of the Revised Code and rule 3745-47-19 of the Administrative Code. (5) The director may waive the submittal and review requirements listed in paragraphs (B)(3)(f) to (B)(3)(h) and (C)(5) of this rule if the applicant is seeking a revised water quality based effluent limit based upon the results of either a site specific study of the water quality criteria or a change in the water quality criteria found in this chapter and the applicant demonstrates that the facility has not complied with the existing water quality based permit limit. The following conditions must be met for this waiver to apply: (a) Any proposed net increase in the discharge of regulated pollutants complies with all applicable water quality standards and will not threaten environmentally sensitive areas such as downstream lakes, reservoirs, wetlands, exceptional warmwater habitats, coldwater habitats, outstanding national resource waters, outstanding state waters, or superior high quality waters. (b) The requirements of paragraphs (B)(3)(d) and (B)(3)(e) of this rule have been met and the director determines that none of the non-degradation alternatives, minimal degradation alternatives or mitigative technique alternatives for the design and operation of the activity are technically feasible and economically justifiable. (E) Categorization of waters; site-specific revisions: (1) All surface waters are categorized as general high quality waters except as follows. (a) Lake Erie is categorized as a superior high quality water. (b) All surface waters of the state meeting the definition of limited quality waters are so categorized, unless the water body is the source of drinking water for a public water supply, in which case it shall be considered a general high quality water for the purposes of this rule. (c) The water bodies listed in table 5-4 of this rule are categorized superior high quality waters. The reserved set aside percentage established pursuant to paragraph (C)(6)(c) of this rule is thirty-five per cent unless indicated otherwise in table 5-4 of this rule. (d) The water bodies listed in table 5-5 of this rule are categorized outstanding state waters due to exceptional ecological values. The reserved set aside percentage established pursuant to paragraph (C)(6)(a) of this rule is seventy per cent of the remaining available pollutant assimilative capacity. (e) The water bodies listed in table 5-6 of this rule are categorized outstanding state waters due to exceptional recreational values. The provisions of paragraph (C)(6)(e) of this rule apply. (f) The water bodies listed in table 5-7 of this rule are categorized outstanding national resource waters. (2) At least once every three years, the director, in consultation with the director of the department of natural resources, shall consider available information on water bodies in Ohio and determine appropriate high quality water categorizations. Each determination shall consider attributes of exceptional recreational or ecological value, the national significance of the water body, and other existing and planned uses of the water body. If the director identifies any waters not properly categorized, the director shall public notice the director's intent to categorize them to the appropriate category upon consideration of public comment. The director shall categorize outstanding national resource waters, outstanding state waters and superior high quality waters in tables 5-4 to 5-7 of this rule. (3) A person adversely affected by the high quality water categorization of a water body pursuant to paragraph (E)(1) or (E)(2) of this rule may petition the director to revise that categorization. Any such petition shall detail the basis for the petition and contain, at a minimum, new relevant and factual information, or relevant and factual information not previously available to the director at the time of the categorization described in paragraph (E)(1) or (E)(2) of this rule. The petition must contain sufficient information, or such additional information as the director may request, to justify a decision by the director to either revise or retain the categorization under paragraph (E)(1) or (E)(2) of this rule. Within three months of receiving a petition containing complete and adequate information, or within such longer time as the director and the petitioner may agree, the director shall either approve or propose to deny the petition in accordance with Chapter 119. of the Revised Code. The director shall subsequently make appropriate revisions to the high quality water categorization of the water body in tables 5-4 to 5-7 of this rule, as appropriate, in accordance with Chapter 119. of the Revised Code. (4) Petitions for revision to set asides. (a) Any person who is or may be adversely affected by a set aside percentage established pursuant to paragraph (C)(6)(a) or (C)(6)(c) of this rule may petition the director to revise that set aside percentage. Any such petition shall detail the basis for the petition and contain sufficient information, or such additional information as the director may request, to justify a decision by the director to either retain the set aside percentage, remove the set aside percentage or establish site specific set asides for one or more pollutants. (b) If the director concludes, based on the information presented in the petition and such other relevant scientific information as is available to the director, that the existing set aside is more or less stringent than necessary to preserve the attributes that justified designation of the water body as an outstanding state water or superior high quality water, the director shall establish a revised, site-specific set aside for that or those pollutants. The revised site-specific set aside for each pollutant shall be set at the percentage of the remaining available pollutants' assimilative capacity that the director concludes, based on the available scientific evidence, must be preserved to adequately protect the attributes that justified designation of the water body as an outstanding state water or superior high quality water. (c) Within three months of receiving a petition containing complete and adequate information, or within such longer time as the director and the petitioner may agree, the director shall either approve, approve with modifications or propose to deny the petition in accordance with Chapter 119. of the Revised Code. The director shall subsequently make appropriate revision to the high quality water categorization of the water body in tables 5-4 to 5-7 of this rule, as appropriate, in accordance with Chapter 119. of the Revised Code. (F) Special provisions for bioaccumulative chemicals of concern in the lake Erie drainage basin. The following special provisions are applicable to the discharge or release to the environment of any bioaccumulative chemical of concern in the lake Erie drainage basin. Unless otherwise noted, these requirements shall apply in addition to the provisions found in paragraphs (A) to (E) of this rule. (1) In lieu of the requirements of paragraph (B)(1) of this rule, any significant lowering of water quality as described in paragraph (F)(2) of this rule shall require the applicant to submit the information required by paragraph (B)(3) of this rule and to complete the demonstration required by paragraph (F)(3) of this rule. The director shall establish conditions in the control document that meet the requirements of paragraph (F)(4) of this rule. (2) Significant lowering of water quality. (a) A significant lowering of water quality occurs when there is a new or increased loading of any bioaccumulative chemical of concern from any regulated existing or new facility, either point source or nonpoint source for which there is a control document or reviewable action, as a result of any activity including, but not limited to: (i) Construction of a new regulated facility or modification of an existing regulated facility such that a new or modified control document is required. (ii) Modification of an existing regulated facility operating under a current control document such that the production capacity of the facility is increased. (iii) Addition of a new source of untreated or pretreated effluent containing or expected to contain any bioaccumulative chemical of concern to an existing wastewater treatment works, whether public or private. (iv) A request for an increased limit in an applicable control document. (v) Other deliberate activities that, based on the information available, could be reasonably expected to result in an increased loading of any bioaccumulative chemical of concern to any waters of the Great Lakes system. (b) Notwithstanding the above, changes in loadings of any bioaccumulative chemical of concern within the existing capacity and processes that are covered by the existing applicable control document, are not subject to an antidegradation review. These changes include, but are not limited to: (i) Normal operational variability including, but not limited to, intermittent increased loadings related to wet weather conditions. (ii) Changes in intake water pollutants. (iii) Increasing the production hours of the facility, (e.g., adding a second shift), provided production hours do not exceed those described in, or used to derive, the existing control document. (iv) Increasing the rate of production, provided production rates do not exceed those described in, or used to derive, the existing control document. (v) Discharges of quantities of a bioaccumulative chemical of concern in the intake water at a facility proposing a new or increased discharge, provided that the new or increased discharge is not expected to result in a net increase in the total load of the bioaccumulative chemical of concern in the receiving water body. (vi) Increasing the sewered area, connection of new sewers and customers, or acceptance of trucked-in wastes such as septage and holding tank wastes by a POTW unless, for a bioaccumulative chemical of concern, there is increased loading due to the collection of wastewater from a significant industrial user and, based on the industry's raw materials and processes, the wastewater is expected to have quantifiable concentrations of the bioaccumulative chemical of concern significantly above levels typically associated with domestic wastewater and non-industrial stormwater. (vii) Increased discharge of a bioaccumulative chemical of concern due to implementation of controls on wet weather-related flows, including, but not limited to, combined sewer overflows and industrial stormwater. (viii) Increased discharges of a bioaccumulative chemical of concern resulting from a change in fuel used by the discharger, provided that the discharger was capable of accommodating the new fuel on October 31, 1997. (c) Also excluded from an antidegradation review are new effluent limits based on improved monitoring data or new water quality criteria or values that are not a result of changes in pollutant loading. (d) Also excluded from the antidegradation submittal and review requirements listed in paragraphs (B)(3)(c) to (B)(3)(h) and (C)(5) of this rule is any imposition of mercury effluent limitations in an NPDES permit for an existing source, where the mercury effluent limitations are based on a variance pursuant to paragraph (D)(10) of rule 3745-1-38 of the Administrative Code. (3) Antidegradation demonstration. Any entity seeking to significantly lower water quality for a bioaccumulative chemical of concern, as defined in paragraph (F)(2) of this rule, in a limited quality water or high quality water must, in addition to the requirement in paragraph (B)(3) of this rule, submit an antidegradation demonstration for consideration by the director pursuant to the review requirements of this paragraph and paragraph (C) of this rule. The antidegradation demonstration shall include the following: (a) Pollution prevention alternatives analysis. Identify any cost-effective pollution prevention alternatives and techniques that are available to the entity, that would eliminate or significantly reduce the loadings of bioaccumulative chemicals of concern. (b) Alternative or enhanced treatment analysis. Identify alternative or enhanced treatment techniques that are available to the entity that would eliminate the lowering of water quality and their costs relative to the cost of treatment necessary to achieve applicable effluent limitations. (4) For limited quality waters and high quality waters, the director shall ensure that no action resulting in a lowering of water quality occurs unless an antidegradation demonstration has been completed pursuant to paragraphs (B)(3) and (F)(3) of this rule and the information thus provided is determined by the director pursuant paragraph (C) of this rule to adequately support the lowering of water quality. (a) The director shall establish conditions in the control document applicable to the regulated facility that prohibit the regulated facility from undertaking any deliberate action, such that there would be an increase in the rate of mass loading of any bioaccumulative chemical of concern, unless an antidegradation demonstration is provided to the director and approved pursuant to paragraph (C) of this rule prior to commencement of the action. Imposition of limits due to improved monitoring data or new water quality criteria or values, or changes in loadings of any bioaccumulative chemical of concern within the existing capacity and processes that are covered by the existing applicable control document, are not subject to an antidegradation review. (b) For bioaccumulative chemicals of concern known or believed to be present in a discharge, from a point or nonpoint source, a monitoring requirement shall be included in the control document. The control document shall also include a provision requiring the source to notify the director of any increased loadings that would be subject to the provisions of the paragraph (F)(2) of this rule and which have not received approval from the director under the conditions specified in this rule. Upon notification, the director shall require actions as necessary to reduce or eliminate the increased loading if the increase is subject to the provisions of the paragraph (F)(2) of this rule. Requirements to reduce or eliminate the increased loading imposed by the director pursuant to this paragraph shall apply unless or until the director approves the increased loadings under the provisions specified in this rule. (c) Fact sheets prepared pursuant to 40 C.F.R. 124.8 and 124.56 shall reflect any conditions developed under paragraph (F) of this rule and included in a permit. | Parameter | Thirty-day Limit | Daily or Seven-day Limit | Maximum/Minimum Limit | | | | | | CBOD5 | 10 mg/l | 15 mg/l | n/a | | Total suspended solids | 12 mg/l | 18 mg/l | n/a | | Ammonia | | | | | (Summer) | 1.0 mg/l | 1.5 mg/l | n/a | | (Winter) | 3.0 mg/l | 4.5 mg/l | | Dissolved oxygen | n/a | n/a | 6.0 mg/l (minimum) | | Total residual chlorine | n/a | n/a | 0.038 mg/l (maximum) | | E. coli* | 126 / 100 ml | 235 / 100 ml | n/a | | * E. coli is to be considered a design standard only. Effluent limitations will not be incorporated into a control document based solely on this table. |
| Common name | Latin name | Comment | | | | | Bigeye chub | Notropis amblops | | | Bigeye shiner | Notropis boops | | | Blacknose shiner | Notropis heterolepis | | | Bluebreast darter | Etheostoma camurum | | | Brindled madtom | Noturus miurus | | | Brook trout | Salvelinus fontinalis | Natives only | | Creek chubsucker | Erimyzon oblongus | | | Eastern sand darter | Ammocrypta pellucida | | | Goldeye | Hiodon alosoides | | | Hornyhead chub | Nocomis biguttatus | | | Lake chubsucker | Erimyzon sucetta | | | Least brook lamprey | Lampetra aepyptera | | | Least darter | Etheostoma microperca | | | Mimic shiner | Notropis volucellus | | | Mooneye | Hiodon tergisus | Lake Erie drainage basin | | Mountain madtom | Noturus eleutherus | | | Muskellunge | Esox masquinongy | Natives only | | North brook lamprey | Ichthyomyzon fossor | | | Northern madtom | Noturus stigmosus | | | Popeye shiner | Notropis ariommus | | | Pugnose minnow | Opsopoeodus emiliae | | | Redside dace | Clinostomus elongatus | | | River chub | Nocomis micropogon | | | River darter | Percina schumardi | Lake Erie drainage basin | | Rosyface shiner | Notropis rubellus | | | Silver lamprey | Ichthyomyzon unicuspis | | | South redbelly dace | Phoxinus erythrogaster | | | Streamline chub | Erimystax dissimilis | | | Tonguetied minnow | Exoglossum laurae | | | Variegate darter | Etheostoma variatum | | | Western banded killifish | Fundulus diaphanus menona | |
| Common name | Latin name | Comment | | | | | Fish | | | | Bigmouth shiner | Notropis dorsalis | | | Bluebreast darter | Etheostoma camurum | | | Lake chubsucker | Erimyzon sucetta | | | Paddlefish | Polyodon spathula | | | River darter | Percina shumardi | | | Rosyside dace | Clinostomus funduloides | | | Silver lamprey | Ichthyomyzon unicuspis | | | Tippecanoe darter | Etheostoma tippencanoe | | | Mollusks | | | | Black sandshell | Liqumia recta | | | Ebonyshell | Fusconaia ebena | | | Fawnsfoot | Truncilla donaciformis | | | Pondhorn | Uniomerus tetralasmus | | | Snuffbox | Epioblasma triquetra | | | Threehorn wartyback | Obliquaria reflexa | | | Other | | | | Sloan's crayfish | Orconectes sloanii | |
| Water body name | Flows into | Drainage basin | | | | | Alum creek - headwaters to West branch (RM 42.8) | Big Walnut creek | Scioto | | Anderson fork - Grog run (RM 11.02) to the mouth | Caesar creek | Little Miami | | Archers fork | Little Muskingum river | Central Ohio tributaries | | Arney run - Black run (RM 2.2) to the mouth | Clear creek | Hocking | | Ashtabula river - confluence of East and West fork (RM 27.54) to adjacent East 23rd street (RM 2.00) | Lake Erie | Ashtabula | | Auglaize river - Kelly road (RM 77.32) to Jennings creek (RM 47.02) | Maumee | Maumee | | Baughman creek | Grand river | Grand | | Beech fork | Salt creek | Scioto | | Bend fork - Joy fork (RM 4.0) to the mouth | Captina creek | Central Ohio tributaries | | Big run | Federal creek | Hocking | | Big Walnut creek - Rocky fork (RM 28.3) to the mouth | Scioto river | Scioto | | Blue creek | Churn creek | Scioto | | Brill run | Marietta run | Hocking | | Buskirk creek | Deer creek | Scioto | | Caesar creek - Caesar Creek lake (RM 13.92) to the mouth | Little Miami river | Little Miami | | Cedar fork | Clear Fork Mohican river | Muskingum | | Cedar Lick creek | Cross creek | Central Ohio tributaries | | Center fork | Elkhorn creek | Central Ohio tributaries | | Chapman creek | Mad river | Great Miami | | Clear creek | Rocky fork | Scioto | | Clear creek - Cattail creek (RM 9.52) to the mouth | Hocking river | Hocking | | Compton creek | North Fork Paint creek | Scioto | | Congo creek | Scippo creek | Scioto | | Deer creek - Bradford/Sugar creek confluence (RM 41.22) to Deer creek reservoir (RM 29.40) | Scioto river | Scioto | | Dismal creek | Witten Fork | Central Ohio tributaries | | East Branch Jelloway creek | Jelloway creek | Muskingum | | East Fork Little Miami river - East Fork lake (RM 20.5) to the mouth | Little Miami river | Little Miami | | East Fork Little Miami river - Howard run (RM 45.18) to Tunnel Mill road (RM 30.1) | Little Miami river | Little Miami | | East Fork Queer creek | Queer creek | Scioto | | Elkhorn creek | Yellow creek | Central Ohio tributaries | | Federal creek - Hyde fork (RM 16.21) to the mouth | Hocking river | Hocking | | Fish Creek - headwaters to the Indiana state line (RM 29.37) | St. Joseph river | Maumee | | Furnace run | Cuyahoga river | Cuyahoga | | Goose run - downstream Winnerline road (RM 3.00) to the mouth | Bantas fork | Great Miami | | Grace run | Cherry fork | Southwest Ohio tributaries | | Great Miami river - Quincy dam (RM 143.4) to Pasco-Montra road (RM 134.8) | Ohio river | Great Miami | | Great Miami river - Sidney water works dam (RM 130.2) to Loramie creek RM (119.9) | Ohio river | Great Miami | | Great Miami river - Lost creek (RM 100.0) to the CSX railroad bridge (RM 84.5) | Ohio river | Great Miami | | Hay run | Deer creek | Scioto | | Hellbranch run - Kropp road RM (5.04) to the mouth | Big Darby creek | Scioto | | Honey creek | Great Miami river | Great Miami | | Huron river - East/West branch confluence (RM 14.7) to the Ohio turnpike (RM 9.1) | Lake Erie | Huron | | Indianfield run | Kokosing river | Muskingum | | Jelloway creek | Kokosing river | Muskingum | | Joes run | Big run | Hocking | | Laurel run | Salt creek | Scioto | | Leith run | Ohio river | Central Ohio tributaries | | Little Darby creek | Big Darby creek | Scioto | | Little Muskingum river - Witten fork (RM 46.44) to Fifteen Mile creek (RM 14.75) | Ohio river | Central Ohio tributaries | | Lower Twin creek | Ohio river | Southwest Ohio tributaries | | Lost creek | Great Miami river | Great Miami | | Long run | Rocky fork | Muskingum | | Lost run | Rocky fork | Muskingum | | Mac-o-chee creek | Mad river | Great Miami | | Mad river - headwaters to Mac-o-chee creek (RM 51.75) | Great Miami river | Great Miami | | Marietta run | Federal creek | Hocking | | Massie creek | Little Miami river | Little Miami | | McCullough creek | Scioto Brush creek | Scioto | | McKee creek | Stony creek | Great Miami | | Middle Fork Laurel run | Laurel run | Scioto | | Middle Fork Salt creek | Salt creek | Scioto | | Mill creek | South Fork Scioto Brush creek | Scioto | | Mohican river - Rocky fork (RM 27.60) to an unnamed tributary (RM 16.10) | Walhonding river | Muskingum | | Morgan fork | Sunfish creek | Scioto | | Muskingum river - confluence of Tuscarawas and Walhonding rivers (RM 111.13) to state route 208 (RM 92.0) | Ohio river | Muskingum | | Muskingum river - Licking river (RM 76.20) to Moxahala creek (RM 73.50) | Ohio river | Muskingum | | Muskingum river - Salt creek (RM 67.03) to Branch run (RM 52.58) | Ohio river | Muskingum | | Muskingum river - McConnelsville dam (RM 49.0) to Madison run (RM 34.4) | Ohio river | Muskingum | | Muskingum river - Beverly dam (RM 24.9) to Cushing run (RM 18.77) | Ohio river | Muskingum | | Muskingum river - Lowell dam (RM 14.1) to Rainbow creek (RM 7.7) | Ohio river | Muskingum | | Muskingum river - Devola dam (RM 5.77) to the mouth | Ohio river | Muskingum | | Nancy run | North Fork Yellow creek | Central Ohio tributaries | | Nellis run | Big run | Hocking | | North Fork Captina creek - Long run (RM 4.0) to the mouth | Captina creek | Central Ohio tributaries | | North Fork Yellow creek | Yellow creek | Cuyahoga | | Ohio Brush creek - headwaters to Beasley Fork road (RM 6.30) | Ohio river | Southwest Ohio tributaries | | Opossum creek | Ohio river | Central Ohio tributaries | | Painter run | Rocky fork | Muskingum | | Pine creek | Salt creek | Scioto | | Pine creek - Hales creek (RM 38.15) to the mouth | Ohio river | Southeast Ohio tributaries | | Piney fork | Sunfish creek | Central Ohio tributaries | | Pretty run | Salt creek | Scioto | | Proctor run | Treacle creek | Scioto | | Queer creek | Salt creek | Scioto | | Randall run | Mill creek | Scioto | | Rarden creek | Scioto Brush creek | Scioto | | Rocky fork - U.S. route 62 (RM 5.1) to the mouth | Big Walnut creek | Scioto | | Rocky fork - headwaters to Rocky fork lake (RM 16.88) | Paint creek | Scioto | | Schenck creek | Kokosing river | Muskingum | | Scioto Brush creek - headwaters to McCullough creek (RM 10.2) | Scioto river | Scioto | | Scioto river - Indian run (RM 145.18) to Olentangy river (RM 132.33) | Ohio river | Scioto | | Scioto river - Scioto Big run (RM 124.40) to Scippo creek (RM 89.61) | Ohio river | Scioto | | Scioto river - Paint creek (RM 63.50) to Salt creek (RM 51.18) | Ohio river | Scioto | | Scioto river - Scioto Brush creek (RM 9.2) to the mouth | Ohio river | Scioto | | Scippo creek - Old Tarlton pike (RM 14.80) to the mouth | Scioto river | Scioto | | Sevenmile creek | Fourmile creek | Great Miami | | South Fork Captina creek | Captina creek | Central Ohio tributaries | | South Fork Eagle creek | Eagle creek | Mahoning | | South Fork Scioto Brush creek - Shawnee creek (RM 8.3) to the mouth | Scioto Brush creek | Scioto | | Spain creek | Big Darby creek | Scioto | | Spring fork | Little Darby creek | Scioto | | Spring run | Federal creek | Hocking | | Stillwater river - Englewood dam (RM 9.0) to the mouth | Great Miami river | Great Miami | | Strawcamp run | Elkhorn creek | Central Ohio tributaries | | Sunfish creek - headwaters to Negro run (RM 1.7) | Ohio river | Central Ohio tributaries | | Trail run | Center fork | Central Ohio tributaries | | Turkey creek | Ohio river | Southwest Ohio tributaries | | Turkey run | Sugartree fork | Muskingum | | Unnamed tributary to East Branch Black river at RM 41.41 | East Branch Black river | Black | | Upper Twin creek | Ohio river | Southwest Ohio tributaries | | West Branch Alum creek - Ashley West Liberty road (RM 5.09) to the mouth | Alum creek | Scioto | | West Branch Huron river - Slate run (RM 10.52) to the mouth | Huron river | Huron | | West Branch St. Joseph river - Michigan state line (RM 11.41) to the mouth | St. Joseph river | Maumee | | West fork - Buck run (RM 9.0) to the mouth | Ohio Brush creek | Southwest Ohio tributaries | | Whitewater river - Indiana state line (RM 8.26) to the mouth | Great Miami river | Great Miami | | Wildcat run | Big run | Hocking | | Winding fork | Wakatomika creek | Muskingum | | Winterstein run | South Fork Scioto Brush creek | Scioto | | Witten fork | Little Muskingum river | Central Ohio tributaries | | Witten run | Clear Fork Little Muskingum river | Central Ohio tributaries | | Yellow creek | Cuyahoga river | Cuyahoga | | Yellow Springs creek | Little Miami river | Little Miami |
| Water body name | Flows into | Drainage basin | | | | | Aurora branch - state route 82 (RM 17.08) to the mouth | Chagrin river | Chagrin | | Bantas fork | Twin creek | Great Miami | | Big Darby creek | Scioto river | Scioto | | Captina creek - North/South forks (RM 25.42) to state route 7 (RM 0.70) | Ohio river | Central Ohio tributaries | | Chagrin river - Woodiebrook road (RM 49.14) to state route 6 (RM 11.1) | Lake Erie | Chagrin | | Conneaut creek - state line (RM 23.83) to the mouth | Lake Erie | Ashtabula | | Cuyahoga river - Troy-Burton township line (RM 83.9) to U.S. route 14 (RM 60.75) | Lake Erie | Cuyahoga | | Deer creek - Deer creek dam (RM 23.89) to the mouth | Scioto river | Scioto | | East Branch Chagrin river - Heath road (RM 14.49) to the mouth | Chagrin river | Chagrin | | Fish creek - Indiana state line (RM 5.57) to the mouth | St. Joseph river | Maumee | | Grand river - state route 322 (RM 67.08) to U.S. route 20 (RM 5.67) | Lake Erie | Grand | | Greenville creek - Indiana state line (RM 34.48) to the mouth | Stillwater river | Great Miami | | Kokosing river | Walhonding river | Muskingum | | Little Beaver creek | Ohio river | Little Beaver creek | | Little Darby creek | Big Darby creek | Scioto | | Little Miami river | Ohio river | Little Miami | | Middle Fork Little Beaver creek - Middle run (RM 8.57) to the mouth | Little Beaver creek | Little Beaver creek | | North Branch Kokosing river | Kokosing river | Muskingum | | North Fork Little Beaver creek - Pennsylvania state line (RM 7.75) to the mouth | Little Beaver creek | Little Beaver creek | | North Fork Little Miami river | Little Miami river | Little Miami | | North Fork Paint creek - Compton creek (RM 24.57) to the mouth | Paint creek | Scioto | | Olentangy river - Delaware dam (RM 32.35) to Old Wilson Bridge road (RM 11.45) | Scioto river | Scioto | | Paint creek - Rocky fork (RM 37.12) to North fork (RM 3.80) | Scioto river | Scioto | | Pleasant run | Big Darby creek | Scioto | | Rocky fork | Licking river | Muskingum | | Salt creek | Scioto river | Scioto | | Sandusky river - U.S. route 30 (RM 82.1) to Roger Young Memorial park in Fremont (RM 16.6) | Lake Erie | Sandusky | | Scioto Brush Creek - McCullough creek (RM 10.20) to the mouth | Scioto river | Scioto | | South Fork Scioto Brush creek - Shawnee creek (RM 8.30) to the mouth | Scioto Brush creek | Scioto | | Stillwater river - Riffle road (RM 55.90) to the Englewood dam (RM 9.01) | Great Miami river | Great Miami | | Twin creek | Great Miami river | Great Miami | | Unnamed tributary to East Branch Black river at RM 39.06 | East Branch Black river | Black | | Vermilion river - Southwest branch (RM 47.66) to state route 2 (RM 3.15) | Lake Erie | Vermilion | | Wakatomika creek | Muskingum river | Muskingum | | Walhonding river | Tuscarawas river | Muskingum | | West Fork Little Beaver creek - Brush creek (RM 15.99) to the mouth | Little Beaver creek | Little Beaver creek |
| Water body name | Flows into | Drainage basin | | | | | Cuyahoga river - Sand run (RM 39.12) to Rockside road (RM 13.13) | Lake Erie | Cuyahoga | | Maumee river - Indiana state line (RM 108.1) to the U.S. route 25 bridge (RM 15.05) | Maumee Bay | Maumee |
| Water body name | Flows into | Drainage basin | | | |
|
Rule 3745-1-06 | Mixing zone demonstration and sizing requirements.
Effective:
March 20, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) Non-thermal mixing zones. Pursuant to this chapter, where necessary to attain or maintain the use designation for a surface water by these water quality standards, the director may establish, as a term of a discharge permit issued pursuant to Chapter 3745-33 of the Administrative Code or a permit to install issued pursuant to Chapter 3745-42 of the Administrative Code, a mixing zone applicable to the non-thermal constitutants constituents of the point source discharge authorized by such permit. (B) Thermal mixing zones. Pursuant to this chapter, the director may establish, as a term of a discharge permit issued pursuant to Chapter 3745-33 of the Administrative Code or a permit to install issued pursuant to Chapter 3745-42 of the Administrative Code, a mixing zone applicable to the thermal component of the point source discharge authorized by such permit. (C) For the purpose of establishing a mixing zone other than as specified in rule 3745-2-05 of the Administrative Code, a mixing demonstration, subject to review by Ohio EPA, shall be performed in accordance with this rule. This rule describes general requirements for all demonstrations, requirements specific to area of initial mixing (AIM) demonstrations, and requirements for sizing acute and chronic mixing zones, and criteria necessary to establish mixing zones for bioaccumulative chemicals of concern (BCCs). (D) Mixing zone demonstrations may be conducted for any of the following situations: (1) To justify water quality based effluent limits (WQBELs) greater than the inside mixing zone maximum (IMZM) criteria for aquatic life and WQBELs greater than 1.0 TUa for whole effluent toxicity pursuant to rule 3745-2-09 of the Administrative Code by use of an AIM. (2) For application of a percentage of the stream design flow other than the default value selected by procedures in rule 3745-2-05 of the Administrative Code. (3) For application of more than ten parts lake water to one part effluent when determining wasteload allocations (WLAs) for discharges to lake Erie or non-flowing waters. (4) For application of a mixing zone for BCCs to existing dischargers after November 15, 2010. (5) In other situations at the director's discretion. (E) All mixing zone demonstrations shall fulfill the following: (1) Describe the amount of dilution occurring at stream design flow conditions, or other conditions found to be most critical with respect to effluent and receiving water mixing, at the boundaries of the proposed mixing zone and the size, shape and location of the area of mixing, including the manner in which diffusion and dispersion occur. (2) For sources discharging to lake Erie or other non-flowing waters, define the location where discharge-induced mixing ceases. (3) Document the substrate character and geomorphology within the mixing zone. (4) Demonstrate that the mixing zone does not interfere with or block passage of fish or aquatic life. (5) Demonstrate that the mixing zone will not jeopardize the continued existence of any endangered or threatened species or result in the destruction or adverse modification of such species' critical habitat. (6) Demonstrate that the mixing zone does not extend to drinking water intakes. (7) Demonstrate that the mixing zone would not otherwise interfere with the designated or existing uses of the receiving water or downstream waters. (8) Document background water quality concentrations. (9) Demonstrate that the mixing zone does not promote undesirable aquatic life or result in a dominance of nuisance species. (10) Provide that by allowing additional mixing/dilution, all of the following: (a) Pollutants will not settle to form objectionable deposits. (b) Floating debris, oil, scum, and other matter in concentrations that form nuisances will not be produced. (c) Objectionable color, odor, taste or turbidity will not be produced. (11) Demonstrate whether or not adjacent mixing zones overlap. (12) Demonstrate whether organisms would be attracted to the area of mixing as a result of the effluent character. (13) Demonstrate whether the habitat supports endemic or naturally occurring species. (14) Demonstrate that the mixing zone does not substantially interfere with the migratory routes, natural movements, survival, reproduction, or growth, or increase the vulnerability to predation, of any representative aquatic species. (15) Demonstrate that the mixing zone does not interfere with or prevent the recovery of an aquatic community or species population that could reasonably be expected when previously limiting water quality conditions improve. (16) Demonstrate that the mixing zone does not include any bathing area where bathhouses or lifeguards are provided. (17) Conditions within the mixing zone shall not be injurious to human health, in the event of a temporary exposure during recreation, such that scalding or burns would result. (F) The mixing zone demonstration shall be submitted to Ohio EPA for review and comment. Following receipt of Ohio EPA's comments, the applicant shall resubmit the demonstration, if necessary, addressing Ohio EPA's comments. (G) For sources discharging to lake Erie or other non-flowing waters, any adjustment to the dilution ratio shall be is limited to the dilution available in the area where discharge-induced mixing occurs. (H) The mixing zone demonstration shall be based on the assumption that a pollutant does not degrade within the proposed mixing zone, unless both of the following: (1) Scientifically valid field studies or other relevant information demonstrate that degradation of the pollutant is expected to occur under the full range of environmental conditions expected to be encountered. (2) Scientifically valid field studies or other relevant information address other factors that affect pollutants in the water column including, but not limited to, resuspension of sediments, chemical speciation and biological and chemical transformation. (I) An As part of an AIM demonstration, the discharger shall be preceded by the submittal of submit the following documentation to Ohio EPA: (1) The discharger shall complete aA completed pollution prevention alternatives assessment and showing that application of cost-effective pollution prevention practices, where practical and possible, will not preclude the need for an AIM. Applicable pollution prevention practices shall be in place, or planned for implementation, before modification or installation of a discharge structure for an approved AIM. (2) The discharger shall showA demonstration that shows that improved treatment, where practical and possible, will not preclude the need for an AIM, or that the cost of such treatment would be economically detrimental to the discharger and its community. The assessments shall include a cost/benefit analysis that represents the costs and benefits of the AIM to the environment, receiving water biota, and the citizens of Ohio as well as to the discharger and local residents. (3) The discharger shall explain An explanation of how an AIM and discharge structure may impact the environment in and around the proposed site. The discharger analysis shall point out include identification of endangered species, important habitats and recreational uses of the area and any potential impact to them. The discharger shall also address the impact of the construction process on the environment. (4) An explanation addressing the impact of the construction process on the environment. (5) The discharger shall submit proposedProposed site and structure information for Ohio EPA's use in determining habitat-related restrictions. (J) If a discharger has submitted information relating to any requirements of paragraph (I) of this rule, or suitable substitutes, during the permit process, then the director may waive one or more of the related AIM prerequisites. (K) An AIM shall beis limited to the space around the discharge structure according to the following restrictions: (1) An AIM shall does not extend beyond both of the following radial distances from the discharge port: (a) A default value of five times the natural receiving water depth (prior to construction) at the discharge point under stream design flow conditions (critical low depth for lakes). (b) A default value of fifty times the length scale factor for the discharge port (the length scale factor is the square root of the port cross-sectional area). (2) The director may accept scientifically defensible field measurements, related studies or computer modeling results defining the area that is uninhabitable (or produces a reasonable minimum exposure time) to aquatic and benthic organisms from the discharger in lieu of the discharger complying with the default values contained in paragraph (K)(1) of this rule. This site-specific information shall be used in conjunction with restrictions in paragraphs (K)(3) and (K)(4) of this rule to size the AIM. (3) An AIM shall be is limited to: the point where any discharge plume contacts the receiving water surface, bank, or bottom or contacts another discharge plume (mixture of effluent and receiving water) from the same discharge structure. An AIM shall also be limited to the point where any discharge plume decreases in center-line velocity (velocity at the geometric center of the plume) to 0.5 meters per second or a minimum center-line velocity, determined through a scientifically defensible demonstration, above which native fish species and other aquatic life are unable or unlikely to inhabit. (a) The point where any discharge plume contacts the receiving water surface, bank, or bottom or contacts another discharge plume (mixture of effluent and receiving water) from the same discharge structure. An AIM shall also be limited to the point where any discharge plume decreases in center-line velocity (velocity at the geometric center of the plume) to 0.5 meters per second or a minimum center-line velocity, determined through a scientifically defensible demonstration, above which native fish species and other aquatic life are unable or unlikely to inhabit. (b) The point where any discharge plume decreases in center-line velocity (velocity at the geometric center of the plume) to 0.5 meters per second or a minimum center-line velocity, determined through a scientifically defensible demonstration, above which native fish species and other aquatic life are unable or unlikely to inhabit. (4) An AIM shall does not contact or block access to important aquatic habitat areas including, but not limited to, tributaries, inlets, bays, wetlands, spawning grounds, and important feeding areas. (5) General location and structural restrictions. The discharge structure producing the AIM shall does not: be exposedextend above the water surface under stream design flow or historical low-level conditions except at the bank; significantly alter the natural currents and erosion and deposition patterns of the receiving water; or cause significant bottom scouring. (6) Location and structural restrictions for mixing zones containing an AIM in streams and rivers. (a) The distance between the edge of the AIM and any other discharge or AIM in the receiving water shall is equal to or exceed exceeds five times the local stream width or one hundred meters, whichever is greater. (b) The distance between the edge of an AIM and any intake of a drinking water source shall is equal to or exceed exceeds ten times the local stream width or two hundred meters, whichever is greater. The discharger shall demonstrate demonstrates that the effluent plume will not impact an intake under any flow condition. (c) The director may accept field measurements, scientific studies and computer modeling studies, in lieu of the discharger complying with the minimum distances contained in paragraphs (K)(6)(a) and (K)(6)(b) of this rule to size the AIM. (7) Location and structural restrictions for mixing zones containing an AIM in lake Erie or non-flowing waters. (a) The distance between the edge of the AIM and any other discharge or AIM in the receiving water shall is equal to or exceed greater than two hundred meters. (b) The distance between the edge of an AIM and any intake of a drinking water source shall is equal to or exceed greater than five hundred meters. The discharger shall also demonstrate that the effluent plume will not impact the intake under any variation in current or lake level. (c) The director may accept field measurements, scientific studies and computer modeling studies from the discharger in lieu of the discharger complying with the minimum distances contained in paragraphs (K)(7)(a) and (K)(7)(b) of this rule to size the AIM. (d) The AIM discharge point should be located as far as reasonably possible from shore, in deep water. Structures sited close to shore or in shallow water shall be are more strictly limited. (8) Construction or modification of the discharge structure producing the AIM shall not do any of the following: (a) Permanently alter the natural physical characteristics of the receiving water such as depth, width, cross-section, and slope. (b) Permanently expose erodible sediments or alter the natural bed materials. (c) Permanently alter bank and riparian characteristics. (d) Impact or damage important areas or habitats. (9) Discharge flow and velocity requirements for structures producing the AIM. (a) Both of the following waste flow velocities shall be maintained from each port of the discharge structure under all discharge and ambient conditions: (i) At least 2.5 meters per second daily average velocity. (ii) 1.75 meters per second minimum velocity at any time. (b) The director may accept scientifically defensible studies from the discharger indicating that alternative discharge velocities will sufficiently discourage habitability or minimize exposure times within the AIM in lieu of the discharger complying with paragraph (K)(9)(a) of this rule. (c) The discharge structure shall be designed such that any discharge to the receiving water may completely cease if the waste flow is insufficient to maintain the required velocities. It shall also be designed such that changes in waste flow can be accommodated quickly, without major changes to the structure and without bypassing the discharge structure. (L) For flowing streams, acute mixing zones and chronic mixing zones shall be are sized on a case-by-case basis at the director's discretion using any appropriate restrictions listed in paragraphs (F), (H), (I) and (J) of this rule. (M) For lake Erie or non-flowing waters, acute mixing zones and chronic mixing zones shall beare sized according to both of the following: (1) Acute mixing zones shall beare sized on a case-by-case basis. (2) Chronic mixing zones shall beare sized on a case-by-case basis and at the director's discretion using any appropriate restrictions listed in paragraphs (F), (H), (I) and (J) of this rule. Specific restrictions include all of the following: (a) A mixing zone shall does not extend to within one hundred meters of a drinking water intake unless the director accepts a scientifically defensible demonstration from the discharger indicating that the mixing zone can safely extend closer to the intake. (b) The maximum dilution available from the mixing zone to meet chronic criteria shall beis fifty parts lake water to one part effluent or the dilution available within sixty meters, whichever is smaller, unless the director accepts a scientifically valid demonstration from the discharger indicating that an alternative dilution ratio is appropriate. (c) The mixing zone shalldoes not extend beyond the point where discharge induced mixing occurs. (N) Mixing zones shall not be established by Ohio EPA for BCCs, beyond the dates established in rule 3745-2-05 of the Administrative Code, unless one of the following exceptions is met: (1) Exception for water conservation. Mixing zones may be granted beyond November 15, 2010 for existing discharges if the discharger demonstrates that failure to grant a mixing zone would preclude water conservation measures that would lead to overall load reductions in BCCs, even though higher concentrations of BCCs exist in the effluent. (2) Exception for technical and economic considerations. The director may grant mixing zones beyond November 15, 2010 for existing discharges upon the request of a discharger subject to all of the following limited circumstances: (a) The discharger is in compliance with its existing NPDES permit and the act and the discharger had reduced the loading of the BCC for which a mixing zone is requested to the maximum extent possible. (b) The availability and feasibility of additional controls for reducing BCCs for the discharger have been considered as well as the economic impact on the affected communities that would occur if the mixing zone were eliminated. (c) Any mixing zone exceptions granted shall adhere to the following: do not result in less stringent limitations than those existing on December 30, 2002; are not likely to jeopardize the continued existence or critical habitat of any endangered or threatened species; protect all designated and existing uses of the receiving water; and meet all applicable criteria and values at the edge of or, as appropriate, within the mixing zone. (i) Do not result in less stringent limitations than those existing on December 30, 2002; are not likely to jeopardize the continued existence or critical habitat of any endangered or threatened species; protect all designated and existing uses of the receiving water; and meet all applicable criteria and values at the edge of or, as appropriate, within the mixing zone. (ii) Are not likely to jeopardize the continued existence of critical habitat of any endangered or threatened species; (iii) Protect all designated and existing uses of the receiving water; (iv) Meet all applicable criteria and values at the edge of or, as appropriate, within the mixing zone. (d) Any mixing zone exceptions granted shall conform to the following: be reevaluated for each successive permit application in which a mixing zone for the BCCs is sought, shall ensure that the discharger has developed and conducted a pollutant minimization program for the BCCs, and that alternative means for reducing BCCs elsewhere in the watershed have been evaluated. (i) Be reevaluated for each successive permit application in which a mixing zone for the BCCs is sought, shall ensure that the discharger has developed and conducted a pollutant minimization program for the BCCs, and that alternative means for reducing BCCs elsewhere in the watershed have been evaluated. (ii) Ensure that the discharger has developed and conducted a pollutant minimization program for the BCCs, (iii) Ensure that alternative means for reducing BCCs elsewhere in the watershed have been evaluated. (O) Thermal mixing zones. (1) The director may establish as a term of a discharge permit issued pursuant to Chapter 3745-33 of the Administrative Code, or a permit to install issued pursuant to Chapter 3745-42 of the Administrative Code, a mixing zone applicable to the thermal component of the point source discharge authorized by such permit. A thermal mixing zone, which allows dilution and cooling of a waste heat discharge, shall beis considered a region in which organism response to temperature is time-dependent. (a) Exposure to temperatures in a thermal mixing zone shall may not cause an irreversible response that results in deleterious effects to the wildlife and aquatic life representative of the receiving waters. (b) The daily average temperature in a thermal mixing zone at the point nearest to the discharge that is accessible to the resident aquatic organisms shall may not exceed the temperatures in table 1 of this rule at the corresponding ambient temperature. (c) At ambient temperatures of fifty-nine degrees Fahrenheit (fifteen degrees Celsius) and above, the daily average temperature in a thermal mixing zone shall be determined on a case-by-case basis. (2) Thermal mixing zone size limitations shall be established by the director pursuant to paragraph (O)(1) of this rule in accordance with paragraph (E) of this rule for all point source discharges subject to permit. (3) Any request for a thermal mixing zone in one of the following waters shall be preceded by an evaluation of treatment alternatives that would preclude the need for a mixing zone., This evaluation shall to include a cost benefit analysis that presents the costs and benefits of the mixing zone to the environment, receiving water biota, and the citizens of Ohio, as well as to the discharger and local residents. The provisions of this paragraph do not apply to demonstrations conducted under Section 316(a) of the act. (a) Any stream designated coldwater habitat. (b) Any stream designated exceptional warmwater habitat. (c) Any lake other than lake Erie The thermal mixing zone shall not cause an increase in pathogens that would contribute to an impairment of a designated use in any area of the water body outside the mixing zone; nor shall the thermal mixing zone cause nuisance growths, colors or odors from harmful, toxic, invasive or noxious organisms. (4) Any thermal mixing zone request involving a new or expanded discharge must also evaluate other discharge alternatives as required by in accordance with rule 3745-1-05 of the Administrative Code. (5) Discharges of closed-cycle cooling blowdown with a flow of less than five per cent of the 7Q10 of the receiving water body are exempt from paragraph (O)(1) of this rule. Table 1. Temperature (a) Daily average temperatures of thermal mixing zones for all waters other than lake Erie at corresponding ambient temperatures as required in accordance with paragraph (O)(1) of this rule. Shown as degrees Fahrenheit and (Celsius). | Ambient - °F (°C) | Daily average temperature -°F (°C) | Ambient - °F (°C) | Daily average temperature -°F (°C) | | 32 (0) | 50 (10.0) | 48 (8.9) | 71 (21.7) | | 33 (0.6) | 50 (10.0) | 49 (9.4) | 73 (22.8) | | 34 (1.1) | 50 (10.0) | 50 (10.0) | 75 (23.9) | | 35 (1.7) | 51 (10.6) | 51 (10.6) | 76 (24.4) | | 36 (2.2) | 52 (11.1) | 52 (11.1) | 78 (25.6) | | 37 (2.8) | 54 (12.2) | 53 (11.7) | 79 (26.1) | | 38 (3.3) | 55 (12.8) | 54 (12.2) | 81 (27.2) | | 39 (3.9) | 57 (13.9) | 55 (12.8) | 83 (28.3) | | 40 (4.4) | 58 (14.4) | 56 (13.3) | 85 (29.4) | | 41 (5.0) | 60 (15.6) | 57 (13.9) | 86 (30.0) | | 42 (5.6) | 62 (16.7) | 58 (14.4 ) | 88 (31.1) | | 43 (6.1) | 63 (17.2) | 59 (15) and above - daily average limit will be determined on a case-by-case basis pursuant to paragraphs (O)(1) and (O)(2) of this rule. | | 44 (6.7) | 65 (18.3) | | 45 (7.2) | 66 (18.9) | | 46 (7.8) | 68 (20.0) | | 47 (8.3) | 70 (21.1) |
(b) Daily average temperatures of thermal mixing zones for lake Erie at corresponding ambient temperatures as required in accordance with paragraph (O)(1) of this rule. Shown as degrees Fahrenheit and (Celsius). | Ambient - °F (°C) | Daily average temperature -°F (°C) | Ambient - °F (°C) | Daily average temperature -°F (°C) | | 32 (0) | 52 (11.1) | 48 (8.9) | 68 (20.0) | | 33 (0.6) | 52.5 (11.4) | 49 (9.4) | 70 (21.1) | | 34 (1.1) | 53.5 (11.9) | 50 (10.0) | 71 (21.7) | | 35 (1.7) | 54.4 (12.4) | 51 (10.6) | 73 (22.8) | | 36 (2.2) | 55 (12.8) | 52 (11.1) | 75 (23.9) | | 37 (2.8) | 56 (13.3) | 53 (11.7) | 77 (25.0) | | 38 (3.3) | 57 (13.9) | 54 (12.2) | 78 (25.6) | | 39 (3.9) | 58 (14.4) | 55 (12.8) | 80 (26.7) | | 40 (4.4) | 59 (15) | 56 (13.3) | 82 (27.8) | | 41 (5.0) | 59.5 (15.3) | 57 (13.9) | 84 (28.9) | | 42 (5.6) | 60 (15.6) | 58 (14.4) | 86 (30.0) | | 43 (6.1) | 61 (16.1) | 59 (15) and above - daily average limit will be determined on a case-by-case basis pursuant to paragraphs (O)(1) and (O)(2) of this rule. | | 44 (6.7) | 62 (16.7) | | 45 (7.2) | 63 (17.2) | | 46 (7.8) | 65 (18.3) | | 47 (8.3) | 66 (18.9) |
Last updated March 21, 2024 at 12:46 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-07 | Beneficial use designations and biological criteria.
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] [Comment: Statewide water quality criteria designed to protect beneficial uses are in rules 3745-1-04 and 3745-1-33 to 3745-1-37 of the Administrative Code. Chemical specific criteria applicable to lake Erie are contained in rule 3745-1-31 of the Administrative Code. Chemical specific criteria applicable to the Ohio river are contained in rule 3745-1-32 of the Administrative Code. Additional chemical specific criteria may be derived as described in rules 3745-1-40 to 3745-1-43 of the Administrative Code.] (A) Water quality standards consist of designated uses, narrative and numeric criteria necessary to protect those uses, antidegradation requirements, and general policies. (1) Each water body in the state is assigned one or more aquatic life habitat use designations. Each water body may be assigned one or more water supply use designations and one recreational use designation. These use designations are defined in paragraph (B) of this rule. Water bodies are assigned use designations in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-32 of the Administrative Code. In addition, water bodies are assigned designations as described in paragraphs (B)(1)(a), (B)(1)(c), (B)(3)(a), (B)(4)(a) and (B)(4)(b) of this rule and in the antidegradation rule (rule 3745-1-05 of the Administrative Code). (2) The most stringent chemical-specific criteria associated with any one of the use designations assigned to a water body will apply to that water body. (B) Use designations are defined as follows: (1) Aquatic life habitat. (a) "Warmwater" - these are waters capable of supporting and maintaining a balanced, integrated, adaptive community of warmwater aquatic organisms having a species composition, diversity, and functional organization comparable to the twenty-fifth percentile of the identified reference sites within each of the following ecoregions: the interior plateau ecoregion, the Erie/Ontario lake plains ecoregion, the western Allegheny plateau ecoregion and the eastern corn belt plains ecoregion. For the Huron/Erie lake plains ecoregion, the comparable species composition, diversity and functional organization are based upon the ninetieth percentile of all sites within the ecoregion. For all ecoregions, the attributes of species composition, diversity and functional organization will be measured using the index of biotic integrity, the modified index of well-being and the invertebrate community index as defined in "Biological Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Volume II, Users Manual for Biological Field Assessment of Ohio Surface Waters," as cited in paragraph (B) of rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code. In addition to those water body segments designated in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-32 of the Administrative Code, all upground storage reservoirs are designated warmwater habitats. Attainment of this use designation (except for upground storage reservoirs) is based in the criteria in table 7-1 of this rule. A temporary variance to the criteria associated with this use designation may be granted as described in paragraph (F) of rule 3745-1-01 of the Administrative Code. (b) "Limited warmwater" - default aquatic life criteria established in paragraph (A) of rule 3745-1-35 of the Administrative Code apply to waters with this designation. (c) "Exceptional warmwater" - these are waters capable of supporting and maintaining an exceptional or unusual community of warmwater aquatic organisms having a species composition, diversity, and functional organization comparable to the seventy-fifth percentile of the identified reference sites on a statewide basis. The attributes of species composition, diversity and functional organization will be measured using the index of biotic integrity, the modified index of well-being and the invertebrate community index as defined in "Biological Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Volume II, Users Manual for Biological Field Assessment of Ohio Surface Waters," as cited in paragraph (B) of rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code. In addition to those water body segments designated in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-32 of the Administrative Code, all lakes and reservoirs, except upground storage reservoirs, are designated exceptional warmwater habitats. Attainment of this use designation (except for lakes and reservoirs) is based on the criteria in table 7-1 of this rule. A temporary variance to the criteria associated with this use designation may be granted as described in paragraph (F) of rule 3745-1-01 of the Administrative Code. (d) "Modified warmwater" - these are waters that have been the subject of a use attainability analysis and have been found to be incapable of supporting and maintaining a balanced, integrated, adaptive community of warmwater organisms due to irretrievable modifications of the physical habitat. Such modifications are of a long lasting duration (i.e., twenty years or longer) and may include the following examples: extensive stream channel modification activities permitted under sections 401 and 404 of the act or Chapter 6131. of the Revised Code, extensive sedimentation resulting from abandoned mine land runoff, and extensive permanent impoundment of free flowing water bodies. The attributes of species composition, diversity and functional organization will be measured using the index of biotic integrity, the modified index of well-being and the invertebrate community index as defined in "Biological Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Volume II, Users Manual for Biological Field Assessment of Ohio Surface Waters," as cited in paragraph (B) of rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code. Attainment of this use designation is based on the criteria in table 7-1 of this rule. Each water body designated modified warmwater habitat will be listed in the appropriate use designation rule (rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-32 of the Administrative Code) and will be identified by ecoregion and type of physical habitat modification as listed in table 7-1 of this rule. The modified warmwater habitat designation can be applied only to those waters that do not attain the warmwater habitat biological criteria in table 7-1 of this rule because of irretrievable modifications of the physical habitat. All water body segments designated modified warmwater habitat will be reviewed on a triennial basis (or sooner) to determine whether the use designation should be changed. A temporary variance to the criteria associated with this use designation may be granted as described in paragraph (F) of rule 3745-1-01 of the Administrative Code. (e) "Seasonal salmonid" - these are rivers, streams and embayments capable of supporting the passage of salmonids from October to May and are water bodies large enough to support recreational fishing. This use will be in effect the months of October to May. Another aquatic life habitat use designation will be enforced the remainder of the year (June to September). A temporary variance to the criteria associated with this use designation may be granted as described in paragraph (F) of rule 3745-1-01 of the Administrative Code. (f) "Coldwater" - these are waters that meet one or both of the characteristics described in paragraphs (B)(1)(f)(i) and (B)(1)(f)(ii) of this rule. A temporary variance to the criteria associated with this use designation may be granted as described in paragraph (F) of rule 3745-1-01 of the Administrative Code. (i) "Coldwater habitat, inland trout streams" - these are waters which support trout stocking and management under the auspices of the Ohio department of natural resources, division of wildlife, excluding waters in lake run stocking programs, lake or reservoir stocking programs, experimental or trial stocking programs, and put and take programs on waters without, or without the potential restoration of, natural coldwater attributes of temperature and flow. The director will designate these waters in consultation with the director of the Ohio department of natural resources. (ii) "Coldwater habitat, native fauna" - these are waters capable of supporting populations of native coldwater fish and associated vertebrate and invertebrate organisms and plants on an annual basis. The director shall designate these waters based upon results of use attainability analyses. (g) "Limited resource water" - these are waters that have been the subject of a use attainability analysis and have been found to lack the potential for any resemblance of any other aquatic life habitat as determined by the biological criteria in table 7-1 of this rule. The use attainability analysis must demonstrate that the extant fauna is substantially degraded and that the potential for recovery of the fauna to the level characteristic of any other aquatic life habitat is realistically precluded due to natural background conditions or irretrievable human induced conditions. For water bodies in the lake Erie drainage basin, the designation of water bodies as limited resource waters shall include demonstrations that the "Outside Mixing Zone Average" water quality criteria and values and chronic whole effluent toxicity levels are not necessary to protect the designated uses and aquatic life pursuant to rule 3745-1-39 of the Administrative Code. All water body segments designated limited resource water will be reviewed on a triennial basis (or sooner) to determine whether the use designation should be changed. A temporary variance to the criteria associated with this use designation may be granted as described in paragraph (F) of rule 3745-1-01 of the Administrative Code. Waters designated limited resource water will be assigned one or more of the following causative factors. These causative factors will be listed as comments in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-30 of the Administrative Code. (i) "Acid mine drainage" - these are surface waters with sustained pH values below 4.1 s.u. or with intermittently acidic conditions combined with severe streambed siltation, and have a demonstrated biological performance below that of the modified warmwater habitat biological criteria. (ii) "Small drainageway maintenance" - these are highly modified surface water drainageways (usually less than three square miles in drainage area) that do not possess the stream morphology and habitat characteristics necessary to support any other aquatic life habitat use. The potential for habitat improvements must be precluded due to regular stream channel maintenance required for drainage purposes. (iii) Other specified conditions. (2) Water supply. (a) "Public" - these are waters that, with conventional treatment, will be suitable for human intake and meet federal regulations for drinking water. Criteria associated with this use designation apply within five hundred yards of surface water intakes. Although not necessarily included in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-30 of the Administrative Code, the bodies of water with one or more of the following characteristics are designated public water supply: (i) All publicly owned lakes and reservoirs, with the exception of Piedmont reservoir. (ii) All privately owned lakes and reservoirs used as a source of public drinking water. (iii) All surface waters within five hundred yards of an existing public water supply surface water intake. (iv) All surface waters used as emergency water supplies. (b) "Agricultural" - these are waters suitable for irrigation and livestock watering without treatment. (c) "Industrial" - these are waters suitable for commercial and industrial uses, with or without treatment. Criteria for the support of the industrial water supply use designation will vary with the type of industry involved. (3) Recreation. These use designations are in effect only during the recreation season, which is the period from May first to October thirty-first. The director may require effluent disinfection, as a term or condition of a national pollutant discharge elimination system (NPDES) permit, administrative findings and orders or a judicial order, during the months outside the recreation season if necessary to protect an unusually high level of water based recreation activity such as, but not limited to, canoeing, kayaking, scuba diving, or sport fishing during spawning runs and, in the normal pursuit of the recreation activity, there is a strong likelihood of exposure to water borne pathogens through ingestion of water or from dermal exposure through fresh cuts or abrasions. (a) "Bathing waters" - these are waters that, during the recreation season, are heavily used for swimming. The bathing water use applies to all waters in areas where a lifeguard or bathhouse facilities are present, and to any additional water bodies designated bathing waters in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-32 of the Administrative Code. (b) "Primary contact" - these are waters that, during the recreation season, are suitable for one or more full body contact recreation activities such as, but not limited to, wading, swimming, boating, water skiing, canoeing, kayaking, and scuba diving. All surface waters of the state are designated as primary contact recreation unless otherwise designated as bathing waters or secondary contact recreation. (c) "Secondary contact" - these are waters that result in minimal exposure potential to water borne pathogens because the waters are: rarely used for water based recreation such as, but not limited to, wading; situated in remote, sparsely populated areas; have restricted access points; and have insufficient depth to provide full body immersion, thereby greatly limiting the potential for water based recreation activities. Waters designated secondary contact recreation are identified in rules 3745-1-08 to 3745-1-30 of the Administrative Code. (C) Biological criteria. Biological criteria presented in table 7-1 of this rule provide a direct measure of attainment of the warmwater habitat, exceptional warmwater habitat and modified warmwater habitat aquatic life uses. Biological criteria, the provisions of this rule, and the allowance in rule 3745-2-03 of the Administrative Code do not apply to any other use designations. (1) Biological criteria (biocriteria) presented in table 7-1 of this rule describe the expected condition of biological assemblages for the warmwater habitat, exceptional warmwater habitat, and modified warmwater habitat aquatic life uses. The attainment status of these aquatic life uses (i.e., attainment or non-attainment) will be determined using biological data gathered consistent with Ohio's established methods and in weight of evidence with other indicators of environmental quality as follows: (a) Rule 3745-2-03 of the Administrative Code contains provisions for the applicability of biocriteria to NPDES permitting. For other program uses, demonstrated attainment of the applicable biological criteria in a water body will be used according to Ohio EPA procedures to determine aquatic life use attainment status upon considering appropriately detailed chemical, physical, and biological data for the water body. (b) Demonstrated nonattainment of the applicable biological criteria in a river or stream reach will cause the director to seek and establish, if possible, the cause of the nonattainment of the designated use. This can include causes associated with point and nonpoint sources and habitat and flow alterations. Options may include the re-evaluation of the existing designated use and, where not attainable, propose to change the designated use. Where the designated use is attainable and the cause of the nonattainment has been established, the director will, wherever necessary and appropriate, implement regulatory controls or make other recommendations regarding water resource management to restore the designated use. | Index | Modified warmwater habitat | Warmwater habitat | Exceptional warmwater habitat | | Sampling site | Channel modified | Mine affected | Impounded | | | | Ecoregion1 | | | | | | | (A) Index of biotic integrity (fish) | | | | | | | (1) Wading sites | | | | | | | HELP | 22 | | | 32 | 50 | | IP | 24 | | | 40 | 50 | | EOLP | 24 | | | 38 | 50 | | WAP | 24 | 24 | | 44 | 50 | | ECBP | 24 | | | 40 | 50 | | | | | | | | | (2) Boat sites | | | | | | | HELP | 20 | | 22 | 34 | 48 | | IP | 24 | | 30 | 38 | 48 | | EOLP | 24 | | 30 | 40 | 48 | | WAP | 24 | 24 | 30 | 40 | 48 | | ECBP | 24 | | 30 | 42 | 48 | | | | | | | | | (3) Headwater sites2 | | | | | | | HELP | 20 | | | 28 | 50 | | IP | 24 | | | 40 | 50 | | EOLP | 24 | | | 40 | 50 | | WAP | 24 | 24 | | 44 | 50 | | ECBP | 24 | | | 40 | 50 | | | | | | | | | (B) Modified index of well being (fish)3 | | | | | | | (1) Wading sites | | | | | | | HELP | 5.6 | | | 7.3 | 9.4 | | IP | 6.2 | | | 8.1 | 9.4 | | EOLP | 6.2 | | | 7.9 | 9.4 | | WAP | 6.2 | 5.5 | | 8.4 | 9.4 | | ECBP | 6.2 | | | 8.3 | 9.4 | | | | | | | | | (2) Boat sites | | | | | | | HELP | 5.7 | | 5.7 | 8.6 | 9.6 | | IP | 5.8 | | 6.6 | 8.7 | 9.6 | | EOLP | 5.8 | | 6.6 | 8.7 | 9.6 | | WAP | 5.8 | 5.4 | 6.6 | 8.6 | 9.6 | | ECBP | 5.8 | | 6.6 | 8.5 | 9.6 | | | | | | | | | (C) Invertebrate community index (macroinvertebrates) | | | | | | | (1) Artificial substrate samplers | | | | | | | HELP | 22 | | | 34 | 46 | | IP | 22 | | | 30 | 46 | | EOLP | 22 | | | 34 | 46 | | WAP | 22 | 30 | | 36 | 46 | | ECBP | 22 | | | 36 | 46 |
1HELP = Huron/Erie lake plain ecoregion. IP = interior plateau ecoregion. EOLP = Erie/Ontario lake plain ecoregion. WAP = western Allegheny plateau ecoregion. ECBP = eastern corn belt plains ecoregion. 2Headwater sites are those that drain less than twenty square miles. 3The modified index of well being does not apply to headwater sites.
Last updated June 30, 2025 at 9:04 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-08 | Hocking river drainage basin.
Effective:
April 23, 2008
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated November 29, 2022 at 10:53 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-09 | Scioto river drainage basin.
Effective:
January 2, 2017
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated April 19, 2022 at 9:22 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-10 | Grand river drainage basin.
Effective:
January 2, 2017
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated August 2, 2024 at 8:24 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-11 | Maumee river drainage basin.
Effective:
April 21, 2021
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated February 12, 2026 at 6:23 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-12 | Sandusky river drainage basin.
Effective:
April 21, 2021
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated March 9, 2026 at 4:34 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-13 | Central Ohio tributaries drainage basin.
Effective:
September 18, 2017
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated August 2, 2024 at 8:24 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-14 | Ashtabula river drainage basin.
Effective:
November 30, 2015
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated August 2, 2024 at 8:24 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-15 | Little Beaver creek drainage basin.
Effective:
November 30, 2015
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated November 29, 2022 at 10:53 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-16 | Southeast Ohio tributaries drainage basin.
Effective:
November 30, 2015
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated April 19, 2022 at 9:22 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-17 | Southwest Ohio tributaries drainage basin.
Effective:
January 2, 2017
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated April 19, 2022 at 9:22 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-18 | Little Miami river drainage basin.
Effective:
November 30, 2015
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated December 19, 2023 at 9:22 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-19 | Huron river drainage basin.
Effective:
April 21, 2021
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated February 14, 2026 at 11:15 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-20 | Rocky river drainage basin.
Effective:
January 2, 2017
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated December 19, 2023 at 9:22 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-21 | Great Miami river drainage basin.
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated April 19, 2022 at 9:22 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-22 | Chagrin river drainage basin.
Effective:
April 23, 2008
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated November 29, 2022 at 10:53 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-23 | Portage river drainage basin.
Effective:
April 21, 2021
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated June 25, 2025 at 6:16 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-24 | Muskingum river drainage basin.
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated August 2, 2024 at 8:24 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-25 | Mahoning river drainage basin.
Effective:
January 2, 2017
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated January 4, 2024 at 10:13 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-26 | Cuyahoga river drainage basin.
Effective:
February 6, 2017
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated April 25, 2021 at 10:59 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-27 | Black river drainage basin.
Effective:
November 30, 2015
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated August 2, 2024 at 8:24 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-28 | Vermilion river drainage basin.
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated August 2, 2024 at 8:24 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-29 | Wabash river drainage basin.
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated November 21, 2023 at 9:05 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-30 | Mill creek drainage basin.
Effective:
January 2, 2017
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
View Appendix
Last updated November 21, 2023 at 9:05 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-31 | Lake Erie standards.
(A) Lake Erie is designated exceptional warmwater habitat, superior high quality water, public water supply, agricultural water supply, industrial water supply and bathing waters, and will meet the criteria set forth in, or derived in accordance with, rules 3745-1-01 to 3745-1-07 and 3745-1-33 to 3745-1-43 of the Administrative Code. However, criteria set forth in this rule supersede the rules listed in this paragraph where applicable. These criteria apply outside the mixing zone. (B) Water temperature in lake Erie shall not: (1) Fluctuate as a result of human activity that causes mortality, long-term avoidance or exclusion from habitat, or adversely affect the reproductive success of representative aquatic species. (2) Exceed the average or daily maximum temperatures indicated in paragraphs (A) and (B) of table 31-1 of this rule. (3) Exceed at any time the daily maximum temperatures indicated in paragraph (C) of table 31-1 of this rule in hypolimnetic waters. Table 31-1. Temperature criteria. (A) Lake Erie western basin - includes the area of lake Erie west of a line drawn from Pelee point, Canada to Scott point on Catawba island. Shown as degrees Fahrenheit and (Celsius). | Jan. 1-31 | Feb. 1-29 | Mar. 1-15 | Mar. 16-31 | Apr. 1-15 | Apr. 16-30 | May 1-15 | May 16-31 | June 1-15 | | Average: | - | - | - | - | - | 53 (11.7) | 59 (15.0) | 65 (18.3) | 75 (23.9) | | Daily Maximum: | 35 (1.7) | 38 (3.3) | 39 (3.9) | 45 (7.2) | 51 (10.6) | 56 (13.3) | 64 (17.8) | 72 (22.2) | 78 (25.6) | | | | | | | | | | | | June 16-30 | July 1-31 | Aug. 1-31 | Sept. 1-15 | Sept. 16-30 | Oct. 1-15 | Oct. 16-31 | Nov. 1-30 | Dec. 1-31 | | Average: | 80 (26.7) | 83 (28.3) | 83 (28.3) | 78 (25.6) | 76 (24.4) | 66 (18.9) | 60 (15.6) | 53 (11.7) | - | | Daily Maximum: | 83 (28.3) | 85 (29.4) | 85 (29.4) | 83 (28.3) | 81 (27.2) | 71 (21.7) | 65 (18.3) | 58 (14.4) | 46 (7.8) | | | | | | | | | | |
(B) Lake Erie central basin - includes the area of lake Erie east of a line drawn from Pelee point, Canada to Scott point on Catawba island to the Pennsylvania-Ohio state line. Shown as degrees Fahrenheit and (Celsius). | Jan. 1-31 | Feb. 1-29 | Mar. 1-15 | Mar. 16-31 | Apr. 1-15 | Apr. 16-30 | May 1-15 | May 16-31 | June 1-15 | | Average: | - | - | - | - | 43 (6.1) | 53 (11.7) | 59 (15.0) | 63 (17.2) | 75 (23.9) | | Daily Maximum: | 35 (1.7) | 38 (3.3) | 39 (3.9) | 45 (7.2) | 48 (8.9) | 56 (13.3) | 63 (17.2) | 72 (22.2) | 78 (25.6) | | | | | | | | | | | | June 16-30 | July 1-31 | Aug. 1-31 | Sept. 1-15 | Sept. 16-30 | Oct. 1-15 | Oct. 16-31 | Nov. 1-30 | Dec. 1-31 | | Average: | 80 (26.7) | 83 (28.3) | 83 (28.3) | 76 (24.4) | 71 (21.7) | 66 (18.9) | 58 (14.4) | 48 (8.9) | - | | Daily Maximum: | 83 (28.3) | 85 (29.4) | 85 (29.4) | 81 (27.2) | 76 (24.4) | 71 (21.7) | 63 (17.2) | 53 (11.7) | 46 (7.8) | | | | | | | | | | |
(C) Seasonal daily maximum temperature limitations for the hypolimnetic regions of lake Erie. Shown as degrees Fahrenheit and (Celsius). | Month | Daily Maximum | | | | January | 44 (6.7) | | February | 44 (6.7) | | March | 44 (6.7) | | April | 47 (8.3) | | May | 51 (10.6) | | June | 54 (12.2) | | July | 59 (15.0) | | August | 59 (15.0) | | September | 55 (12.8) | | October | 46 (7.8) | | November | 41 (5.0) | | December | 38 (3.3) |
Last updated June 25, 2025 at 6:29 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-32 | Ohio river standards.
Effective:
January 18, 2021
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) The Ohio river is designated warmwater habitat, public water supply, agricultural water supply, industrial water supply and bathing waters, and will meet the most stringent criteria set forth in, or derived in accordance with, this rule, rules 3745-1-01 to 3745-1-07 and 3745-1-33 to 3745-1-40 of the Administrative Code. Table 32-1. Water quality criteria for the Ohio river. | Chemical | Form1 | Units2 | IMZM3 | OMZM3 | OMZA3 | | Bacteria (E. coli)a | T | cfu/100 mL | 126 | 126 | 126 | | Bacteria (E. coli)b | T | cfu/100 mL | 410 | 410 | 410 | | Bacteria (fecal coliform)c | T | cfu/ 100 mL | 2,000 | 2,000 | 2,000 | | Cyanide | free | µg/l | 44 | 22 | 5.2 | | Dissolved oxygen4 | T | mg/l | -- | 4.0d | 5.0 | | Radionuclides | T | | -- | e | e | | Temperature | -- | °F | -- | Table 32-3 | Table 32-3 |
1T = total. 2mg/l = milligrams per liter (parts per million); µg/l = micrograms per liter (parts per billion); °F = degrees Fahrenheit; cfu/100 mL = colony forming units per one hundred milliliters. 3IMZM = inside mixing zone maximum; OMZM = outside mixing zone maximum; OMZA = outside mixing zone average. 4For dissolved oxygen, OMZM means outside mixing zone minimum at any time and OMZA means outside mixing zone minimum daily average. aCriterion applies for contact recreation during the months of May through October and is expressed as a ninety-day geometric mean. b Criterion applies for contact recreation during the months of May through October and is not to be exceeded in more than ten per cent of samples taken during any ninety-day period. c Criterion applies at all times and is expressed as a monthly geometric mean based on not less than five samples per month. For the months of May through October, measurements of E. coli bacteria may be substituted for fecal coliform. dA minimum of 5.0 mg/l at any time shall be maintained during the April fifteen to June fifteen spawning season. eGross total alpha particle activity (including radium-226, but excluding radon and uranium) shall not exceed fifteen picocuries per liter (pci/l) and combined radium-226 and radium-228 shall not exceed four pci/l. The concentration of total gross beta particle activity shall not exceed fifty pci/l. The concentration of total strontium-90 shall not exceed eight pci/l. Table 32-2. Ohio river water quality criteria for the protection of human health. | | | OMZA3 | | Chemical | Form1 | Units2 | Intakes | Elsewhere | | Acenaphthene | T | µg/l | 70 | 70 | | Acrolein | T | µg/l | 3.0 | 3.0 | | Acrylonitrile5 | T | µg/l | 0.51 | 0.51 | | Alachlor | T | µg/l | 2.0a | -- | | Aldrin5 | T | µg/l | 7.7*10-6 | 7.7*10-6 | | Anthracene | T | µg/l | 300 | 300 | | Antimony | TR | µg/l | 5.6 | 5.6 | | Arsenic | TR | µg/l | 10a | 50 | | Asbestos | T | Mf/l | 7.0a | -- | | Atrazine | T | µg/l | 3.0a | -- | | Barium | TR | µg/l | 1,000 | 1,000 | | Benzene5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 12 | | Benzidine5 | T | µg/l | 0.00086 | 0.00086 | | Benzo(a)anthracene5 | T | µg/l | 0.012 | 0.012 | | Benzo(a)pyrene5 | T | µg/l | 0.0012 | 0.0012 | | Benzo(b)fluoranthene5 | T | µg/l | 0.012 | 0.012 | | Benzo(k)fluoranthene5 | T | µg/l | 0.038 | 0.038 | | Beryllium | TR | µg/l | 4.0a | 16 | | Bromate | T | µg/l | 10a | -- | | Bromoform (Tribromomethane)5 | T | µg/l | 43 | 43 | | Butylbenzyl phthalate5 | T | µg/l | 1.0 | 1.0 | | Cadmium | TR | µg/l | 5.0a | -- | | Carbofuran | T | µg/l | 40a | -- | | Carbon tetrachloride5 | T | µg/l | 2.3 | 2.3 | | Chloramine | T | µg/l | 4,000a | -- | | Chlordane5 | T | µg/l | 0.0031 | 0.0031 | | Chlorides | T | mg/l | 250a | 250 | | Chlorine | T | µg/l | 4,000a | -- | | Chlorine dioxide | T | µg/l | 800a | -- | | Chlorite | T | µg/l | 1,000a | -- | | Chloroacetic acid6 | T | µg/l | 60a | -- | | Chlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 100a | 100 | | Chlorodibromomethane5 | T | µg/l | 4.0 | 4.0 | | Bis(2-Chloro-1-methylethyl) ether | T | µg/l | 200 | 200 | | Bis(2-Chloroethyl) ether5 | T | µg/l | 0.30 | 0.30 | | Chloroform5 | T | µg/l | 57 | 57 | | bis(2-Chloroisopropyl) ether | T | µg/l | 1,400 | 1,400 | | bis(2-Chloromethyl) ether5 | T | µg/l | 0.0015 | 0.0015 | | 2-Chloronaphthalene | T | µg/l | 800 | 800 | | 2-Chlorophenol | T | µg/l | 30 | 30 | | Chromium | TR | µg/l | 100a | -- | | Chrysene5 | T | µg/l | 0.038 | 0.038 | | Cyanide | free | µg/l | 4.0 | 4.0 | | 2,4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxy-acetic acid) | T | µg/l | 70a | 1,300 | | Dalapon | T | µg/l | 200a | -- | | 4,4'-DDD5 | T | µg/l | 0.0012 | 0.0012 | | 4,4'-DDE5 | T | µg/l | 0.00018 | 0.00018 | | 4,4'-DDT5 | T | µg/l | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | | Dibenzo (a,h) anthracene5 | T | µg/l | 0.0012 | 0.0012 | | Dibromochloropropane | T | µg/l | 0.2a | -- | | Di-n-butyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 20 | 20 | | Dichloroacetic acid6 | T | µg/l | 60a | -- | | 1,2-Dichlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 420 | 420 | | 1,3-Dichlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 7.0 | 7.0 | | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 63 | 63 | | 3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine5 | T | µg/l | 0.21 | 0.21 | | Dichlorobromomethane5 | T | µg/l | 5.5 | 5.5 | | 1,2-Dichloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 3.8 | 3.8 | | 1,1-Dichloroethylene5 | T | µg/l | 7.0a | 300 | | cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene | T | µg/l | 70a | -- | | trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene | T | µg/l | 100a | 100 | | 2,4-Dichlorophenol | T | µg/l | 10 | 10 | | 1,2-Dichloropropane5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 5.0 | | 1,3-Dichloropropene5 | T | µg/l | 2.7 | 2.7 | | Dieldrin5 | T | µg/l | 1.2*10-5 | 1.2*10-5 | | Di (2-ethylhexyl) adipate | T | µg/l | 400a | -- | | Diethyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 600 | 600 | | 2,4-Dimethylphenol | T | µg/l | 100 | 100 | | Dimethyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 2,000 | 2,000 | | 4,6-Dinitro-o-cresol (4,6- Dinitro-2-methylphenol) | T | µg/l | 2.0 | 2.0 | | Dinitrophenols4 | T | µg/l | 10 | 10 | | 2,4-Dinitrotoluene5 | T | µg/l | 0.49 | 0.49 | | 2,4-Dinitrophenol | T | µg/l | 10 | 10 | | Dinoseb | T | µg/l | 7.0a | -- | | 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine | T | µg/l | 0.30 | 0.30 | | Diquat | T | µg/l | 20a | -- | | Dissolved solids | T | mg/l | 750/500a,b | -- | | alpha-Endosulfan7 | T | µg/l | 20 | 20 | | beta-Endosulfan7 | T | µg/l | 20 | 20 | | Endosulfan sulfate7 | T | µg/l | 20 | 20 | | Endothall | T | µg/l | 100a | -- | | Endrin8 | T | µg/l | 0.03 | 0.03 | | Endrin aldehyde8 | T | µg/l | 0.29 | 0.29 | | Ethylbenzene | T | µg/l | 68 | 68 | | Ethylene dibromide (EDB) | T | µg/l | 0.050a | -- | | bis (2-Ethylhexyl) phthalate5 | T | µg/l | 3.2 | 3.2 | | Fluoranthene | T | µg/l | 20 | 20 | | Fluorene | T | µg/l | 50 | 50 | | Fluoride | T | µg/l | 1,000 | 1,000 | | Glyphosate | T | µg/l | 700a | -- | | Heptachlor5 | T | µg/l | 5.9*10-5 | 5.9*10-5 | | Heptachlor epoxide5 | T | µg/l | 0.00032 | 0.00032 | | Hexachlorobenzene5 | T | µg/l | 0.00079 | 0.00079 | | Hexachlorobutadiene5 | T | µg/l | 0.1 | 0.1 | | alpha-Hexachlorocyclohexane5 | T | µg/l | 0.0036 | 0.0036 | | beta-Hexachlorocyclohexane5 | T | µg/l | 0.08 | 0.08 | | gamma-Hexachlorocyclohexane (Lindane) | T | µg/l | 0.20a | 0.98 | | Hexachlorocyclohexane - technical grade5 | T | µg/l | 0.066 | 0.066 | | Hexachlorocyclopentadiene | T | µg/l | 4.0 | 4.0 | | Hexachloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 1.0 | 1.0 | | Indeno (1,2,3-c,d) pyrene5 | T | µg/l | 0.012 | 0.012 | | Iron | S | µg/l | 300a | -- | | Isophorone5 | T | µg/l | 340 | 340 | | Mercury | TR | µg/l | 0.012 | 0.012 | | Methoxychlor | T | µg/l | 0.02 | 0.02 | | Methyl bromide | T | µg/l | 47 | 47 | | 3-Methyl-4-chlorophenol | T | µg/l | 500 | 500 | | Methylene chloride5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 46 | | Nickel | TR | µg/l | 610 | 610 | | Nitrate-N + Nitrite-N | T | µg/l | 10,000a | 10,000 | | Nitrite-N | T | µg/l | 1,000a | 1,000 | | Nitrobenzene | T | µg/l | 10 | 10 | | Nitrosoamines5 | T | µg/l | 0.0080 | 0.0080 | | N-Nitrosodibutylamine5 | T | µg/l | 0.063 | 0.063 | | N-Nitrosodiethylamine5 | T | µg/l | 0.0080 | 0.0080 | | N-Nitrosodimethylamine5 | T | µg/l | 0.0069 | 0.0069 | | N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine5 | T | µg/l | 0.050 | 0.050 | | N-Nitrosodiphenylamine5 | T | µg/l | 33 | 33 | | N-Nitrosodipyrrolidine5 | T | µg/l | 0.16 | 0.16 | | Oxamyl (Vydate) | T | µg/l | 200a | -- | | Pentachlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 0.1 | 0.1 | | Pentachlorophenol5 | T | µg/l | 0.3 | 0.3 | | Phenol | T | µg/l | 4,000 | 4,000 | | Phenolics | T | µg/l | 5.0 | -- | | Picloram | T | µg/l | 500a | -- | | Polychlorinated biphenyls5 | T | µg/l | 0.00064 | 0.00064 | | Pyrene | T | µg/l | 20 | 20 | | Selenium | TR | µg/l | 50a | 170 | | Silver | T | µg/l | 50 | 50 | | Silvex (2, 4, 5-TP, 2- [2, 4, 5-Trichlorophenoxy] propionic acid | T | µg/l | 50a | 100 | | Simazine | T | µg/l | 4.0a | -- | | Styrene | T | µg/l | 100a | -- | | Sulfates | T | mg/l | 250a | -- | | 1, 2, 4, 5-Tetrachlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 0.03 | 0.03 | | 2, 3, 7, 8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin5 | T | µg/l | 5.0*10-8 | 5.0*10-8 | | 1, 1, 2, 2-Tetrachloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 1.7 | 1.7 | | Tetrachloroethylene5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 6.9 | | Thallium | TR | µg/l | 1.7 | 1.7 | | Toluene | T | µg/l | 57 | 57 | | Toxaphene5 | T | µg/l | 0.0028 | 0.0028 | | Trichloroacetic acid6 | T | µg/l | 60a | -- | | 1, 2, 4-Trichlorobenzene5 | T | µg/l | 0.71 | 0.71 | | 1, 1, 1-Trichloroethane | T | µg/l | 200a | 10,000 | | 1, 1, 2-Trichloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 5.5 | | Trichloroethylene5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 6.0 | | 2, 4, 5-Trichlorophenol | T | µg/l | 300 | 300 | | 2, 4, 6-Trichlorophenol5 | T | µg/l | 14 | 14 | | Vinyl chloride5 | T | µg/l | 0.22 | 0.22 | | Xylenes | T | µg/l | 10,000a | -- | | Zinc | T | µg/l | 7,400 | 7,400 | | | 1 S = soluble; T = total; TR = total recoverable. | | 2 mg/l = milligrams per liter (parts per million); µg/l = micrograms per liter (parts per billion); Mf/l = million fibers per liter. | | 3 OMZA = outside mixing zone average. Criteria in the "Intakes" column apply within five hundred yards of drinking water intakes. Criteria in the "Elsewhere" column apply at all other locations. | | 4The criteria for this chemical apply to the sum of all dinitrophenols. | | 5Criteria for this chemical are based on a carcinogenic endpoint. | | 6The criterion for this chemical applies to the sum of chloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid. | | 7The criteria for this chemical apply to the sum of alpha-endosulfan, beta-endosulfan and endolsufan sulfate. | | 8The criteria for this chemical apply to the sum of endrin and endrin aldehyde. | | aThis criterion is the maximum contaminant level (MCL) developed under the "Safe Drinking Water Act". | | bEquivalent 25°C specific conductance values are 1200 micromhos/cm as a maximum and 800 micromhos/cm as a thirty-day average. |
| PA state line to Greenup Lock and Dam (RM 341.1) | PA state line to Greenup Lock and Dam (RM 341.1) | Greenup Lock and Dam (RM 341.1) to IN state line | Greenup Lock and Dam (RM 341.1) to IN state line | | Month/date | Period Average (ºF) | Instantaneous Maximum (ºF) | Period Average (ºF) | Instantaneous Maximum (ºF) | | January 1 - 31 | 45.7 | 47.0 | 46.8 | 47.2 | | February 1 - 29 | 43.9 | 46.3 | 47.9 | 52.8 | | March 1 - 31 | 51.2 | 56.4 | 57.4 | 62.4 | | April 1 -30 | 61.2 | 66.3 | 66.9 | 71.1 | | May 1 -31 | 71.2 | 76.5 | 76.4 | 81.4 | | June 1 - 14 | 78.8 | 81.0 | 83.5 | 85.7 | | June 15 - 30 | 87.0 | 87.0 | 87.0 | 87.0 | | July 1 -31 | 89.0 | 89.0 | 89.0 | 89.0 | | August 1- 31 | 89.0 | 89.0 | 89.0 | 89.0 | | September 1 - 15 | 87.0 | 87.0 | 87.0 | 87.0 | | September 16 - 30 | 81.0 | 83.1 | 84.7 | 87.0 | | October 1 - 31 | 74.1 | 78.3 | 76.7 | 81.6 | | November 1 - 30 | 65.0 | 69.0 | 66.2 | 70.8 | | December 1 -31 | 55.8 | 60.0 | 55.6 | 60.4 |
Last updated January 14, 2026 at 3:53 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-33 | Water quality criteria for water supply use designations.
Effective:
January 18, 2021
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) Human health water quality criteria [public water supply]. (1) The chemical specific criteria listed in table 33-1 of this rule, or site-specific modifications thereof, apply as "Outside Mixing Zone Averages" and shall apply to all water bodies located within five hundred yards of drinking water intakes. For the purpose of setting water quality based effluent limits, these criteria shall be met after the effluent and the receiving water are reasonably well mixed as provided in rules 3745-1-06 and 3745-2-05 of the Administrative Code. (2) Water bodies located within the Ohio river drainage basin. Any methodologies and procedures acceptable under 40 C.F.R. 131, effective July 1, 2019 may be used when developing or revising human health water quality criteria or implementing narrative criteria contained in rule 3745-1-04 of the Administrative Code. For any pollutant for which it is demonstrated that a methodology or procedure cited in this rule is not scientifically defensible, the director may apply an alternative methodology or procedure acceptable under 40 C.F.R. 131 when developing water quality criteria. (3) Water bodies located within the lake Erie drainage basin. The methodologies contained in rules 3745-1-41 and 3745-1-42 of the Administrative Code shall be used when adopting or revising numeric human health criteria and when implementing the narrative water quality criteria contained in rule 3745-1-04 of the Administrative Code. For pollutants listed in table 33-2 of this rule, any methodologies and procedures acceptable under 40 C.F.R. 131 may be used when developing water quality criteria or implementing narrative criteria. For any pollutant other than those in table 33-2 of this rule, for which it is demonstrated that a methodology or procedure cited in this rule is not scientifically defensible, the director may apply an alternative methodology or procedure acceptable under 40 C.F.R. 131 when developing water quality criteria. | | | OMZA3 | | Chemical | Form1 | Units2 | Drinking | | | | Ohio river | Lake Erie | | Acenaphthene | T | µg/l | 70 | | | Acrolein | T | µg/l | 3.0 | | | Acrylonitrile5 | T | µg/l | 0.51 | | | Alachlor | T | µg/l | 2.0a | 2.0a | | Aldrin5 | T | µg/l | 7.7*10-6 | | | Anthracene | T | µg/l | 300 | | | Antimony5 | TR | µg/l | 5.6 | 6.0a | | Arsenic | TR | µg/l | 10a | 10a | | Asbestos | T | Mf/l | 7.0a | 7.0a | | Atrazine | T | µg/l | 3.0a | 3.0a | | Barium5 | TR | µg/l | 1,000 | 2,000a | | Benzene5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 5.0a | | Benzidine5 | T | µg/l | 0.00086 | | | Benzo(a)anthracene5 | T | µg/l | 0.012 | 0.2a | | Benzo(a)pyrene5 | T | µg/l | 0.0012 | | | Benzo(b)fluoranthene5 | T | µg/l | 0.012 | | | Benzo(k)fluoranthene5 | T | µg/l | 0.038 | | | Beryllium | TR | µg/l | 4.0a | 4.0a | | Bromate | T | µg/l | 10a | 10a | | Bromoform (Tribromomethane)5 | T | µg/l | 43 | | | Butylbenzyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 0.10 | | | Cadmium | TR | µg/l | 5.0a | 5.0a | | Carbofuran | T | µg/l | 40a | 40a | | Carbon tetrachloride5 | T | µg/l | 2.3 | 5.0a | | Chloramine | T | µg/l | 4,000a | 4,000a | | Chlordane5 | T | µg/l | 0.0031 | 0.00025 | | Chlorides | T | mg/l | 250a | 250a | | Chlorine | T | µg/l | 4,000a | 4,000a | | Chlorine dioxide | T | µg/l | 800a | 800a | | Chlorite | T | µg/l | 1,000a | 1,000a | | Chloroacetic acid6 | T | µg/l | 60a | 60a | | Chlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 100a | 100a | | Chlorodibromomethane5 | T | µg/l | 4.0 | | | Bis(2-Chloro-1-methylethyl) ether | T | µg/l | 200 | | | Bis(2-Chloroethyl)ether5 | T | µg/l | 0.30 | | | Chloroform5 | T | µg/l | 57 | | | bis(2-Chloroisopropyl)ether | T | µg/l | 1,400 | | | bis(2-Chloromethyl)ether5 | T | µg/l | 0.0015 | | | 2-Chloronaphthalene | T | µg/l | 800 | | | 2-Chlorophenol | T | µg/l | 30 | | | Chromium | TR | µg/l | 100a | 100a | | Chrysene5 | T | µg/l | 0.038 | | | Cyanide | free | µg/l | 4.0 | 4.0 | | 2,4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxy-acetic acid) | T | µg/l | 70a | 70a | | Dalapon | T | µg/l | 200a | 200a | | 4,4'-DDD5 | T | µg/l | 0.0012 | | | 4,4'-DDE5 | T | µg/l | 0.00018 | | | 4,4'-DDT5 | T | µg/l | 0.0003 | 0.00015 | | Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene5 | T | µg/l | 0.0012 | | | Dibromochloropropane | T | µg/l | 0.2a | 0.2a | | Di-n-butyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 20 | | | Dichloroacetic acid6 | T | µg/l | 60a | 60a | | 1,2-Dichlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 420 | 600a | | 1,3-Dichlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 7.0 | | | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 63 | 75a | | 3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine5 | T | µg/l | 0.21 | | | Dichlorobromomethane5 | T | µg/l | 5.5 | | | 1,2-Dichloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 3.8 | 5.0a | | 1,1-Dichloroethylene5 | T | µg/l | 0.57 | 7.0a | | cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene | T | µg/l | 70a | 70a | | trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene | T | µg/l | 100a | 100a | | 2,4-Dichlorophenol | T | µg/l | 10 | | | 1,2-Dichloropropane5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 5.0a | | 1,3-Dichloropropene | T | µg/l | 2.7 | | | Dieldrin5 | T | µg/l | 1.2*10-5 | 0.0000065 | | Di(2-ethylhexyl)adipate | T | µg/l | 400a | 400a | | Diethyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 600 | | | 2,4-Dimethylphenol | T | µg/l | 100 | 100 | | Dimethyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 2,000 | | | 4,6-Dinitro-o-cresol (4,6-Dinitro-2-methylphenol) | T | µg/l | 2.0 | | | Dinitrophenols4 | T | µg/l | 10 | | | 2,4-Dinitrophenol | T | µg/l | 10 | 10 | | 2,4-Dinitrotoluene5 | T | µg/l | 0.49 | | | Dinoseb | T | µg/l | 7.0a | 7.0a | | 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine5 | T | µg/l | 0.30 | | | Diquat | T | µg/l | 20a | 20a | | Dissolved solids | T | mg/l | 750/500a,b | 750/500a,b | | alpha-Endosulfan7 | T | µg/l | 20 | | | beta-Endosulfan7 | T | µg/l | 20 | | | Endosulfan sulfate7 | T | µg/l | 20 | | | Endothall | T | µg/l | 100a | 100a | | Endrin8 | T | µg/l | 0.03 | 2.0a | | Endrin aldehyde8 | T | µg/l | 0.29 | | | Ethylbenzene | T | µg/l | 68 | 700a | | Ethylene dibromide (EDB) | T | µg/l | 0.050a | 0.050a | | bis(2-Ethylhexyl)phthalate5 | T | µg/l | 3.2 | 6.0a | | Fluoranthene | T | µg/l | 20 | | | Fluorene | T | µg/l | 50 | | | Fluoride | T | µg/l | 1,000 | 4,000a | | Glyphosate | T | µg/l | 700a | 700a | | Heptachlor5 | T | µg/l | 5.9*10-5 | 0.4a | | Heptachlor epoxide5 | T | µg/l | 0.00032 | 0.2a | | Hexachlorobenzene5 | T | µg/l | 0.00079 | 0.00045 | | Hexachlorobutadiene5 | T | µg/l | 0.10 | | | alpha-Hexachlorocyclohexane5 | T | µg/l | 0.0036 | | | beta-Hexachlorocyclohexane5 | T | µg/l | 0.08 | | | gamma-Hexachlorocyclohexane (Lindane)5 | T | µg/l | 0.20 | 0.20a | | Hexachlorocyclohexane - technical grade5 | T | µg/l | 0.066 | | | Hexachlorocyclopentadiene | T | µg/l | 4.0 | 50a | | Hexachloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 1.0 | 1.0 | | Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene5 | T | µg/l | 0.012 | | | Iron | S | µg/l | 300a | 300a | | Isophorone5 | T | µg/l | 340 | | | Mercury | TR | µg/l | 0.012 | 0.0031 | | Methoxychlor | T | µg/l | 0.02 | 40a | | Methyl bromide | T | µg/l | 47 | | | 3-Methyl-4-chlorophenol | T | µg/l | 500 | | | Methylene chloride5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 5.0a | | Nickel | TR | µg/l | 610 | | | Nitrate-N + Nitrite-N | T | µg/l | 10,000a | 10,000a | | Nitrite-N | T | µg/l | 1,000a | 1,000a | | Nitrobenzene | T | µg/l | 10 | | | Nitrosoamines5 | T | µg/l | 0.0080 | | | N-Nitrosodibutylamine5 | T | µg/l | 0.063 | | | N-Nitrosodiethylamine5 | T | µg/l | 0.0080 | | | N-Nitrosodimethylamine5 | T | µg/l | 0.0069 | | | N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine5 | T | µg/l | 0.050 | | | N-Nitrosodiphenylamine5 | T | µg/l | 33 | | | N-Nitrosodipyrrolidine5 | T | µg/l | 0.16 | | | Oxamyl (Vydate) | T | µg/l | 200a | 200a | | Pentachlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 0.1 | | | Pentachlorophenol5 | T | µg/l | 0.3 | 1.0a | | Phenol | T | µg/l | 4,000 | | | Picloram | T | µg/l | 500a | 500a | | Polychlorinated biphenyls5 | T | µg/l | 0.00064 | 0.000026 | | Pyrene | T | µg/l | 20 | | | Selenium | TR | µg/l | 50a | 50a | | Silvex (2,4,5-TP, 2-[2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxy]propionic acid | T | µg/l | 10 | 50a | | Simazine | T | µg/l | 4.0a | 4.0a | | Styrene | T | µg/l | 100a | 100a | | Sulfates | T | mg/l | 250a | 250a | | 1,2,4,5-Tetrachlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 0.03 | | | 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin5 | T | µg/l | 5.0*10-8 | 5.0*10-8 | | 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 1.7 | | | Tetrachloroethylene5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 5.0a | | Thallium | TR | µg/l | 1.7 | | | Toluene | T | µg/l | 57 | 57 | | Toxaphene5 | T | µg/l | 0.0028 | 0.000068 | | Trichloroacetic acid6 | T | µg/l | 60a | 60a | | 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene5 | T | µg/l | 0.71 | 70a | | 1,1,1-Trichloroethane | T | µg/l | 200a | 200a | | 1,1,2-Trichloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 5.0a | | Trichloroethylene5 | T | µg/l | 5.0a | 5.0a | | 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | T | µg/l | 300 | | | 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol5 | T | µg/l | 14 | | | Vinyl chloride5 | T | µg/l | 0.22 | 2.0a | | Xylenes | T | µg/l | 10,000a | 10,000a | | Zinc | T | µg/l | 7,400 | |
1 S = soluble; T = total; TR = total recoverable. 2 mg/l = milligrams per liter (parts per million); µg/l = micrograms per liter (parts per billion); Mf/l = million fibers per liter. 3 OMZA = outside mixing zone average. 4 The criteria for this chemical apply to the sum of all dinitrophenols. 5 Criteria for this chemical are based on a carcinogenic endpoint. 6 The criterion for this chemical applies to the sum of chloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid. 7 The criteria for this chemical apply to the sum of alpha-endosulfan, beta-endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate. 8 The criteria for this chemical apply to the sum of endrin and endrin aldehyde. a This criterion is the maximum contaminant level (MCL) developed under the "Safe Drinking Water Act". b Equivalent 25ºC specific conductance values are 1200 micromhos/cm as a maximum and 800 micromhos/cm as a thirty day average. | Alkalinity | | Ammonia | | Bacteria | | Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) | | Chlorine | | Color | | Dissolved oxygen | | Dissolved solids | | pH | | Phosphorus | | Salinity | | Temperature | | Total and suspended solids | | Turbidity |
(B) Agricultural water supply criteria. (1) The chemical-specific criteria listed in table 33-3 of this rule apply as "Outside Mixing Zone Averages." For the purpose of setting water quality based effluent limits, the criteria shall be met after the effluent and the receiving water are reasonably well mixed as provided in rules 3745-1-06 and 3745-2-05 of the Administrative Code. (2) The water quality criteria for the protection of agricultural uses, or site-specific modifications thereof, adopted in, or developed pursuant to, this rule shall apply outside the mixing zone to all water bodies assigned the agricultural water supply use designation. (3) For any pollutant in table 33-3 of this rule for which it is demonstrated that a methodology or procedure cited in this chapter is not scientifically defensible, the director may apply an alternative methodology or procedure acceptable under 40 C.F.R. 131 when developing water quality criteria. | Chemical | Form1 | Units2 | OMZA3 | | Arsenic | TR | µg/l | 100 | | Beryllium | TR | µg/l | 100 | | Cadmium | TR | µg/l | 50 | | Total chromium | TR | µg/l | 100 | | Copper | TR | µg/l | 500 | | Fluoride | T | µg/l | 2,000 | | Iron | TR | µg/l | 5,000 | | Lead | TR | µg/l | 100 | | Mercury | TR | µg/l | 10 | | Nickel | TR | µg/l | 200 | | Nitrates+nitrites | T | mg/l | 100 | | Selenium | TR | µg/l | 50 | | Zinc | TR | µg/l | 25,000 |
1T = total; TR = total recoverable. 2mg/l = milligrams per liter (parts per million); µg/l = micrograms per liter (parts per billion). 3OMZA = outside mixing zone average.
Last updated January 18, 2026 at 7:46 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-34 | Water quality criteria for the protection of human health [fish consumption].
Effective:
January 18, 2021
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) The chemical specific criteria listed in table 34-1 of this rule, or site-specific modifications thereof, apply as "Outside Mixing Zone Averages" and shall apply to all water bodies. For the purpose of setting water quality based effluent limits, these criteria shall be met after the effluent and the receiving water are reasonably well mixed as provided in rules 3745-1-06 and 3745-2-05 of the Administrative Code. (B) Water bodies located within the Ohio river drainage basin. Any methodologies and procedures acceptable under 40 C.F.R. 131, effective July 1, 2019 may be used when developing or revising human health water quality criteria or implementing narrative criteria contained in rule 3745-1-04 of the Administrative Code. For any pollutant for which it is demonstrated that a methodology or procedure cited in this rule is not scientifically defensible, the director may apply an alternative methodology or procedure acceptable under 40 C.F.R. 131 when developing water quality criteria. (C) Water bodies located within the lake Erie drainage basin. The methodologies contained in rules 3745-1-41 and 3745-1-42 of the Administrative Code shall be used when adopting or revising numeric human health criteria and when implementing the narrative water quality criteria contained in rule 3745-1-04 of the Administrative Code. For pollutants listed in table 34-2 of this rule, any methodologies and procedures acceptable under 40 C.F.R. 131 may be used when developing water quality criteria or implementing narrative criteria. For any pollutant other than those in table 33-2 of this rule, for which it is demonstrated that a methodology or procedure cited in this rule is not scientifically defensible, the director may apply an alternative methodology or procedure acceptable under 40 C.F.R. 131 when developing water quality criteria. | | | OMZA3 | | Chemical | Form1 | Units2 | Ohio river | Lake Erie | | Acenaphthene | T | µg/l | 90 | -- | | Acrolein | T | µg/l | 400 | -- | | Acrylonitrile5 | T | µg/l | 70 | -- | | Aldrin5 | T | µg/l | 7.7*10-6 | -- | | Anthracene | T | µg/l | 400 | -- | | Antimony | TR | µg/l | 640 | -- | | Benzene5 | T | µg/l | 160 | 160 | | Benzidine5 | T | µg/l | 0.11 | -- | | Benzo(a)anthracene5 | T | µg/l | 0.013 | -- | | Benzo(a)pyrene5 | T | µg/l | 0.0013 | -- | | Benzo(b)fluoranthene5 | T | µg/l | 0.013 | -- | | Benzo(k)fluoranthene5 | T | µg/l | 0.13 | -- | | Beryllium | TR | µg/l | 280 | -- | | Bromoform5 | T | µg/l | 1,200 | -- | | Butylbenzyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 1.0 | -- | | Carbon tetrachloride5 | T | µg/l | 50 | -- | | Chlordane5 | T | µg/l | 0.0032 | 0.00025 | | Chlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 800 | 800 | | Chlorodibromomethane5 | T | µg/l | 210 | -- | | Bis(2-Chloro-1-methylethyl)ether | T | µg/l | 4,000 | | | Bis(2-Chloroethyl)ether5 | T | µg/l | 22 | -- | | Chloroform5 | T | µg/l | 20,000 | -- | | bis(2-Chloromethyl)ether5 | T | µg/l | 0.17 | -- | | 2-Chloronaphthalene | T | µg/l | 1,000 | -- | | 2-Chlorophenol | T | µg/l | 800 | -- | | Chrysene5 | T | µg/l | 1.3 | -- | | Cyanide | free | µg/l | 400 | 400 | | 2,4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxy-acetic acid) | T | µg/l | 12,000 | | | 4,4'-DDD5 | T | µg/l | 0.0012 | -- | | 4,4'-DDE5 | T | µg/l | 0.00018 | -- | | 4,4'-DDT5 | T | µg/l | 0.0003 | 0.00015 | | Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene5 | T | µg/l | 0.0013 | -- | | Di-n-butyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 30 | -- | | 1,2-Dichlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 3,000 | -- | | 1,3-Dichlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 10 | -- | | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 900 | -- | | 3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine5 | T | µg/l | 1.5 | -- | | Dichlorobromomethane5 | T | µg/l | 270 | -- | | 1,2-Dichloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 6,500 | -- | | 1,1-Dichloroethylene | T | µg/l | 20,000 | -- | | trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene | T | µg/l | 4,000 | -- | | 2,4-Dichlorophenol | T | µg/l | 60 | -- | | 1,2-Dichloropropane5 | T | µg/l | 310 | -- | | 1,3-Dichloropropene5 | T | µg/l | 120 | -- | | Dieldrin5 | T | µg/l | 1.2*10-5 | 0.0000065 | | Diethyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 600 | -- | | 2,4-Dimethylphenol | T | µg/l | 3,000 | 3,000 | | Dimethyl phthalate | T | µg/l | 2,000 | -- | | 4,6-Dinitro-o-cresol (4,6-Dinitro-2-methylphenol) | T | µg/l | 30 | -- | | Dinitrophenols4 | T | µg/l | 1,000 | | | 2,4-Dinitrophenol | T | µg/l | 300 | 300 | | 2,4-Dinitrotoluene5 | T | µg/l | 17 | -- | | 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine5 | T | µg/l | 2.0 | -- | | alpha-Endosulfan6 | T | µg/l | 30 | -- | | beta-Endosulfan6 | T | µg/l | 40 | -- | | Endosulfan sulfate6 | T | µg/l | 40 | -- | | Endrin6 | T | µg/l | 0.03 | -- | | Endrin aldehyde6 | T | µg/l | 1.0 | -- | | Ethylbenzene | T | µg/l | 130 | -- | | bis(2-Ethylhexyl)phthalate5 | T | µg/l | 3.7 | -- | | Fluoranthene | T | µg/l | 20 | -- | | Fluorene | T | µg/l | 70 | -- | | Heptachlor5 | T | µg/l | 5.9*10-5 | -- | | Heptachlor epoxide5 | T | µg/l | 0.00032 | -- | | Hexachlorobenzene5 | T | µg/l | 0.00079 | 0.00045 | | Hexachlorobutadiene5 | T | µg/l | 0.1 | -- | | alpha-Hexachlorocyclohexane5 | T | µg/l | 0.0039 | -- | | beta-Hexachlorocyclohexane5 | T | µg/l | 0.14 | -- | | gamma-Hexachlorocyclohexane (Lindane)5 | T | µg/l | 44 | 0.50 | | Hexachlorocyclohexane - technical grade5 | T | µg/l | 0.1 | -- | | Hexachlorocyclopentadiene | T | µg/l | 4.0 | -- | | Hexachloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 1.0 | 1.0 | | Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene5 | T | µg/l | 0.013 | -- | | Isophorone5 | T | µg/l | 18,000 | -- | | Methoxychlor | T | µg/l | 0.02 | | | Mercury | TR | µg/l | 0.012 | 0.0031 | | 3-Methyl-4-Chlorophenol | TR | µg/l | 2,000 | | | Methyl bromide | T | µg/l | 10,000 | -- | | Methylene chloride5 | T | µg/l | 10,000 | 2,600 | | Nickel | TR | µg/l | 4,600 | -- | | Nitrobenzene | T | µg/l | 600 | -- | | Nitrosoamines5 | T | µg/l | 12.4 | -- | | N-Nitrosodibutylamine5 | T | µg/l | 2.2 | -- | | N-Nitrosodiethylamine5 | T | µg/l | 12.4 | -- | | N-Nitrosodimethylamine5 | T | µg/l | 30 | -- | | N-Nitrosodi-n-propylamine5 | T | µg/l | 5.1 | -- | | N-Nitrosodiphenylamine5 | T | µg/l | 60 | -- | | N-Nitrosodipyrrolidine5 | T | µg/l | 340 | -- | | Pentachlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 0.1 | -- | | Pentachlorophenol5 | T | µg/l | 0.4 | -- | | Phenol | T | µg/l | 300,000 | -- | | Polychlorinated biphenyls5 | T | µg/l | 0.00064 | 0.000026 | | Pyrene | T | µg/l | 30 | -- | | Selenium | TR | µg/l | 4,200 | -- | | Silvex (2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxypropionic acid) | T | µg/l | 400 | | | 1,2,4,5-Tetrachlorobenzene | T | µg/l | 0.03 | -- | | 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin5 | T | pg/l | 0.051 | 0.0086 | | 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 30 | -- | | Tetrachloroethylene5 | T | µg/l | 290 | -- | | Toluene | T | µg/l | 520 | 520 | | Toxaphene5 | T | µg/l | 0.0071 | 0.000068 | | 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene5 | T | µg/l | 0.76 | -- | | 1,1,1-Trichloroethane | T | µg/l | 200,000 | | | 1,1,2-Trichloroethane5 | T | µg/l | 89 | -- | | Trichloroethylene5 | T | µg/l | 70 | 70 | | 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | T | µg/l | 600 | -- | | 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol5 | T | µg/l | 28 | -- | | Vinyl chloride5 | T | µg/l | 16 | -- | | Zinc | T | µg/l | 26,000 | -- |
1 S = soluble; T = total; TR = total recoverable. 2 mg/l = milligrams per liter (parts per million); µg/l = micrograms per liter (parts per billion); pg/l = picograms per liter (parts per quadrillion). 3 OMZA = outside mixing zone average. 4 The criteria for this chemical apply to the sum of all dinitrophenols. 5 Criteria for this chemical are based on a carcinogenic endpoint. 6 The criteria for this chemical apply to the sum of alpha-endosulfan, beta-endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate. 7 The criteria for this chemical apply to the sum of endrin and endrin aldehyde. | Alkalinity | | Ammonia | | Bacteria | | Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) | | Chlorine | | Color | | Dissolved oxygen | | Dissolved solids | | pH | | Phosphorus | | Salinity | | Temperature | | Total and suspended solids | | Turbidity |
|
Rule 3745-1-35 | Site-specific modifications to criteria and
values.
Effective:
February 6, 2017
This rule was filed with the Legislative Service Commission in PDF format and is presented here as filed.
View Rule Text
Last updated April 4, 2023 at 9:38 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-37 | Water quality criteria for recreation use designations and aesthetic conditions.
Effective:
February 6, 2017
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) General information. The chemical-specific criteria listed in this rule apply as "Outside Mixing Zone" or "Inside Mixing Zone Maximum." For the purpose of setting water quality based effluent limits, the criteria which apply "Outside Mixing Zone" shall be met after the effluent and the receiving water are reasonably well mixed as provided in rules 3745-1-06 and 3745-2-05 of the Administrative Code. The criteria listed as "Inside Mixing Zone Maximum" shall be applicable as end-of-pipe maximum effluent limits or as criteria to be met within a short distance of the effluent pipe except as provided in rule 3745-2-08 of the Administrative Code. (B) Aesthetic conditions. (1) The water quality criteria for the protection against adverse aesthetic conditions, or site-specific modifications thereof, shall apply as follows: (a) The "Inside Mixing Zone Maximum" and "Outside Mixing Zone Maximum" water quality criteria, or site-specific modifications thereof, shall apply to all water bodies. (b) The "Drinking" water quality criteria shall apply to all water bodies within five hundred yards of drinking water intakes. (2) For any pollutant for which it is demonstrated that a methodology or procedure cited in this chapter is not scientifically defensible, the director may apply an alternative methodology or procedure acceptable under 40 C.F.R. 131 when developing water quality criteria. | Chemical | Form1 | Units2 | IMZM3 | OMZM3 | Drinking | | 2-Chlorophenol | T | g/l | -- | -- | 0.1a | | 2,4-Dichlorophenol | T | g/l | -- | -- | 0.3a | | MBAS (foaming agents) | T | mg/l | -- | 0.50 | -- | | Oil & grease | T | mg/l | -- | 10b | -- | | Phenol | T | g/l | -- | -- | 1.0a | | Phosphorus | T | mg/l | C | -- | C |
1 T= total. 2 mg/l = milligrams per liter (parts per million); g/l = micrograms per liter (parts per billion). 3 IMZM = inside mixing zone maximum; OMZM = outside mixing zone maximum. a This criterion is based on the protection against organoleptic (taste or odor) effects. b Surface waters shall be free from floating oils and shall at no time produce a visible sheen or color film. Levels of oils or petrochemicals in the sediment or on the banks of a watercourse which cause deleterious effects on the biota will not be permitted. c Total phosphorus as P shall be limited to the extent necessary to prevent nuisance growths of algae, weeds, and slimes that result in a violation of the water quality criteria set forth in paragraph (E) of rule 3745-1-04 of the Administrative Code or, for public water supplies, that result in taste or odor problems. In areas where such nuisance growths exist, phosphorus discharges from point sources determined significant by the director shall not exceed a daily average of one milligram per liter as total P, or such stricter requirements as may be imposed by the director in accordance with the international joint commission (United States-Canada agreement). (C) Recreation. (1) The water quality criteria for the protection of recreational uses shall apply outside the mixing zone to all water bodies assigned a recreation use designation. | Recreation use | E. coli (colony counts per 100 ml) | | 90-day geometric mean | Statistical threshold value1 | | Bathing water | 126 | 410a | | Primary contact recreation | 126 | 410 | | Secondary contact recreation | 1030 | 1030 |
1 These criteria shall not be exceeded in more than ten per cent of the samples taken during any ninety-day period. a A beach action value of 235 E. coli colony counts per 100 ml shall be used for the purpose of issuing beach and bathing water advisories. a A beach action value of 235 E. coli colony counts per 100 ml shall be used for the purpose of issuing beach and bathing water advisories.
|
Rule 3745-1-38 | Variances from water quality standards for point sources.
Effective:
December 2, 2025
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government
publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations,
federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see
rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) Applicability. (1) The director may grant a water
quality standards (WQS) variance for a specific criterion or value adopted in
or developed under this chapter that is the basis of a water quality-based
effluent limit (WQBEL) included in any existing, draft, or proposed control
document, as defined in paragraph (A) of rule 3745-1-05 of the Administrative
Code in accordance with the following: (a) A variance may be adopted for a permittee or water body
or water body segment but only applies to the permittee, authorized discharges,
or water body or water body segment specified in the variance. (b) A variance does not affect, nor does the director need
to modify, the underlying designated use and criterion for the water
body. (c) Any limitations and requirements necessary to implement
the WQS variance will be included as enforceable conditions for the control
document subject to the WQS variance. (2) This rule does not
apply to any of the following: (a) Any discharge of pollutants, as defined in 40 C.F.R.
122.2, approved in any control document from any building, structure, facility,
or installation the construction of which commenced after March 23, 1997,
unless: (i) Such a discharge occurs as a result of a response or
remedial action taken pursuant to the Comprehensive Environmental Response,
Compensation and Liability Act, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, or
the Ohio EPA voluntary action program (VAP). (ii) WQS or method detection limit is issued, modified, or
adopted after the national pollutant discharge elimination system (NPDES)
permit for the discharge is issued. (iii) The discharge results from rerouting all or a portion
of an existing permitted discharge to a new discharge point that discharges to
the same body of water, and there is a pollutant reduction included in the
control document for the discharge being rerouted. (iv) A new or expanded discharge of bioaccumulative
chemicals of concern (BCC) from a publicly owned treatment works or sewerage
system is necessary to prevent or mitigate a public health threat to the
community. (v) The discharge occurs as a result of an overall
reduction in emissions of a pollutant from a facility existing as of March 23,
1997 to air, waters of the state, or other media to which people or aquatic
life are exposed. (vi) The variance is a
multi-discharger ammonia variance issued under paragraph (M) of this
rule. (b) Any source for which a control document was revoked or
not renewed and for which a new control document has been subsequently issued,
except that such a source may be eligible to receive a variance if a water
quality criterion or value, or method detection limit, is issued, modified, or
adopted after the source's new control document is issued. (c) If the variance would likely jeopardize the continued
existence of any threatened or endangered species as defined in rule 3745-1-02
of the Administrative Code or result in the destruction or adverse modification
of such species' critical habitat. (d) If WQS will be attained by implementing effluent limits
required under sections 301(b) and 306 of the act as defined in rule 3745-33-01
of the Administrative Code and by the permittee implementing cost-effective and
reasonable best management practices for nonpoint source control over which the
permittee has control. (B) Conditions to grant a variance and application
requirements. (1) A variance may be
granted if the director determines, based on data and information provided by
the permittee or data and information independently available to the director,
that attainment of the WQS is not feasible because of any of the
following: (a) Lake, wetland, or stream restoration through dam
removal or other significant reconfiguration activities preclude attainment of
the designated use and criterion while the actions are being
implemented. (b) Naturally occurring pollutant concentrations prevent
the attainment of the WQS. (c) Natural, ephemeral, intermittent, or low flow
conditions or water levels prevent the attainment of the WQS, unless these
conditions may be compensated for by the discharge of sufficient volume of
effluent to enable WQS to be met. (d) Human-caused conditions or sources of pollution prevent
the attainment of the WQS and cannot be remedied, or would cause more
environmental damage to correct than to leave in place. (e) Dams, diversions, or other types of hydrologic
modifications preclude the attainment of the WQS, and it is not feasible to
restore the water body to its original condition or to operate such
modification in a way that would result in the attainment of the
WQS. (f) Physical conditions related to the natural features of
the water body, such as the lack of a proper substrate, cover, flow, depth,
pools, riffles, and the like, unrelated to chemical water quality, preclude
attainment of WQS related to aquatic life use designations. (g) Controls more stringent than those described in
sections 301(b) and 306 of the act would result in substantial and widespread
economic and social impact. (2) Submittal of variance application.
The permittee shall submit an application for a variance to Ohio EPA. The
variance application is a separate application from the control document
application. The variance application shall include the following: (a) The pollutant or water quality parameters, the water
body or water body segment for which the WQS variance applies, and, if
discharger-specific, the permittee subject to the WQS variance. (b) An alternatives analysis that, at a minimum, addresses
the following alternatives: (i) Alternative locations
for the discharge. (ii) Consolidation with
other wastewater treatment facilities. (iii) Reduction in scale
of the discharge. (iv) Water recycling
measures within the facility. (v) Reclaimed water
use. (vi) Process
changes. (vii) Alternative or
advanced treatment. (viii) Improved operation
and maintenance. (ix) Seasonal or
controlled discharge. (x) Watershed
trading. (xi) Land application of
wastewater. (xii) Total
containment. (c) The highest attainable condition of the water body or
water body segment as a quantifiable expression that is one of the
following: (i) For a water body or water body segment WQS variance,
either of the following: (a) The highest attainable interim use and
criterion. (b) The interim use and criterion that reflects the
greatest pollutant reduction achievable with installed pollutant control
technologies if no additional feasible pollutant control technology can be
identified, and the adoption and implementation of a pollutant minimization
program (PMP). (ii) For a discharger-specific WQS variance, any of the
following: (a) The highest attainable interim criterion. (b) The interim effluent condition that reflects the
greatest pollutant reduction achievable. (c) The interim criterion or the interim effluent condition
that reflects the greatest pollutant reduction achievable with installed
pollutant control technologies if no additional feasible pollutant control
technology can be identified, and the adoption and implementation of a
PMP. (d) The proposed term of the WQS variance. The term of the
variance may only be as long as necessary to achieve the highest attainable
condition. (e) All pollutant control activities necessary to achieve
the highest attainable condition, including activities identified through a
PMP. (f) A PMP if the variance is from a WQS for a BCC in the
lake Erie drainage basin and not otherwise required by paragraph (C)(i)(b) or
(C)(ii)(c) of this rule. The PMP shall include the following, at a minimum, in
addition to the requirements in rule 3745-33-07 of the Administrative
Code: (i) Data documenting the facility's current influent
and effluent concentrations for the BCC. (ii) A preliminary identification of potential
sources. (iii) A proposed schedule for evaluating those
sources. (iv) A proposed schedule for identifying and evaluating
potential reduction, elimination, and prevention methods. (g) For a WQS variance that applies to a water body or
water body segment, all of the requirements of paragraph (B)(2) of this rule
and the identification of any cost effective and reasonable best management
practices for nonpoint source controls related to the pollutant or water
quality parameter and water body or water body segment specified that could be
implemented to make progress towards attaining the underlying designated use
and criterion. (h) An attachment to the application that includes the
following information, at a minimum, if the applicant is requesting a variance
under paragraph (B)(1)(g) of this rule: (i) For municipal dischargers: (a) A general plan including a brief description of
existing facilities; a brief description of lowest cost improvements to attain
WQS; capital cost of improvements; and total annual operation and maintenance
cost of facility after improvements. (b) Existing rate structure with a copy of the authorizing
ordinance. (c) Audited annual financial reports for the facility for
the previous five years. (d) Average daily flow for the following: total,
residential, commercial, industrial, institutional/other, inflow and
infiltration. (e) Number of residential customers and non-residential
customers served by the facility. (f) Any information that may indicate conditions in
paragraph (B)(1)(g) of this rule for granting a variance. (ii) For industrial dischargers: (a) A general plan including a brief description of
existing facilities; a brief description of lowest cost improvements to attain
WQS; capital cost of improvements; and total operation and maintenance cost of
facility after improvements. (b) Audited annual financial reports for the facility for
the most recent five years. (c) Standard industrial classification for
facility. (d) Total number of employees and total annual salary,
wage, and overhead costs. (e) Any additional information that may indicate conditions
in paragraph (B)(1)(g) of this rule for granting a variance. (i) In addition to the requirements of paragraphs (B)(1)
and (B)(2) of this rule, the permittee shall do the following: (i) Show that the variance requested complies with the
antidegradation requirements of rule 3745-1-05 of the Administrative
Code. (ii) Characterize the extent of any increased risk to human
health and the environment associated with granting the variance compared with
compliance with the WQS absent the variance, such that the director is able to
conclude that any such increased risk is consistent with the protection of the
public health, safety, and welfare. (C) Review of variance application. Upon
receipt of a complete application for a variance, the director shall consider,
at a minimum, the following factors when evaluating substantial and widespread
economic and social impact: (1) The costs,
cost-effectiveness, measured in dollars per pound equivalent, and affordability
of pollutant removal that would result from implementing measures capable of
attaining the WQS. (2) The reduction in
concentrations and loadings attainable by using measures capable of attaining
WQS. (3) The financial effects
on the permittee of implementing measures capable of attaining the
WQS. (4) The type and
magnitude of adverse or beneficial environmental impacts resulting from
implementing measures capable of attaining the WQS. (5) The overall impact on
employment at the facility and on the economy of the area in which the
discharger is located resulting from implementing measures capable of attaining
the WQS. (D) Multiple discharger determinations.
Where necessary to address widespread WQS nonattainment issues, the director
may make determinations about the factors listed in paragraph (B)(1) of this
rule for a category of dischargers where the director has enough information to
determine that variances are necessary for that category according to one or
more of the conditions in paragraph (B)(1) of this rule, and where the director
is able to identify a common set of highest attainable condition (HAC)
requirements, or a common method of establishing HAC requirements, for the
category of discharges. The determination also identifies the term during which
the determination is effective. These determinations and specific application
requirements are made by rule. Dischargers applying for a variance based on
multiple discharger determinations shall submit information demonstrating that
the determinations of the director are applicable to the individual
discharger. (E) Public notice of preliminary
decision. (1) Upon making a preliminary decision
regarding the variance, the director shall public notice: (a) The variance application, and the draft control
document if the variance is sent to public notice as part of a draft NPDES
permit or control document. (b) The availability of the public record. (c) The availability of the PMP, if
applicable. (d) The preliminary decision on the variance request for
public comment. (e) The date, time, and location of a public hearing at
least forty-five days prior to the scheduled hearing in accordance with rule
3745-49-04 of the Administrative Code. (2) For discharges in the
lake Erie drainage basin, the other Great Lakes states and tribes shall be
notified of the director's preliminary decision. These public notice
requirements may be satisfied by including the supporting information for the
variance and preliminary decision in the public notice of a draft NPDES permit
or Clean Water Act section 401 certification. (3) The director will
also submit the variance or the draft control document containing the variance
to U.S. EPA for review. (F) Final decision on variance
request. (1) The director shall
issue a variance or propose to deny a variance in accordance with Chapter 119.
of the Revised Code. If all or part of the variance is approved by the
director, the decision includes all control document conditions needed to
implement those parts of the variance so approved. Such control document
conditions shall, at a minimum, require all of the following: (a) Compliance with an initial effluent limitation that, at the
time the variance is granted, represents the level currently achievable by the
permittee, and that is no less stringent than that achieved under the previous
control document. (b) That reasonable progress be made toward attaining the WQS for
the water body through appropriate control document conditions which may
include actions identified in the PMP. (c) When the duration of a variance is shorter than the duration
of a control document, compliance with an effluent limitation sufficient to
meet the underlying WQS upon the expiration of said variance. (d) A provision that allows the director to reopen and modify the
control document based on any Ohio EPA WQS revisions to the
variance. (e) Such monitoring or analyses as are necessary in order to
assess the impact of the variance on public health, safety, and welfare, that
may include tests of the amount of the variance parameter in the
discharger's influent and effluent, in fish tissue of resident species in
the receiving water, or in the sediments in the vicinity of the
discharge. (f) Any limits or other conditions necessary to attain or
maintain the highest attainable condition identified at the start of the
variance, or the highest attainable condition identified during a reevaluation
performed under paragraph (I) of this rule, whichever is more
stringent. (g) Provisions regarding the frequency for the director to
review the variance in accordance with paragraph (I) of this rule. (2) The director will
deny a variance request in accordance with Chapter 119. of the Revised Code if
the permittee fails to meet the applicability requirements and make the
demonstrations required under paragraphs (A) and (B) of this rule. Control
document issuance is not affected if the variance is denied. If all, or part,
of the variance is denied by the director, the decision may include, if
necessary, an interim effluent limitation as specified under paragraph
(F)(1)(a) of this rule and a compliance schedule to meet final limits, at a
minimum. (3) For proposed
variances, the director shall submit the following items to U.S. EPA for review
and approval: (a) The variance application and PMP, if
applicable. (b) The director's preliminary decision. (c) Public comments received during the public notice
comment period. (d) The director's final determination. (e) The final control document. (f) A certification from the Ohio attorney general that the
variance from WQS was duly approved pursuant to state law. (G) Incorporating variance into a control
document. If the director and U.S. EPA have approved the variance, the director
will establish and incorporate into the control document all conditions needed
to implement the variance as determined under paragraph (F)(1) of this rule. If
an NPDES permit is administratively continued in accordance with Chapter 119.
of the Revised Code and paragraph (C) of rule 3745-33-04 of the Administrative
Code, the NPDES permit and the limits and conditions contained within it remain
in effect until the director issues a final action on the NPDES permit renewal
application unless the application for renewal of the variance is not
substantially complete or not submitted within one hundred and eighty days
prior to the date of expiration of the permit or unless the permittee did not
substantially comply with the conditions of the existing variance. (H) Length of a variance. (1) A WQS variance shall
not exceed five years for water bodies in the lake Erie basin, nor for any
control document issued in the lake Erie basin, except that a variance may be
issued for longer than five years in the lake Erie basin for pollutants listed
in table 33-2 of rule 3745-1-33 of the Administrative Code. (2) In the Ohio river
basin, a variance may be issued for a period of greater than five years if
necessary to attain the highest attainable condition. WQS variances in the Ohio
river basin shall be reviewed every five years by the director. (3) The director reviews
and modifies as necessary WQS variances as part of each WQS review pursuant to
section 303(c) of the act. (I) Review of a variance. (1) The director shall
review existing WQS variances with terms greater than five years, at least
every five years or every cycle of a control document to re-evaluate the
highest attainable condition using all existing and readily available
information. This review may result in a more stringent highest attainable
condition. (2) The director will
solicit public comments on the results of the variance review along with the
renewal of the associated control document or separately, if necessary.
(3) The results of the
review shall be submitted to U.S. EPA within thirty days of the completion of
the review. (4) The WQS variance will
no longer be the applicable water quality standard for the discharger or water
body or water body segment if the director does not re-evaluate the highest
attainable condition within five years or every cycle of a control document, or
other timeframe specified in the variance, or if the results of the review are
not submitted to U.S. EPA. (J) Renewal of a variance. (1) A variance may be
renewed, subject to the requirements of paragraphs (A) to (I) of this
rule. (2) As part of any renewal application,
the permittee shall again demonstrate that attaining WQS is not feasible based
on the requirements of paragraph (B)(1) of this rule, unless the variance being
renewed was approved under paragraphs (L) and (M) of this rule. (3) For variances
approved under paragraphs (L) and (M) of this rule, the permittee shall, as
part of any renewal application, resubmit the applicable information described
in paragraphs (L)(1), (L)(2), (M)(1), and (M)(2) of this rule, the
certification described in paragraph (L)(4)(e) of this rule, and the permit, as
well as a status report on the progress being made in the PMP. The
permittee's application also shall contain information concerning its
compliance with the conditions incorporated into its permit as part of the
previous variance. Reasonable progress shall have been made in implementing the
pollutant minimization program under the existing permit prior to renewing
variances approved under paragraph (L) or (M) of this rule. The director may
deny any variance renewal if the permittee did not comply with the conditions
of the previous variance. (K) WQS revisions. All variances shall be
distributed with this chapter and are made available upon request to all
interested parties. The distributed information includes at a minimum: the
discharger receiving the variance; the term (beginning and ending dates) of the
variance; the water body or water bodies affected by the variance; the
pollutants affected by the variance; and the modified allowable ambient
concentration values for those pollutants. (L) Multiple discharger mercury variance. The director has
reviewed the available information on mercury removal and the cost. The
director has determined that requiring removal of mercury by construction of
end-of-pipe controls to attain mercury WQS that apply in the lake Erie basin,
requiring controls more stringent than those required by sections 301(b) and
306 of the act would result in substantial and widespread social and economic
impact. The director may determine whether there are other means by which the
permittee could comply with the WQBEL without constructing end-of-pipe
treatment based on the information provided by the permittee in the application
submitted in accordance with this paragraph. The director has also determined
that the increased risk to human health and the environment associated with
granting the variance compared with compliance with the WQS absent the
variance, is consistent with the protection of the public health, safety, and
welfare. This variance is effective for five years from date of U.S. EPA
approval. Before the end of the term, the variance may be updated and
resubmitted to U.S. EPA. If U.S. EPA approves the variance, the effective date
may be extended based on the updated term of the variance. (1) The director may
grant a variance under paragraph (L) of this rule without giving any additional
consideration to the factors specified in paragraphs (B)(1) and (B)(2)(i)(ii)
of this rule where the director determines all of the following: (a) That an average mercury WQBEL based on the human health or
wildlife criteria adopted in this chapter would be necessary for a particular
permittee to comply with water quality standards in the absence of a
variance. (b) That the permittee is not currently complying with the WQBEL
and information available from the application described in paragraph (L)(2) of
this rule indicates that there is no readily apparent means of complying with
the WQBEL without constructing end-of-pipe controls more stringent than those
required by sections 301 (b) and 306 of the act. (c) That the discharger is currently able to achieve an annual
average mercury effluent concentration of twelve ng/l on the date that the
variance is granted. For the purpose of determining eligibility under paragraph
(L) of this rule, the annual average mercury effluent concentration is the
average of the most recent twelve months of effluent data. (2) In lieu of complying
with the requirements of paragraph (B) of this rule, a discharger seeking a
variance under paragraph (L) of this rule may submit to the director an
application containing the following information in writing: (a) A certification that the discharger intends to be subject to
the terms of paragraph (L) of this rule. (b) A description of measures taken to date for mercury reduction
or elimination projects. (c) A PMP for the identification and evaluation of potential
mercury sources and potential methods for reducing or eliminating mercury from
the discharger's effluent. The PMP shall include the following, at a
minimum: data documenting the facility's current influent and effluent
mercury concentrations; identification of all known mercury sources; a
description of current plans to reduce or eliminate known sources of mercury; a
preliminary identification of other potential mercury sources; a proposed
schedule for evaluating the mercury sources; and a proposed schedule for
identifying and evaluating potential reduction, elimination, and prevention
methods. (d) An explanation of the discharger's basis for concluding
that there are no readily available means of complying with the WQBEL without
construction of end-of-pipe controls. (e) A demonstration of compliance with the conditions in
paragraph (B)(2)(i)(i) of this rule. (3) The director will
deny the applicability of paragraph (L)(1) of this rule to a discharger if the
discharger fails to fulfill the requirements specified in paragraphs (L)(1) and
(L)(2) of this rule. (4) If the conditions of
paragraphs (L)(1) and (L)(2) of this rule are met, the director issues the
variance and incorporate the following requirements, at a minimum, into the
discharger's NPDES permit: (a) All conditions required under paragraph (F)(1) of this
rule. (b) A requirement that the discharger's average mercury
effluent concentration as defined in paragraph (L)(1) of this rule remains less
than or equal to twelve ng/l. The requirements of paragraph (L)(6) of this rule
shall be included in the permit. (c) Permit conditions needed to implement the PMP submitted under
paragraph (L)(2)(c) of this rule. (d) A requirement that the discharger use an approved U.S. EPA
analytical method that is capable of quantifying the applicable water quality
standard. (e) A requirement that upon completion of the actions identified
in the PMP described in paragraph (F)(1)(b) of this rule, the permittee shall
submit to the director a certification that all permit conditions imposed to
implement the PMP have been satisfied, including in this certification a
statement as to whether compliance with the WQBEL has been achieved and can be
maintained. This certification shall be accompanied by the
following: (i) All available data
documenting the discharger's current influent and effluent mercury
concentrations. (ii) Data documenting all
known significant sources of mercury and the steps that have been taken to
reduce or eliminate those sources. (iii) A determination of
the lowest mercury concentration that currently available data indicate can be
reliably achieved through implementation of the PMP. (5) Upon receipt of the
certification required by paragraph (L)(4)(e) of this rule, the director will
take either of the following actions: (a) If the permittee certifies that it has achieved and can
maintain compliance with the WQBEL, the director incorporates the WQBEL into
the permit in lieu of the variance either via a permit modification if the
permit has not yet expired or as a part of any renewal of the permit if it has
expired. (b) If the permittee certifies that it has not achieved or can
not maintain compliance with the WQBEL, the director reviews the data submitted
with the certification and such other relevant information as may be available,
and: (i) If the director
concurs with the certification, the director allows the variance to continue in
force if the variance has not expired or renew the variance in accordance with
paragraph (J) of this rule if the variance has expired. (ii) If the director
concludes, despite contrary certification by the permittee, that the permittee
has achieved and can maintain compliance with the WQBEL, the director
incorporates the WQBEL into the permit in lieu of the variance via a permit
modification if the permit has not yet expired or as a part of any renewal of
the permit if it has expired. (6) If at any time after
the date specified in a variance by which the discharger is to have met an
average annual mercury effluent concentration of twelve ng/l, as defined in
paragraph (I)(1) of this rule, the discharger's average mercury effluent
concentration as defined in paragraph (I)(1) of this rule exceeds twelve ng/l,
the discharger shall submit an individual variance application, if a variance
is desired, or request a permit modification for a compliance schedule to
attain compliance with the WQBEL. Paragraph (I) of this rule no longer applies
to the discharger on the date the director acts on the discharger's
individual variance application or the date the permit modification becomes
effective. The requirements of this paragraph will not apply to the discharger
if the discharger demonstrates to the satisfaction of the director that the
mercury level in the discharger's effluent exceeds twelve ng/l due
primarily to the presence of mercury in discharger's intake
water. (7) Multiple discharger
mercury variances approved for dischargers in the Ohio river basin prior to the
effective date of this rule remain in effect until the discharger's permit
is renewed or an individual variance application is approved, whichever occurs
first. (8) The variance and the
highest attainable condition will be reviewed every five years to determine
whether the variance is still needed, or if the highest attainable condition
needs to be revised based on the mercury reduction options and the mercury
concentrations achievable at that time, and the results of the review will be
submitted to U.S. EPA. (M) Multiple discharger ammonia variance,
applicable upon the effective date of the adoption of revised ammonia water
quality criteria for the protection of aquatic life in rule 3745-1-35 of the
Administrative Code. The director has reviewed the available information on
ammonia removal by controlled discharge wastewater lagoons and the cost. Based
on effluent data for NPDES permittees with this treatment technology, as well
as federal data on these plants and the communities where they are located, the
director has determined that requiring removal of ammonia by construction of
end-of-pipe controls to attain ammonia WQBELs would result in substantial and
widespread social and economic impact. The director may determine whether there
are other means by which the permittee could comply with the WQBEL without
constructing end-of-pipe treatment based on the information provided by the
permittee in the application submitted in accordance with this paragraph. The
director has also determined that the increased risk to human health and the
environment associated with granting the variance compared with compliance with
the WQS absent the variance, is consistent with the protection of the public
health, safety, and welfare. The variance is effective for twenty years from
date of U.S. EPA approval. Before the end of the term, the variance may be
updated and resubmitted to U.S. EPA. If U.S. EPA approves the variance, the
effective date may be extended based on the updated term of the
variance. [Comment: controlled discharge lagoons are
defined as facultative lagoons consisting of multiple treatment cells that are
able to control the timing of their discharge.] (1) The director may
grant a variance under paragraph (M) of this rule without giving any additional
consideration to the factors specified in paragraphs (B)(1) and (B)(2)(i)(ii)
of this rule where the director determines all of the following: (a) That a monthly average ammonia WQBEL based on the
aquatic life criteria adopted in this chapter would be necessary for a
particular permittee to comply with water quality standards in the absence of a
variance. (b) That the permittee is not currently complying with the
WQBEL and information available from the application described in paragraph
(M)(2) of this rule indicates that there is no readily apparent means of
complying with the WQBEL without constructing end-of-pipe controls more
stringent than those required by sections 301 (b) and 306 of the
act. (2) In lieu of complying
with the requirements of paragraph (B) of this rule, a discharger seeking a
variance under paragraph (M) of this rule shall submit to the director an
application containing the following information in writing: (a) A demonstration that the discharge cannot meet the
wasteload allocation for ammonia-nitrogen. (b) A certification that the discharger intends to be
subject to the terms of paragraph (M) of this rule. (c) A description of measures taken to date to minimize
ammonia in the final discharge. (d) A PMP for the evaluation and optimization of ammonia
reduction from the treatment plant to the discharger's effluent. The PMP
shall include the following, at a minimum: (i) A schedule for
removing sludges in order to maintain adequate treatment capacity; (ii) Facility flow
management that ensures optimal treatment. (e) An explanation of the discharger's basis for
concluding that there are no readily available means of complying with the
WQBEL without construction of end-of-pipe controls and documentation of
resultant significant and widespread social and economic impact. (f) A demonstration of compliance with the conditions in
paragraph (B)(2)(i)(i) of this rule. (3) The director shall
deny the applicability of paragraph (M)(1) of this rule to a discharger if the
discharger fails to fulfill the requirements specified in paragraphs (M)(1) and
(M)(2) of this rule. (4) If the conditions of
paragraphs (M)(1) and (M)(2) of this rule are met, the director shall issue the
variance and the following requirements, at a minimum, into the
discharger's NPDES permit: (a) All conditions described in paragraph (F)(1) of this
rule; (b) An effluent limit that represents an interim HAC
achievable by the discharge; (c) Permit conditions needed to implement the PMP submitted
under paragraph (M)(2)(d) of this rule; (d) A variance term no longer than twenty
years. (5) The variance and the
HAC will be reviewed every five years to determine whether the variance is
still needed, or if the HAC needs to be revised based on the ammonia reduction
options and the ammonia concentrations achievable at that time, and the results
of the review will be submitted to U.S. EPA.
Last updated December 4, 2025 at 2:24 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-39 | Site-specific modifications to criteria and values.
Effective:
March 20, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government
publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations,
federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see
rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) Requirements for site-specific
modifications to criteria and values. Criteria and values adopted in, or
developed pursuant to, this chapter may be modified on a site-specific basis to
reflect local environmental conditions. These criteria and values shall be
developed and approved in accordance with the following provisions:
(1) Any such
modifications are protective of designated uses , aquatic life, wildlife, and
human health and are submitted to the U.S. EPA for approval. (2) Any site-specific
modifications are based on a sound scientific rationale. (3) Any site-specific
modifications that result in less stringent criteria are not likely to
jeopardize the continued existence of threatened or endangered species or
result in the destruction or adverse modification of such species'
critical habitat. More stringent modifications are developed to protect
threatened or endangered species, where such modifications are necessary to
ensure that water quality is not likely to jeopardize the continued existence
of such species or result in the destruction or adverse modification of such
species' critical habitat. More stringent modifications may also be
developed to protect candidate (C1) species being considered by the United
States fish and wildlife service for listing under section 4 of the Endangered
Species Act, where such modifications are necessary to protect such
species. (B) Aquatic life. (1) Aquatic life criteria
or values may be modified on a site-specific basis to provide an additional
level of protection where the toxicity or exposure potential is greater than
the toxicity or exposure potential assumptions used to derive the criteria or
values in question. (2) Less stringent
site-specific modifications to chronic or acute aquatic life criteria or values
may be developed when either of the following occur: (a) The local water quality characteristics (such as, but not
limited to, pH, hardness, temperature or color) lessen the biological
availability or toxicity of a pollutant. (b) The sensitivity of the aquatic organisms species that occur
at the site differs from the species actually tested in developing the
criteria. The phrase "occur at the site" includes the species,
genera, families, orders, classes, and phyla that: are usually present at the
site; are present at the site only seasonally due to migration; are present
intermittently because they periodically return to or extend their ranges into
the site; were present at the site in the past and are not currently present at
the site due to degraded conditions but are expected to return to the site when
conditions improve; are present in nearby bodies of water and are not currently
present at the site due to degraded conditions but are expected to be present
at the site when conditions improve. The taxa that "occur at the
site" cannot be determined merely by sampling downstream and/or upstream
of the site at one point in time. "Occur at the site" does not
include taxa that were once present at the site but cannot exist at the site
now due to permanent physical alteration of the habitat at the site resulting,
for example, from dams. (3) Less stringent
modifications also may be developed to acute and chronic aquatic life criteria
or values to reflect local physical and hydrological conditions. (4) Less stringent
modifications to the whole effluent toxicity level for limited resource waters,
as specified in rule 3745-2-09 of the Administrative Code, may be applied.
Documentation provided by the permittee or independently available to the
director shall show that the modification, not to exceed 1.0 acute toxic unit,
is protective of the resident aquatic community. (5) Any modifications to
protect threatened or endangered aquatic species specified in paragraph (A) of
this rule may be accomplished using either of the two following
procedures: (a) If the species mean acute value (SMAV) for a listed or
proposed species, or for a surrogate of such species, is lower than the
calculated final acute value (FAV), such lower SMAV may be used instead of the
calculated FAV in developing site-specific modified criteria. (b) The site-specific criteria may be calculated using the
recalculation procedure for site-specific modifications described in chapter 3
of the "U.S. EPA Water Quality Standards Handbook." (C) Wildlife. (1) Wildlife water
quality criteria may be modified on a site-specific basis to provide an
additional level of protection where the toxicity or exposure potential is
greater than the toxicity or exposure potential assumptions used to derive the
criteria in question. (2) Less stringent
site-specific modifications to wildlife water quality criteria may be developed
provided all the following criteria apply: (a) The modification demonstration addresses both the mobility of
prey organisms and wildlife populations in defining the site for which the
modification is developed. (b) The modification reflects a site-specific bioaccumulation
factor. (c) There is a showing that both: (i) Any increased uptake
of the toxicant by prey species utilizing the site will not cause adverse
effects in wildlife populations. (ii) Wildlife populations
utilizing the site or downstream waters will continue to be fully
protected. (3) Any modification to
protect threatened or endangered wildlife species specified in paragraph (A) of
this rule must consider both the mobility of prey organisms and wildlife
populations in defining the site for which criteria are developed, and may be
accomplished by using the following recommended method: (a) Use the methodology contained in rule 3745-1-43 of the
Administrative Code, substituting appropriate species-specific toxicological,
epidemiological, or exposure information, including changes to the
BAF. (b) Use an interspecies uncertainty factor of one where
epidemiological data are available for the species in question. If necessary,
species-specific exposure parameters can be derived in accordance with rule
3745-1-43 of the Administrative Code. (c) Apply an intraspecies uncertainty factor (to account for
protection of individuals within a wildlife population) in the denominator of
the effect part of the wildlife equation contained in rule 3745-1-43 of the
Administrative Code in a manner consistent with the other uncertainty factors
described in rule 3745-1-43 of the Administrative Code. (d) Compare the resulting wildlife value for the species in
question to the two class-specific wildlife values which were previously
calculated, then select the lowest of the three as the site-specific
modification. (D) Bioaccumulation factors. (1) BAFs may be modified
on a site-specific basis, pursuant to the methodology contained in rule
3745-1-41 of the Administrative Code, to larger values where reliable data show
that local bioaccumulation is greater than the basin-wide value. (2) BAFs may be modified
on a site-specific basis, pursuant to the methodology contained in rule
3745-1-41 of the Administrative Code, to lower values if any of the following
occur: (a) The fraction of the total chemical that is freely dissolved
in the ambient water is different than that used to derive the system-wide BAFs
(i.e., the concentrations of particulate organic carbon and the dissolved
organic carbon are different than those used to derive the system-wide
BAFs). (b) Input parameters of the Gobas model, such as the structure of
the aquatic food web and the disequilibrium constant, are different at the site
than those used to derive the system-wide BAFs. (c) The per cent lipid of aquatic organisms that are consumed and
occur at the site is different than that used to derive the system-wide
BAFs. (d) Site-specific field-measured BAFs or biota-sediment
accumulation factor (BSAFs) are determined. (3) Any more stringent
modifications to protect threatened or endangered species specified in
paragraph (A) of this rule shall be derived using procedures set forth in the
methodology contained in rule 3745-1-41 of the Administrative
Code. (E) Human health. (1) Human health criteria
or values may be modified on a site-specific basis to provide an additional
level of protection where the toxicity or exposure potential is greater than
the toxicity or exposure potential assumptions used to derive the criteria or
values in question. Human health criteria or values shall be modified on a
site-specific basis to provide additional protection appropriate for highly
exposed subpopulations. (2) Less stringent
site-specific modifications to human health criteria or values may be developed
when either of the following occur: (a) Local fish consumption rates are lower than the rate used to
derive human health criteria or values under rule 3745-1-42 of the
Administrative Code (this option is not be available for water bodies subject
to a fish consumption advisory). (b) A site-specific BAF is derived which is lower than that used
to derive human health criteria or values under rule 3745-1-42 of the
Administrative Code. (F) Notification requirements. When the
director proposes a site-specific modification to a criterion or value as
allowed or specified in paragraph (A) of this rule, the director shall notify
the other Great Lakes states of such a proposal and, for less stringent
criteria, supplies appropriate justification. (G) Notwithstanding paragraphs (A) to (F)
of this rule, any chemical-specific criterion listed in this chapter or derived
pursuant to rule 3745-1-40, 3745-1-41, 3745-1-42 or 3745-1-43 of the
Administrative Code may be modified for a particular surface water body or
segment if specific information is provided to the director which shows either
of the following: (1) That all, or
portions, of the data used to derive the criterion are inapplicable or not
relevant to that surface water body or segment. (2) That the otherwise
applicable criterion is more or less stringent than necessary to protect human
health, aquatic life, wildlife or agricultural use. In such cases, the director may adopt a less or
more stringent site-specific criterion if it can be scientifically justified
based on new toxicological data or site-specific conditions of water quality,
pollutant bioavailability, resident species, or human exposure. (H) Within the lake Erie drainage basin,
paragraph (G) of this rule applies only when it results in modifications at
least as protective as modifications resulting from paragraphs (A) to (F) of
this rule.
Last updated March 20, 2024 at 8:47 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-40 | Methodologies for development of aquatic life criteria and values.
Effective:
March 20, 2024
All pollutants or combinations of pollutants, for which aquatic life criteria have not been adopted in rule 3745-1-35 of the Administrative Code, may not exceed the water quality criteria or values derived using the procedures contained in this rule. (A) Tier I acute aquatic criterion (AAC) and tier II acute aquatic value (AAV). This criterion and value apply outside the mixing zone to all aquatic life habitat use designations. This criterion and value are expressed as the quantity of chemical per liter of water (e.g., mg/l or ug/l). Paragraphs (A)(1) to (A)(3) of this rule shall be used to calculate the tier I AAC when acute toxicity data are available for species in at least eight families. Paragraph (A)(4) of this rule shall be used to calculate the tier II AAV when there are not enough toxicity data to use the procedures in paragraphs (A)(1) to (A)(3) of this rule but there is at least one EC50 or LC50 value for a species in one of the following three genera of the family Daphnidae: Ceriodaphnia sp., Daphnia sp., or Simocephalus sp. (1) The procedures in paragraphs (A)(1) to (A)(3) of this rule shall be used to calculate the tier I AAC when LC50 or EC50 data are available for at least one species of freshwater animal in at least the eight different families identified as follows: (a) The family Salmonidae in the class Osteichthyes. (b) One other family (preferably a commercially or recreationally important warmwater species) in the class Osteichthyes (e.g., bluegill, channel catfish). (c) A third family in the phylum Chordata (e.g., fish, amphibian). (d) A planktonic crustacean (e.g., a cladoceran, copepod). (e) A benthic crustacean (e.g., ostracod, isopod, amphipod, crayfish). (f) An insect (e.g., mayfly, dragonfly, damselfly, stonefly, caddisfly, mosquito, midge). (g) A family in a phylum other than Arthropoda or Chordata (e.g., Rotifera, Annelida, Mollusca). (h) A family in any order of insect or any phylum not already represented. (2) When data are not available to show that acute toxicity to two or more species is similarly related to a water quality characteristic (e.g., hardness, pH or temperature), the tier I AAC shall be calculated using the procedures in paragraphs (A)(2)(a) to (A)(2)(i) of this rule. (a) For each species for which at least one acute value is available, the species mean acute value (SMAV) is calculated as the geometric mean of the results of all acceptable flow-through acute toxicity tests in which the concentrations of test material were measured with the most sensitive tested life stage of the species. For a species for which no such result is available, the SMAV is calculated as the geometric mean of all acceptable acute toxicity tests with the most sensitive tested life stage, i.e., results of flow-through tests in which the concentrations were not measured and results of static and renewal tests based on initial concentrations (nominal concentrations are acceptable for most test materials if measured concentrations are not available) of test material. (b) For each genus for which one or more SMAVs are available, the genus mean acute value (GMAV) is calculated as the geometric mean of the SMAVs available for the genus. (c) The GMAVs are ordered from high to low. (d) Ranks (R) are assigned to the GMAVs from "one" for the lowest to "N" for the highest. If two or more GMAVs are identical, successive ranks are arbitrarily assigned. (e) The cumulative probability (P), is calculated for each GMAV as R / (N + 1). (f) The GMAVs selected are those four which have cumulative probabilities closest to 0.05. If there are fewer than fifty-nine GMAVs, these will always be the four lowest GMAVs. (g) Using the four selected GMAVs and Ps, the final acute value (FAV) is calculated as follows:  (h) If, for a commercially, recreationally or ecologically important species, the geometric mean of the acute values from flow-through tests in which the concentrations of test material were measured is lower than the calculated FAV, then that geometric mean is used as the FAV instead of the calculated FAV. (i) The AAC is calculated by dividing the FAV by two. (3) When enough data are available to show that acute toxicity to two or more species is similarly related to a water quality characteristic (e.g., hardness, pH or temperature), the tier I FAV shall be calculated using the procedures in paragraphs (A)(3)(a) to (A)(3)(l) of this rule or using an analysis of covariance. The two methods are equivalent and produce identical results. If two or more factors affect toxicity, multiple regression analysis shall be used. (a) For each species for which comparable acute toxicity values are available at two or more different values of the water quality characteristic, a least squares regression of the acute toxicity values on the corresponding values of the water quality characteristic is performed to obtain the slope and its ninety-five per cent confidence limits for each species. Because the best documented relationship is that between hardness and acute toxicity of metals and a log-log relationship fits these data, geometric means and natural logarithms of both toxicity and water quality are used in the rest of this method. For relationships based on other water quality characteristics, such as pH or temperature, no transformation or a different transformation might fit the data better, and appropriate changes are necessary throughout this method. (b) Data for each species are evaluated as to whether or not they are relevant, taking into account the range and number of the tested values of the water quality characteristic and the degree of agreement within and between species. If useful slopes are not available for at least one fish and one invertebrate, or if the available slopes are too dissimilar, or if too few data are available to adequately define the relationship between acute toxicity and the water quality characteristic, the AAC is calculated using the procedures in paragraph (A)(2) of this rule, using the results of tests conducted under conditions and in waters similar to those commonly used for toxicity tests with the species. (c) For each species, the geometric mean of the available acute values shall be calculated and then each of the acute values for a species is divided by the mean for the species. This calculation normalizes the acute values so that the geometric mean of the normalized values for each species individually and for any combination of species is 1.0. (d) The values of the water quality characteristic are similarly normalized for each species individually using the procedure in paragraph (A)(3)(c) of this rule. (e) For each species, a least squares regression is calculated using the normalized acute toxicity values and the corresponding water quality characteristic. The resulting slopes and ninety-five per cent confidence limits will be identical to those obtained in paragraph (A)(3)(a) of this rule. If, however, the data are actually plotted, the line of best fit for each individual species will go through the point 1, 1 in the center of the graph. (f) All the normalized data are treated as if they were for the same species and a least squares regression of all the normalized acute values on the corresponding normalized values of the water quality characteristic is performed to obtain the pooled acute slope, V, and its ninety-five per cent confidence limits. If all of the normalized data are actually plotted, the line of best fit will go through the point 1, 1 in the center of the graph. (g) For each species the geometric mean, W, of the acute toxicity values and the geometric mean, X, of the values of the water quality characteristic are calculated. These were calculated in paragraphs (A)(3)(c) and (A)(3)(d) of this rule. (h) For each species the natural logarithm (ln), Y, of the SMAV at a selected value, Z, of the water quality characteristic is calculated using the equation: Y = ln W - V(ln X - ln Z). (i) For each species the SMAV at Z is calculated using the equation: SMAV = eY. (j) The FAV is obtained by using the procedures described in paragraphs (A)(2)(b) to (A)(2)(g) of this rule. (k) If, for a commercially or recreationally important species the geometric mean of the acute values at Z from flow-through tests in which the concentrations of the test material were measured is lower than the FAV at Z, then the geometric mean is used as the FAV instead of the FAV. (l) The final acute equation is written as: FAV = e(V[ln(water quality characteristic)] + A - V[ln Z]), Where: V = pooled acute slope, and A = ln (FAV at Z). Because V, A, and Z are known, the FAV can be calculated for any selected value of the water quality characteristic. (m) For any value of Z, the AAC is calculated by dividing the FAV by two. (4) Tier II values. (a) If the data needed to derive the tier I AAC in paragraphs (A)(1) to (A)(3) of this rule are not present in the acute toxicity data base and at least one EC50 or LC50 value is available for a species in one of the following three genera of the family Daphnidae - Ceriodaphnia sp., Daphnia sp., or Simocephalus sp., a tier II secondary acute value (SAV) shall be calculated by dividing the lowest GMAV in the data base by the secondary acute factor (SAF) (see table 40-1 of this rule) corresponding to the number of satisfied minimum data requirements listed in the tier I methodology (see paragraph (A)(1) of this rule). (b) The tier II AAV equals the SAV divided by two. (c) If appropriate, the AAV shall be made a function of a water quality characteristic in a manner similar to that described in paragraph (A)(3) of this rule. (B) Tier I chronic aquatic criterion (CAC) and tier II chronic aquatic value (CAV). This criterion and value apply outside the mixing zone to all aquatic life habitat use designations except the limited resource water use designation. This criterion and value are expressed as the quantity of chemical per liter of water (e.g., mg/l or ug/l). Paragraphs (B)(1) and (B)(2) of this rule are used to calculate the tier I CAC when there are sufficient toxicity data, and paragraphs (B)(3) and (B)(4) of this rule are used to calculate the tier II CAV when such data is insufficient. Please note that CAC may also be referred to as the criterion continuous concentration (CCC); both of these terms refer to the same criterion and calculation process. (1) If chronic values are available for species in eight families as described in paragraph (A)(1) of this rule, a species mean chronic value (SMCV) shall be calculated as follows: (a) A species mean chronic calue (SMCV) is calculated for each species for which at least one chronic value is available by calculating the geometric mean of the results of all acceptable life-cycle and partial life-cycle toxicity tests with the species; for a species of fish for which no such result is available, the SMCV shall be the geometric mean of all acceptable early life-stage tests. (b) Appropriate genus mean chronic values (GMCVs) are calculated from the SMCVs obtained in pargraph (B)(1)(a) of this rule. A GMCV is the geometric mean of the SMCVs for the genus. (c) The CAC is obtained using the procedure contained in paragraphs (A)(1) to (A)(3) of this rule, substituting CAC for FAV, SMCV for SMAV, and GMCV for GMAV. (2) If chronic data for a chemical are not available for at least eight freshwater species meeting the requirements in paragraph (A)(1) of this rule, the CAC shall be calculated by dividing the FAV by a final acute-chronic ratio (FACR). (a) Acute-chronic ratios (ACRs) are required for at least one species of aquatic animal in at least three different families provided that of the three species conform to the following: (i) At least one is a fish. (ii) At least one is an invertebrate. (iii) At least one species is an acutely sensitive freshwater species (the other two may be saltwater species). (b) For each chronic value for which at least one corresponding appropriate acute value is available, an ACR shall be calculated using the chronic value for the denominator and using the geometric mean of the results of all acceptable flow-through (except static is acceptable for daphnids and midges) acute tests in the same dilution water in which the concentrations are measured for the numerator. For fish, the acute test shall be conducted with juveniles. The acute test should be part of the same study as the chronic test. If acute tests were not conducted as part of the same study, but were conducted as part of a different study in the same laboratory and dilution water, then they may be used. If no such acute tests are available, results of acute tests conducted in the same dilution water in a different laboratory may be used. If no such acute tests are available, an ACR is not calculated. (c) For each species, the species mean ACR shall be calculated as the geometric mean of all ACRs available for that species. If the minimum ACR data requirements (as described in paragraph (B)(2)(a) of this rule) are not met with freshwater data alone, saltwater data may be used along with the freshwater data. (d) For some materials, the ACR seems to be the same for all species, but for other materials the ratio seems to increase or decrease as the SMAV increases. Thus the FACR shall be obtained in the following ways: (i) If the species mean ACR seems to increase or decrease as the SMAVs increase, the FACR is calculated as the geometric mean of the ACRs for species whose SMAVs are close to the FAV. (ii) If no major trend is apparent and the ACRs for all species are within a factor of ten, the FACR is calculated as the geometric mean of all of the species mean ACRs. (iii) If the most appropriate species mean ACRs are less than 2.0, the FACR is assumed to be 2.0. (e) The FCV shall be calculated by dividing the FAV by the FACR. (f) If the SMCV of a commercially or recreationally important species is lower than the calculated CAC, then that SMCV shall be used as the CAC instead of the calculated CAC. (3) Secondary acute-chronic ratio. If fewer than three acceptable experimentally determined ACRs are available for the chemical, the secondary acute-chronic ratio (SACR) shall be determined using enough assumed ACRs of eighteen so that the total number of ACRs equals three. Calculate the SACR as the geometric mean of the three ACRs. If no experimentally determined ACRs are available, the SACR is eighteen. (4) Tier II chronic aquatic value. (a) The CAV shall be calculated using one of the following equations: (i) CAV = FAV / SACR (Use FAV from paragraph (A) of this rule and use SACR from paragraph (B)(3) of this rule). (ii) CAV = SAV / FACR (Use SAV from paragraph (A)(4) of this rule and use FACR from paragraph (B)(2) of this rule). (iii) CAV = SAV/ SACR (Use SAV from paragraph (A)(4) of this rule and use SACR from paragraph (B)(3) of this rule). (b) If appropriate, the CAV shall be made a function of a water quality characteristic in a manner similar to that described in paragraph (A)(3) of this rule. (c) If the SMCV of a commercially or recreationally important species is lower than the calculated CAV, then that SMCV shall be used as the CAV instead of the calculated CAV. (C) Final plant value (FPV). This value applies in place of the CAC or CAV if it is lower than the CAC or CAV. Results of at least one acceptable test with a freshwater algae or vascular plant is required. If plants are among the aquatic organisms most sensitive to the material, results of a test with a plant in another phylum (division) shall also be available. (1) A plant value shall be the result of a ninety-six-hour test conducted with an alga or a chronic test conducted with an aquatic vascular plant. A test of the toxicity of a metal to a plant shall not be used if the medium contained an excessive amount of a complexing agent, such as EDTA, that might affect the toxicity of the metal. Concentrations of EDTA above two hundred micrograms per liter are considered excessive. (2) The FPV shall be obtained by selecting the lowest result from a test with an important aquatic plant species in which the concentrations of test material are measured and the endpoint is biologically important. (D) Application of criteria and values shall be as follows: (1) The FAV and SAV are applied as maximum concentrations inside the mixing zone. (2) The AAC and AAV are applied as maximum concentrations outside the mixing zone. (3) The CAC, CAV, and FPV if available are applied as thirty-day average concentrations outside the mixing zone. Table 40-1. Secondary acute factors | Number of minimum data requirements satisfied | Secondary acute factor | | 1................................... | 21.9 | | 2 and neither requirement includes the family Salmonidae........... | 13.0 | | 2 and one requirement includes the family Salmonidae........... | 7.9 | | 3................................... | 8.0 | | 4................................... | 7.0 | | 5................................... | 6.1 | | 6................................... | 5.2 | | 7................................... | 4.3 |
Last updated March 20, 2024 at 8:48 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-41 | Methodology for deriving bioaccumulation factors.
Effective:
March 20, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] (A) The purpose of this rule is to describe procedures for deriving bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) to be used in the calculation of human health tier I criteria and tier II values and wildlife tier I criteria. A subset of the human health BAFs are also used to identify the chemicals that are considered bioaccumulative chemicals of concern (BCCs). (B) Review and selection of data. (1) Field-measured BAFs. The following procedural and quality assurance requirements shall be met for field-measured BAFs. (a) The field studies used are limited to those conducted in the Great Lakes system with fish in trophic levels three or four. (b) The trophic level of the fish species is to be determined. (c) The site of the field study is not to be so unique such that the BAF cannot be extrapolated to other locations where the criteria and values will apply. (d) For organic chemicals, the per cent lipid is either measured or reliably estimated for the tissue used in the determination of the BAF. (e) The concentration of the chemical in the water is measured in a way that can be related to particulate organic carbon (POC) or dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and is relatively constant during the steady-state time period. (f) For organic chemicals with log Kow greater than four, the concentrations of POC and DOC in the ambient water are either measured or reliably estimated. (g) For inorganic and organic chemicals, BAFs can be used only if they are expressed on a wet weight basis; BAFs reported on a dry weight basis cannot be converted to wet weight unless a conversion factor is measured or reliably estimated for the tissue used in the determination of the BAF. (2) Field-measured biota-sediment accumulation factors (BSAFs). The following procedural and quality assurance requirements shall be met for field-measured BSAFs. (a) The field studies used are limited to those conducted in the Great Lakes system with fish in trophic levels three or four. (b) Samples of surface sediments are from locations where there is net deposition of fine sediment (zero to one centimeter is ideal) and that are representative of average surface sediments in the vicinity of the organism. (c) The Kows used are of acceptable quality as described in paragraph (B)(5) of this rule. (d) The site of the field study shall not be so unique such that the resulting BAF cannot be extrapolated to other locations where the criteria and values will apply. (e) The trophic level of each fish species is determined. (f) The per cent lipid is either measured or reliably estimated for the tissue used in the determination of the BAF. (3) Laboratory-measured bioconcentration factors (BCFs). The following procedural and quality assurance requirements shall be met for laboratory-measured BCFs. (a) The test organism is not diseased, unhealthy, or adversely affected by the concentration of the chemical. (b) The total concentration of the chemical in the water is measured and shall be relatively constant during the steady-state time period. (c) The organisms are exposed to the chemical using a flow-through or renewal procedure. (d) For organic chemicals, the per cent lipid is either measured or reliably estimated for the tissue used in the determination of the BCF. (e) For organic chemicals with log Kow greater than four, the concentrations of POC and DOC in the test solution are either measured or reliably estimated. (f) Laboratory-measured BCFs should be determined using fish species, but BCFs determined with mollusks and other invertebrates may be used if appropriate. (g) In a bioconcentration test, if laboratory-measured BCFs increase or decrease as the concentration of the chemical increase in the test solutions, the BCF measured at the lowest test concentration that is above concentrations existing in the control water shall be used (i.e., a BCF shall not be calculated from a control treatment). If the chemical is inorganic and a micronutrient, its concentrations in a bioconcentration test shall be greater than both normal background levels and levels required for normal nutrition of the test species, but below levels that adversely affect the species. (h) For inorganic and organic chemicals, BCFs are used only if they are expressed on a wet weight basis. BCFs reported on a dry weight basis cannot be converted to wet weight unless a conversion factor is measured or reliably estimated for the tissue used in the determination of the BAF. (i) BCFs for organic chemicals may be based on measurement of radioactivity only when the BCF is intended to include metabolites or when there is confidence that there is no interference due to metabolites. (j) The calculation of the BCF addresses growth dilution. (k) Other aspects of the methodology used are similar to those described in "Standard Guide for Conducting Bioconcentration Tests with Fishes and Saltwater Bivalve Mollusks. Standard E1022." (4) Predicted BCFs. The following procedural and quality assurance requirements shall be met for predicted BCFs. (a) The Kow used is of acceptable quality as described in paragraph (B)(5) of this rule. (b) The predicted baseline BCF shall be calculated using the equation Predicted baseline BCF = Kow Where: Kow = octanol-water partition coefficient. (5) Octanol-water partition coefficient (Kow). (a) The value of Kow used for an organic chemical shall be determined by giving priority to the experimental and computational techniques used as shown in table 41-1 of this rule. (b) The value of Kow used for an organic chemical shall be either the geometric mean of the available Kows with highest priority or the arithmetic mean of the available log Kows with the highest priority. Because it is an intermediate value in the derivation of a BAF, the values used for the Kow and log Kow of a chemical shall not be rounded to fewer than three significant digits after the decimal point. (c) A value of Kow that seems to be different from the others may be considered an outlier and not used. (C) Baseline BAFs shall be derived using the following four methods, which are listed from most preferred to least preferred. (1) A measured baseline BAF for an organic or inorganic chemical derived from a field study of acceptable quality. (2) A predicted baseline BAF for an organic chemical derived using field-measured BSAFs of acceptable quality. (3) A predicted baseline BAF for an organic or inorganic chemical derived from a BCF measured in a laboratory study of acceptable quality and a food-chain multiplier (FCM). (4) A predicted baseline BAF for an organic chemical derived from a Kow of acceptable quality and an FCM. For comparative purposes, baseline BAFs are derived for each chemical by as many of the four methods as available data allow. (D) Calculation of baseline BAFs for organic chemicals. (1) Lipid normalization. (a) It is assumed that BAFs and BCFs for organic chemicals can be extrapolated on the basis of per cent lipid from one tissue to another and from one aquatic species to another in most cases. (b) Because BAFs and BCFs for organic chemicals are related to the per cent lipid, it does not make any difference whether the tissue sample is whole body or edible portion, but both the BAF (or BCF) and the per cent lipid shall be determined for the same type of tissue. The per cent lipid of the tissue should be measured during the BAF or BCF study, but in some cases it may be reliably estimated from measurements on tissue from other organisms. If per cent lipid is not reported for the test organisms in the original study, it may be obtained from the author. In the case of a laboratory study, lipid data for the same or a comparable laboratory population of test organisms that were used in the original study may be used. (c) The lipid-normalized concentration (Cl) of a chemical in tissue is defined using the following equation: Cl = (CB/fl) Where: CB= concentration of the organic chemical in the tissue of aquatic biota (either whole organism or specified tissue) expressed in micrograms per gram. fl = fraction of the tissue that is lipid. (2) Bioavailability. By definition, baseline BAFs and BCFs for organic chemicals, whether measured or predicted, are based on the concentration of the chemical that is freely dissolved in the ambient water in order to account for bioavailability. For the purposes of this rule, the relationship between the total concentration of the chemical in the ambient water (i.e., that which is freely dissolved plus that which is sorbed to particulate organic carbon or to dissolved organic carbon) to the freely dissolved concentration of the chemical in the ambient water shall be calculated using the following equation: Cwfd = (ffd) (Cwt) Where: Cwfd = freely dissolved concentration of the organic chemical in the ambient water. Cwt = total concentration of the organic chemical in the ambient water. ffd = fraction of the total chemical in the ambient water that is freely dissolved. The fraction of the total chemical in the ambient water that is freely dissolved (ffd), shall be calculated using the following equation:  Where: DOC = concentration of dissolved organic carbon, expressed as kilograms of dissolved organic carbon per liter of water. Kow = octanol-water partition coefficient of the chemical. POC = concentration of particulate organic carbon, expressed as kilograms of particulate organic carbon per liter of water. (3) Food-chain multiplier (FCM). In the absence of a field-measured BAF or a predicted BAF derived from a BSAF, an FCM shall be used to calculate the baseline BAF for trophic levels three and four from a laboratory-measured or predicted BCF. The FCM used shall be derived from table 41-2 of this rule using the chemical's log Kow and linear interpolation. An FCM greater than 1.0 applies to most organic chemicals with a log Kow of four or more. The trophic level used shall take into account the age or size of the fish species consumed by the human, avian or mammalian predator. (4) Calculation of a baseline BAF from a field-measured BAF. A baseline BAF shall be calculated from a field-measured BAF using the following equation:  Where: BAFt= BAF based on total concentration in tissue and water. fl = Fraction of the tissue that is lipid. ffd = Fraction of the total chemical that is freely dissolved in the ambient water. The trophic level to which the baseline BAF applies is the same as the trophic level of the organisms used in the determination of the field-measured BAF. For each trophic level, a species mean measured baseline BAF shall be calculated as the geometric mean if more than one measured baseline BAF is available for a given species. For each trophic level, the geometric mean of the species mean measured baseline BAFs shall be calculated. If a baseline BAF based on a measured BAF is available for either trophic level three or four, but not both, a measured baseline BAF for the other trophic level shall be calculated using the ratio of the FCMs that are obtained by linear interpolation from table 41-2 of this rule for the chemical. (5) Calculation of a baseline BAF from a field-measured BSAF. A baseline BAF for organic chemical "I" shall be calculated from a field-measured BSAF using the following equations: (a)  Where: (BSAF)i = BSAF for chemical "i". (BSAF)r = BSAF for the reference chemical "r". (Kow)i = octanol-water partition coefficient for chemical "i". (Kow)r = octanol-water partition coefficient for the reference chemical "r". (b) A BSAF is calculated using the following equation: BSAF = (Cl/CSOC) Where: Cl = the lipid-normalized concentration of the chemical in tissue. Csoc = the organic carbon-normalized concentration of the chemical in sediment. (c) The organic carbon-normalized concentration of a chemical in sediment (Csoc), is calculated using the following equation: CSOC = (Cs/fOC) Where: CS = concentration of chemical in sediment (expressed as micrograms per gram sediment). fOC = fraction of the sediment that is organic carbon. (d) Predicting BAFs from BSAFs requires data from a steady-state (or near steady-state) condition between sediment and ambient water for both a reference chemical "r" with a field-measured BAFfdl and other chemicals "N=i" for which BSAFs are to be determined. (e) The trophic level to which the baseline BAF applies is the same as the trophic level of the organisms used in the determination of the BSAF. For each trophic level, a species mean baseline BAF is calculated as the geometric mean if more than one baseline BAF is predicted from BSAFs for a given species. For each trophic level, the geometric mean of the species mean baseline BAFs derived using BSAFs is calculated. (f) If a baseline BAF based on a measured BSAF is available for either trophic level three or four, but not both, a baseline BAF for the other trophic level is calculated using the ratio of the FCMs that are obtained by linear interpolation from table 41-2 of this rule for the chemical. (6) Calculation of a baseline BAF from a laboratory-measured BCF. A baseline BAF for trophic level three and a baseline BAF for trophic level four shall be calculated from a laboratory-measured BCF of acceptable quality and an FCM using the following equation:  Where: BCFt = BCF based on total concentration in tissue and water. fl = fraction of the tissue that is lipid. ffd = fraction of the total chemical in the test water that is freely dissolved. FCM = the food-chain multiplier obtained from table 41-2 of this rule by linear interpolation for trophic level three or four, as necessary. For each trophic level the following shall be calculated: (a) If more than one baseline BAF is predicted from laboratory-measured BCFs for a given species, calculate the geometric mean as a species mean baseline BAF. (b) The geometric mean of the species mean baseline BAFs based on laboratory-measured BCFs. (7) Calculation of a baseline BAF from an octanol-water partition coefficient. A baseline BAF for trophic level three and a baseline BAF for trophic level four shall be calculated from a Kow of acceptable quality and an FCM using the following equation: Baseline BAF = (FCM) (predicted baseline BCF) = (FCM) (Kow) Where: FCM = the food-chain multiplier obtained from table 41-2 of this rule by linear interpolation for trophic level three or four, as necessary. Kow = octanol-water partition coefficient. (E) Human health and wildlife BAFs for organic chemicals. (1) To calculate human health and wildlife BAFs for an organic chemical, the Kow of the chemical shall be used with a POC concentration of 0.00000004 kg/l and a DOC concentration of 0.000002 kg/l to yield the fraction freely dissolved (ffd) using the following equations:    (2) The human health BAFs for an organic chemical shall be calculated using the equations. (a) For trophic level three Human health BAFHH TL3 = [(baseline BAF) (0.0182)+1] (ffd) and (b) For trophic level four Human health BAFHHTL4 = [(baseline BAF) (0.0310) + 1] (ffd) Where: 0.0182 and 0.0310 are the standardized fraction lipid values for trophic levels three and four, respectively, that are used to derive human health criteria and values pursuant to rule 3745-1-42 of the Administrative Code. (3) The wildlife BAFs for an organic chemical shall be calculated using the following equations: (a) For trophic level three: Wildlife BAFWLTL3 = [(baseline BAF) (0.0646) + 1] (ffd) (b) For trophic level four: Wildlife BAFWLTL4 = [(baseline BAF) (0.1031) + 1] (ffd) Where: 0.0646 and 0.1031 are the standardized fraction lipid values for trophic levels three and four, respectively, that are used to derive wildlife criteria pursuant to rule 3745-1-43 of the Administrative Code. (F) Human health and wildlife BAFs for inorganic chemicals. (1) For inorganic chemicals, the baseline BAFs for trophic levels three and four are both assumed to equal the BCF determined for the chemical with fish, i.e., the FCM is assumed to be 1.0 for both trophic levels three and four. However, an FCM greater than 1.0 might be applicable to some metals, such as mercury, if, for example, an organometallic form of the metal biomagnifies. (2) BAFs for human health criteria and values. (a) Measured BAFs and BCFs used to determine human health BAFs for inorganic chemicals shall be based on edible tissue of freshwater fish unless it is demonstrated that whole-body BAFs or BCFs are similar to edible-tissue BAFs or BCFs. BCFs and BAFs based on measurements of aquatic plants and invertebrates should not be used in the derivation of human health criteria and values. (b) If one or more field-measured baseline BAFs for an inorganic chemical are available from studies conducted in the Great Lakes system with the edible tissue of fish, then for each trophic level: (i) A species mean measured baseline BAF shall be calculated as the geometric mean if more than one measured BAF is available for a given species. (ii) The geometric mean of the species mean measured baseline BAFs shall be used as the human health BAF for that chemical. (c) If an acceptable measured baseline BAF is not available for an inorganic chemical and one or more acceptable edible-portion laboratory-measured BCFs are available for the chemical, a predicted baseline BAF shall be calculated by multiplying the geometric mean of the BCFs times an FCM. The FCM is 1.0 unless chemical-specific biomagnification data support using a multiplier other than 1.0. The predicted baseline BAF shall be used as the human health BAF for that chemical. (3) BAFs for wildlife criteria. (a) Measured BAFs and BCFs used to determine wildlife BAFs for inorganic chemicals shall be based on whole-body freshwater fish and invertebrate data unless it is demonstrated that edible-tissue BAFs or BCFs are similar to whole-body BAFs or BCFs. (b) If one or more field-measured baseline BAFs for an inorganic chemical are available from studies conducted in the Great Lakes system with whole body fish or invertebrates, then for each trophic level: (i) A species mean measured baseline BAF shall be calculated as the geometric mean if more than one measured BAF is available for a given species. (ii) The geometric mean of the species mean measured baseline BAFs shall be used as the wildlife BAF for that chemical. (c) If an acceptable field-measured baseline BAF is not available for an inorganic chemical and one or more acceptable whole-body laboratory-measured BCFs are available for the chemical, a predicted baseline BAF shall be calculated by multiplying the geometric mean of the BCFs times an FCM. The FCM shall be 1.0 unless chemical-specific biomagnification data support using a multiplier other than 1.0. The predicted baseline BAF shall be used as the wildlife BAF for that chemical. (G) Final review. For both organic and inorganic chemicals, human health and wildlife BAFs for both trophic levels are reviewed by Ohio EPA for consistency with all available data concerning the bioaccumulation, bioconcentration, and metabolism of the chemical. BAFs derived in accordance with this methodology shall be modified if changes are justified by available data. Table 41-1. Priorities for Kow experimental and computational techniques for organic chemicals. | Priority | Priority | Technique | | Log KOW < or = 4.0 | Log KOW > 4.0 | | | 1 | 1 | Slow-stir | | 1 | 1 | Generator-column | | 1 | 4 | Shake-flask | | 2 | 2 | Reverse-phase liquid chromatography on C18 chromatography packing with extrapolation to zero per cent solvent | | 3 | 3 | Reverse-phase liquid chromatography on C18 chromatography packing without extrapolation to zero per cent solvent | | 4 | 5 | Calculated by the CLOGP program (a computer program available from Pomona college) |
Table 41-2. Food-chain multipliers for trophic levels 2, 3 and 4. | Log Kow | Trophic level 2 | Trophic1 level 3 | Trophic level 4 | | 2.0 | 1.000 | 1.005 | 1.000 | | 2.5 | 1.000 | 1.010 | 1.002 | | 3.0 | 1.000 | 1.028 | 1.007 | | 3.1 | 1.000 | 1.034 | 1.007 | | 3.2 | 1.000 | 1.042 | 1.009 | | 3.3 | 1.000 | 1.053 | 1.012 | | 3.4 | 1.000 | 1.067 | 1.014 | | 3.5 | 1.000 | 1.083 | 1.019 | | 3.6 | 1.000 | 1.103 | 1.023 | | 3.7 | 1.000 | 1.128 | 1.033 | | 3.8 | 1.000 | 1.161 | 1.042 | | 3.9 | 1.000 | 1.202 | 1.054 | | 4.0 | 1.000 | 1.253 | 1.072 | | 4.1 | 1.000 | 1.315 | 1.096 | | 4.2 | 1.000 | 1.380 | 1.130 | | 4.3 | 1.000 | 1.491 | 1.178 | | 4.4 | 1.000 | 1.614 | 1.242 | | 4.5 | 1.000 | 1.766 | 1.334 | | 4.6 | 1.000 | 1.950 | 1.459 | | 4.7 | 1.000 | 2.175 | 1.633 | | 4.8 | 1.000 | 2.452 | 1.871 | | 4.9 | 1.000 | 2.780 | 2.193 | | 5.0 | 1.000 | 3.181 | 2.612 | | 5.1 | 1.000 | 3.643 | 3.162 | | 5.2 | 1.000 | 4.188 | 3.873 | | 5.3 | 1.000 | 4.803 | 4.742 | | 5.4 | 1.000 | 5.502 | 5.821 | | 5.5 | 1.000 | 6.266 | 7.079 | | 5.6 | 1.000 | 7.096 | 8.551 | | 5.7 | 1.000 | 7.962 | 10.209 | | 5.8 | 1.000 | 8.841 | 12.050 | | 5.9 | 1.000 | 9.716 | 13.964 | | 6.0 | 1.000 | 10.556 | 15.996 | | 6.1 | 1.000 | 11.337 | 17.783 | | 6.2 | 1.000 | 12.064 | 19.907 | | 6.3 | 1.000 | 12.691 | 21.677 | | 6.4 | 1.000 | 13.228 | 23.281 | | 6.5 | 1.000 | 13.662 | 24.604 | | 6.6 | 1.000 | 13.980 | 25.645 | | 6.7 | 1.000 | 14.223 | 26.363 | | 6.8 | 1.000 | 14.355 | 26.669 | | 6.9 | 1.000 | 14.388 | 26.669 | | 7.0 | 1.000 | 14.305 | 26.242 | | 7.1 | 1.000 | 14.142 | 25.468 | | 7.2 | 1.000 | 13.852 | 24.322 | | 7.3 | 1.000 | 13.474 | 22.856 | | 7.4 | 1.000 | 12.987 | 21.038 | | 7.5 | 1.000 | 12.517 | 18.967 | | 7.6 | 1.000 | 11.708 | 16.749 | | 7.7 | 1.000 | 10.914 | 14.388 | | 7.8 | 1.000 | 10.069 | 12.050 | | 7.9 | 1.000 | 9.162 | 9.840 | | 8.0 | 1.000 | 8.222 | 7.798 | | 8.1 | 1.000 | 7.278 | 6.012 | | 8.2 | 1.000 | 6.361 | 4.519 | | 8.3 | 1.000 | 5.489 | 3.311 | | 8.4 | 1.000 | 4.683 | 2.371 | | 8.5 | 1.000 | 3.949 | 1.663 | | 8.6 | 1.000 | 3.296 | 1.146 | | 8.7 | 1.000 | 2.732 | 0.778 | | 8.8 | 1.000 | 2.246 | 0.521 | | 8.9 | 1.000 | 1.837 | 0.345 | | 9.0 | 1.000 | 1.493 | 0.226 |
1The FCMs for trophic level 3 are the geometric mean of the FCMs for sculpin and alewife.
Last updated June 25, 2025 at 6:16 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-42 | Methodologies for development of human health criteria and values for the lake Erie drainage basin.
Effective:
March 20, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government
publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations,
federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see
rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] This rule applies to water bodies located in the
lake Erie drainage basin. All pollutants or combinations of pollutants, for
which human health criteria have not been adopted in rule 3745-1-33 or
3745-1-34 of the Administrative Code, shall not exceed the water quality
criteria or values derived using the procedures contained in this rule. (A) General provisions. (1) The purpose of this
rule is to describe procedures for calculating human health criteria and values
that provide protection of humans from unacceptable exposure to toxicants
through consumption of contaminated fish and drinking water and from ingesting
water as a result of participation in water-oriented recreational
activities. (2) Level of protection.
The criteria and values developed shall provide a level of protection likely to
be without appreciable risk of carcinogenic or noncarcinogenic
effects as follows: (a) Ambient criteria and values for single
carcinogens are not set at a level
representing a lifetime upper-bound incremental risk greater than one in one
hundred thousand of developing cancer using the hazard assessment techniques
and exposure assumptions described in this rule. (b) Criteria and values affording protection
from noncarcinogenic effects are established at levels that, taking into
account uncertainties, are considered likely to be without an appreciable risk
of adverse human health effects (i.e., acute, subchronic and chronic toxicity
including reproductive and developmental effects) during a lifetime of
exposure, using the risk assessment techniques and exposure assumptions
described in this rule. (3) Two-tiered
classification. Chemical concentration levels in surface water protective of
human health shall be derived based on either a tier I or tier II
classification. The two tiers are primarily distinguished by the amount of
toxicity data available for deriving the concentration levels and the quantity
and quality of data on bioaccumulation. (B) Minimum data requirements. The best
available toxicity data on the adverse health effects of a chemical and the
best data on bioaccumulation factors shall be used when developing human health
tier I criteria or tier II values as follows: The best available toxicity data includes data from
well-conducted epidemiologic or animal studies which provide, in the case of
carcinogens, an adequate weight of evidence of potential human carcinogenicity
and, in the case of noncarcinogens, a dose-response relationship involving
critical effects biologically relevant to humans. Such data is obtained from the U.S. EPA integrated risk
information system (IRIS) database, scientific literature, and other
informational databases, studies and reports containing adverse health effects
data of adequate quality for use in this rule, when available. Strong
consideration shall be given to the most currently available guidance provided
by IRIS in deriving criteria or values, supplemented with any recent data not
incorporated into IRIS. The best available bioaccumulation data includes data
from field studies and well-conducted laboratory studies. (1) Carcinogens. (a) Tier I human cancer criteria (HCC) and tier II human cancer
values (HCV) shall be derived using the methodologies described in paragraph
(C)(1) of this rule when there is adequate evidence of potential human
carcinogenic effects for a chemical. The U.S. EPA classification system for
chemical carcinogens, which is described in "Guidelines for Carcinogen
Risk Assessment, Risk Assessment Forum, U.S. Environmental Protection
Agency" shall be used in determining whether adequate evidence of
potential carcinogenic effects exists. Carcinogens are classified, depending on
the weight of evidence, as carcinogenic to humans, likely to be carcinogenic to
humans, or having suggestive evidence of carcinogenic potential. The human
evidence is considered inadequate and
therefore the chemical cannot be classified as a human carcinogen, if any of
the following conditions exists: (i) There is little or no
pertinent information. (ii) Some studies provide
evidence of carcinogenicity but other studies of equal quality with animals of
the same sex and strain are negative. (iii) There are negative
results that are not sufficiently robust for the descriptor "not likely to
be carcinogenic to humans." (iv) There is animal
evidence that demonstrates lack of carcinogenic effect in both sexes in
well-designed and well-conducted studies in at least two appropriate animal
species (in the absence of other animal or human data suggesting a potential
for cancer effects). (v) There is convincing
and extensive experimental evidence showing that the only carcinogenic effects
observed in animals are not relevant to humans. (vi) There is convincing
evidence that carcinogenic effects are not likely by a particular exposure
route. (vii) There is convincing
evidence that carcinogenic effects are not likely below a defined dose
range. (b) Chemicals are described as "carcinogenic to humans"
when either: there is convincing epidemiological evidence of a causal
association between human exposure and cancer; or when all of the following
conditions are met: (i) There is strong
evidence of an association between human exposure and either cancer or the key
precursor events of a chemical's mode of action but not enough for a
causal association. (ii) There is extensive
evidence of carcinogenicity in animals. (iii) The mode or modes
of carcinogenic action and associated precursor events have been identified in
animals. (iv) There is strong
evidence that the key precursor events that precede the cancer response in
animals are anticipated to occur in humans and progress to tumors, based on
biological information. (c) Chemicals described as "likely to be carcinogenic to
humans" include chemicals for which the weight of evidence is adequate to
demonstrate carcinogenic potential to humans but does not reach the weight of
evidence for the descriptor "carcinogenic to humans." Chemicals with
weight of evidence demonstrating carcinogenic potential to humans can include,
but are not limited to the following: (i) Chemicals for which a
plausible association is demonstrated between human exposure and cancer, in
most cases with some supporting biological, experimental evidence, though not
necessarily carcinogenicity data from animal experiments. (ii) Chemicals that
tested positive for carcinogenicity in animal experiments in more than one
species, sex, strain, site, or exposure route, with or without evidence of
carcinogenicity in humans. (iii) Chemicals for which
positive tumor study results are demonstrated that raise additional biological
concerns beyond that of a statistically significant result, for example, a high
degree of malignancy or an early age of onset. (iv) Chemicals for which
a rare animal tumor response in a single experiment is demonstrated that is
assumed to be relevant to humans. (v) Chemicals for which
positive tumor study results are demonstrated that are strengthened by other
lines of evidence, for example, either plausible association between human
exposure and cancer or evidence that the chemical or an important metabolite
causes events generally known to be associated with tumor formation likely to
be related to tumor response in this case. (d) "Suggestive evidence of carcinogenic potential" is
evidence used to describe chemicals where the weight of evidence is suggestive
of carcinogenicity; a concern for potential carcinogenic effects in humans is
raised, but the data are judged not sufficient for a stronger conclusion.
Chemicals with weight of evidence suggestive of carcinogenicity can include,
but are not limited to the following: (i) Chemicals with
studies that show a small, and possibly not statistically significant, increase
in tumor incidence observed in a single animal or human study that does not
reach the weight of evidence for the descriptor "likely to be carcinogenic
to humans." (ii) Chemicals with
studies that show a small increase in a tumor with a high background rate in
that sex and strain, when there is some but insufficient evidence that the
observed tumors may be due to intrinsic factors that cause background tumors
and not to the chemical being assessed. (iii) Chemicals with
evidence of a positive response in a study whose power, design, or conduct
limits the ability to draw a confident conclusion, but where the carcinogenic
potential is strengthened by other lines of evidence. (iv) Chemicals with
studies that show a statistically significant increase at one dose only, but no
significant response at the other doses and no overall trend. (e) Development of Tier I criteria.
Chemicals with the necessary weight of evidence of
potential human carcinogenic effects sufficient to derive a HCC generally include chemicals that are carcinogenic to humans and likely to
be carcinogenic to humans. Such chemicals
can also include, on a case-by-case basis as determined by the
director, chemicals with suggestive evidence of carcinogenic potential if
studies have been well-conducted when compared to studies used in classifying
chemicals that are carcinogenic to humans or likely to be carcinogenic to
humans. The decision to use data from a chemical
that has suggestive evidence of carcinogenic
potential for deriving tier I criteria is
a case-by-case determination. In
determining whether to derive a HCC, additional evidence that shall be
considered includes but is not limited to available information on mode of
action, such as mutagenicity/genotoxicity (determinations of whether the
chemical interacts directly with DNA), structure activity, and
metabolism. (f) Development of Tier II value.
Chemicals with the necessary weight of evidence of
effects suggestive of carcinogenic
potential sufficient to derive a HCV shall include those chemicals with
suggestive evidence of carcinogenic potential for which there are, at a
minimum, data sufficient for quantitative risk assessment, but for which data
are inadequate for tier I criterion development due to a tumor response of
marginal statistical significance or inability to derive a strong dose-response
relationship. In determining whether to derive tier II human cancer values,
additional evidence that shall be considered includes but is not limited to
available information on mode of action such as mutagenicity/genotoxicity
(determinations of whether the chemical interacts directly with DNA), structure
activity and metabolism. The decision to use data on chemicals with suggestive
evidence of carcinogenic potential to derive tier II values is made on a case-by-case basis by the
director. (2) Noncarcinogens. (a) All available toxicity data shall be evaluated considering
the full range of possible health effects of a chemical, i.e., acute/subacute,
chronic/subchronic and reproductive/developmental effects, in order to best
describe the dose-response relationship of the chemical, and to calculate human
noncancer criteria (HNC) and human noncancer values (HNV) which will protect
against the most sensitive endpoint of toxicity. Paragraphs (B)(2)(b) and
(B)(2)(c) of this rule provide the minimum data sets necessary to calculate HNC
and HNV, respectively. (b) Tier I. The minimum data set sufficient to derive an HNC
shall include at least one well-conducted epidemiologic study or animal
study which meets the following requirements:
(i) A
well-conducted epidemiologic study for an HNC quantifies exposure level and demonstrates positive association between exposure to a
chemical and adverse effect in humans. (ii) A well-conducted study in
animals demonstrates a dose response relationship involving one or more
critical effect biologically relevant to humans. The duration of a study should
span multiple generations of exposed test species or at least a major portion
of the lifespan of one generation. By the use of uncertainty adjustments,
shorter term studies (such as ninety-day subchronic studies) with evaluation of
more limited effect may be used to extrapolate to longer exposures or to
account for a variety of adverse effects. For an HNC developed pursuant to this
rule, such a limited study must be conducted for at least ninety days in
rodents or ten per cent of the lifespan of other appropriate test species and
demonstrate a no observable adverse effect level (NOAEL). Chronic studies of
one year or longer in rodents or fifty per cent of the lifespan or greater in
other appropriate test species that demonstrate a lowest observable adverse
effect level (LOAEL) may be sufficient for use in tier I criterion derivation
if the effects observed at the LOAEL were relatively mild and reversible as
compared to effects at higher doses. This does not preclude the use of a LOAEL
from a study (of chronic duration) with only one or two doses if the effects
observed appear minimal when compared to effect levels observed at higher doses
in other studies. (c) Tier II. When the minimum data for deriving tier I criteria
are not available to meet the tier I data requirements, a more limited database
may be considered for deriving tier II values as
follows: (i) As
with tier I criteria, all available data shall be considered and shall address
a range of adverse health effects with exposure over a substantial portion of
the lifespan (or multiple generations) of the test species. (ii) With the use of
appropriate uncertainty factors to account for a less extensive database, the
minimum data sufficient to derive a tier II value shall include a NOAEL from at
least one well-conducted short-term repeated dose study. This study is of at
least twenty-eight days duration, in animals demonstrating a dose-response, and
involving effects biologically relevant to humans. (iii) Data from studies of
longer duration (greater than twenty-eight days) and LOAELS from such studies
(greater than twenty-eight days) may be more appropriate in some cases for
derivation of tier II values. Use of a LOAEL is based on consideration of the
following information: severity of effect, quality of the study and duration of
the study. (3) Bioaccumulation
factors (BAFs). (a) Tier I for carcinogens and noncarcinogens. To be considered a
tier I cancer or noncancer human health criterion, along with satisfying the
minimum toxicity data requirements of paragraphs (B)(1) and (B)(2) of this
rule, a chemical shall have the following minimum bioaccumulation data. For all
organic chemicals either: A field-measured BAF; a BAF derived using the
biota-sediment accumulation factor (BSAF) methodology; or
a BAF less than one hundred twenty-five regardless of how the BAF was derived.
For all inorganic chemicals, including organometals such as mercury, either: a
field-measured BAF; or a laboratory-measured BCF. (b) Tier II for carcinogens and noncarcinogens: a chemical is
considered a tier II cancer or noncancer human health value if it does not meet
either the minimum toxicity data requirements of paragraph (B)(1) or (B)(2) of
this rule or the minimum bioaccumulation data requirements of paragraph
(B)(3)(a) of this rule. (C) Principles for development of tier I
criteria or tier II values. The fundamental components of the procedure to
calculate tier I criteria or tier II values are the same. However, certain
aspects of the procedure designed to account for short-duration studies or
other limitations in data are more likely to be relevant in deriving tier II
values than tier I criteria. (1) Carcinogens. (a) A non-threshold mechanism of carcinogenesis shall be assumed
unless biological data adequately demonstrate the existence of a threshold on a
chemical-specific basis. (b) All appropriate human epidemiologic data and animal cancer
bioassay data shall be considered as follows: (i) Data specific to an environmentally
appropriate route of exposure are used. Oral exposure should be used
preferentially over dermal and inhalation since, in most cases, the exposure
routes of greatest concern are fish consumption and drinking water/incidental
ingestion. (ii) The risk associated dose
is set at a level corresponding to an incremental cancer risk of one in one
hundred thousand. (a) If acceptable human
epidemiologic data are available for a chemical, they are used to derive the
risk associated dose. (b) If acceptable human
epidemiologic data are not available, the risk associated dose is derived from
available animal bioassay data. Data from a species that is considered most
biologically relevant to humans is preferred where all other considerations
regarding quality of data are equal. In the absence of data to distinguish the
most relevant species, data from the most sensitive species tested, i.e., the
species showing a carcinogenic effect at the lowest administered dose, are
used. (c) When animal bioassay data are used and a non-threshold
mechanism of carcinogenicity is assumed, the data shall be fitted to a
linearized multistage model. The upper-bound ninety-five per cent confidence
limit on risk (or, the lower ninety-five per cent confidence limit on dose) at
the one in one hundred thousand risk level shall be used to calculate a risk
associated dose (RAD). Other models, including modifications or variations of
the linear multistage model, which are more appropriate to the available data
may be used where scientifically justified. (d) If the duration of the study is significantly less than the
natural lifespan of the test animal, the slope may be adjusted on a
case-by-case basis to compensate for latent tumors which were not expressed. In
the absence of alternative approaches which compensate for study durations
significantly less than lifetime, the process described in "Methodology
for Deriving Ambient Water Quality Criteria for the Protection of Human Health,
Office of Science and Technology, Office of Water, U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency" shall be used. (e) A species scaling factor shall be used to account for
differences between test species and humans. It shall be assumed that
milligrams per surface area per day is an equivalent dose between species. All
doses presented in mg/kg body weight shall be converted to an equivalent
surface area dose by raising the mg/kg dose to the two-thirds power. However,
if adequate pharmacokinetic and metabolic studies are available, these data may
be factored into the adjustment for species differences. (f) Additional data selection and adjustment decisions shall also be made in the process of quantifying
risk as follows: (i) Consideration is given to tumor selection
for modeling. (ii) All doses are adjusted to
give an average daily dose over the study duration. (iii) Adjustments in the rate
of tumor response are made for early mortality in test species. (iv) The goodness-of-fit of the
model to the data is also be assessed. (g) When a linear, non-threshold dose response relationship is
assumed, the RAD shall be calculated using the following equation: RAD = (0.00001/ql*) Where: RAD = risk associated dose in milligrams of
toxicant per kilogram body weight per day (mg/kg/day). 0.00001 (1 x 10-5) = incremental risk of developing cancer
equal to one in one hundred thousand. q1*
= slope factor (mg/kg/day)-1. (h) If human epidemiologic data or other animal biological data
indicate that a chemical causes cancer through a threshold mechanism, the risk
associated dose may be calculated using a method which assumes that a threshold
mechanism is operative. (2) Noncarcinogens. (a) Noncarcinogens shall generally be assumed to have a threshold
dose or concentration below which no adverse effects should be observed.
Therefore, the tier I criterion or tier II value is the maximum water concentration of a substance at or below
which a lifetime exposure from drinking the water, consuming fish caught in the
water, and ingesting water as a result of participating in water-related
recreation activities is likely to be without appreciable risk of deleterious
effects. For some noncarcinogens, there may not be a threshold dose below which
no adverse effects are observed. Chemicals acting as genotoxic teratogens and
germline mutagens are thought to possibly produce reproductive or developmental
effects via a genetically linked mechanism which may have no threshold. Other
chemicals also may not demonstrate a threshold. Criteria and values for these
types of chemicals are established on
a case-by-case basis using appropriate assumptions reflecting the likelihood
that no threshold exists. (b) All appropriate human and animal toxicologic data shall be
reviewed and evaluated. To the maximum extent possible, data most specific to
the environmentally relevant route of exposure shall be used. Oral exposure
data should be used preferentially over dermal and inhalation since, in most
cases, the exposure routes of greatest concern are fish consumption and
drinking water/incidental ingestion. When acceptable human data are not
available (e.g., well-conducted epidemiologic studies), animal data from
species most biologically relevant to humans shall be used. In the absence of
data to distinguish the most relevant species, data from the most sensitive
animal species tested, i.e., the species showing a toxic effect at the lowest
administered dose (given a relevant route of exposure), shall be
used. (c) Minimum data requirements are specified in paragraph (B)(2)
of this rule. The experimental exposure level representing the highest level
tested at which no adverse effects were demonstrated (NOAEL) from studies
satisfying the provisions of paragraph (B)(2) of this rule shall be used for
criteria calculations. In the absence of a NOAEL, the LOAEL from studies
satisfying the provisions of paragraph (B)(2) of this rule may be used if it is
based on mild and reversible effects. (d) Uncertainty factors shall be used to account for the
uncertainties in predicting acceptable dose levels for the general human
population based upon experimental animal data or limited human
dataas follows: (i) An uncertainty factor
of ten is used when extrapolating
from valid experimental results from studies on prolonged exposure to average
healthy humans. This ten-fold factor is used to protect sensitive members of
the human population. (ii) An uncertainty
factor of one hundred is used when
extrapolating from valid results of long-term studies on experimental animals
when results of studies of human exposure are not available or are inadequate.
In comparison to paragraph (C)(2)(d)(i) of this rule, this represents an
additional ten-fold uncertainty factor in extrapolating data from the average
animal to the average human. (iii) An uncertainty
factor of up to one thousand is used
when extrapolating from animal studies for which the exposure duration is less
than chronic, but greater than ninety days length, or when other significant
deficiencies in study quality are present, and when useful long-term human data
are not available. (iv) An uncertainty
factor of up to three thousand is
used when extrapolating from animal studies for which the exposure
duration is less than twenty-eight days. (v) An additional
uncertainty factor of between one and ten may be used when deriving a criterion
from a LOAEL. The level of additional uncertainty applied depends upon the severity and the incidence
of the observed adverse effect. (vi) An additional
uncertainty factor of between one and ten may be applied when there are limited
effects data or incomplete sub-acute or chronic toxicity data (e.g.,
reproductive/developmental data). The level of quality and quantity of the
experimental data available as well as structure-activity relationships
are used to determine the factor
selected. (vii) When deriving an
uncertainty factor in developing a tier I criterion or tier II value, the total
uncertainty, as calculated following the guidance of paragraphs (C)(2)(d)(i) to
(C)(2)(d)(vi) of this rule, does not exceed ten
thousand for tier I criteria and thirty thousand for tier II
values. (e) All study results shall be converted, as necessary, to the
standard unit for acceptable daily exposure of milligrams of toxicant per
kilogram of body weight per day (mg/kg/day). Doses shall be adjusted for
continuous exposure. (3) Criteria and value
derivation. (a) Carcinogens. The tier I HCC and tier II HCV shall be
calculated using the following equation: 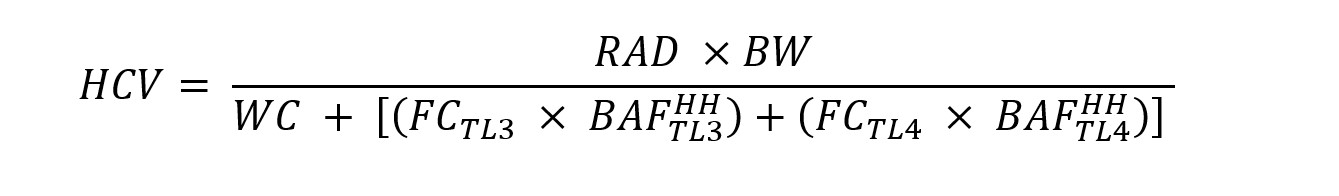 Where: HCV = human cancer value in milligrams per
liter (mg/l). RAD = risk associated dose in milligrams
toxicant per kilogram body weight per day (mg/kg/day) that is associated with a
lifetime incremental cancer risk equal to one in one hundred thousand. BW = weight of an average human (seventy
kilograms). WC = per capita water consumption (two
liters/day for surface waters designated as public water supplies and 0.01
liters/day for surface waters not designated as public water supplies). FCTL3 = mean consumption of trophic level three of
regionally caught freshwater fish (0.0036 kilogram/day). FCTL4 = mean consumption of trophic level four of
regionally caught freshwater fish (0.0114 kilogram/day). BAFHHTL3
= bioaccumulation factor for trophic level three fish, as derived using the BAF
methodology contained in rule 3745-1-41 of the Administrative Code. BAFHHTL4
= bioaccumulation factor for trophic level four fish, as derived using the BAF
methodology contained in rule 3745-1-41 of the Administrative Code. (b) Noncarcinogens. The tier I HNC or tier II HNV shall be
calculated using the following equation: 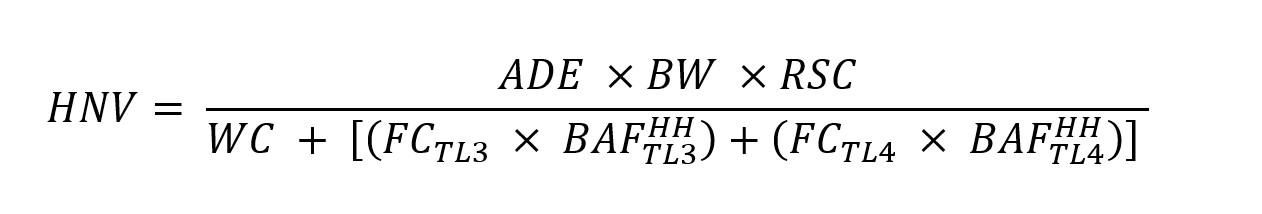 Where: HNV = human noncancer value in milligrams per
liter (mg/l). ADE = acceptable daily exposure in milligrams
toxicant per kilogram body weight per day (mg/kg/day). RSC = relative source contribution factor of
0.8. An RSC derived from actual exposure data may be developed using the
methodology outlined in "Methodology for Deriving Ambient Water Quality
Criteria for the Protection of Human Health, Office of Science and Technology,
Office of Water, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency." BW = weight of an average human (seventy
kilograms). WC = per capita water consumption (two
liters/day for surface waters designated as public water supplies and 0.01
liters/day for surface waters not designated as public water supplies). FCTL3= mean consumption of trophic level three fish
by regional sport fishers of regionally caught freshwater fish (0.0036
kilogram/day). FCTL4= mean consumption of trophic level four fish
by regional sport fishers of regionally caught freshwater fish (0.0114
kg/day). BAFHHTL3
= human health bioaccumulation factor for edible portion of trophic level three
fish, as derived using the BAF methodology contained in rule 3745-1-41 of the
Administrative Code. BAFHHTL4
= human health bioaccumulation factor for edible portion of trophic level four
fish, as derived using the BAF methodology contained in rule 3745-1-41 of the
Administrative Code. (D) Application of criteria and values.
The HCC, HCV, HNC and HNV shall be applied as thirty-day average concentrations
outside the mixing zone.
Last updated March 25, 2024 at 10:07 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-43 | Methodology for the development of wildlife criteria for the lake Erie drainage basin.
Effective:
March 20, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] This rule applies to water bodies located in the lake Erie drainage basin. This rule establishes the methodology required when developing tier I wildlife criteria for bioaccumulative chemicals of concern (BCCs). (A) General provisions. (1) A tier I wildlife criterion is the concentration of a substance which is likely to, if not exceeded, protect avian and mammalian wildlife populations inhabiting the lake Erie drainage basin from adverse effects resulting from the ingestion of water and aquatic prey taken from surface waters of the lake Erie drainage basin. These criteria are based on existing toxicological studies of the substance of concern and quantitative information about the exposure of wildlife species to the substance through food and water consumption. Separate avian and mammalian values are developed using taxonomic class-specific toxicity data and exposure data for five representative wildlife species. The wildlife species selected are representative of avian and mammalian species resident in the Great Lakes basin which are likely to experience the highest exposures to bioaccumulative contaminants through the aquatic food web; they are the bald eagle, herring gull, belted kingfisher, mink, and river otter. (2) Rule 3745-1-39 of the Administrative Code describes the procedures for calculating site-specific wildlife criteria. (3) The term "wildlife value" (WV) is used to denote the value for each representative species which results from using the equation in this rule, the value obtained from averaging species values within a class, or any value derived from application of the site-specific procedure provided in rule 3745-1-39 of the Administrative Code. The WVs calculated for the representative species are used to calculate taxonomic class-specific WVs. The WV is the concentration of a substance which, if not exceeded, should better protect the taxon in question. (4) "Tier I wildlife criterion," or "tier I criterion" is used to denote the number derived from data meeting the tier I minimum database requirements, and which will be protective of the two classes of wildlife. (B) Calculation of wildlife values for tier I criteria. (1) Equation for avian and mammalian wildlife values. Tier I wildlife values (WV) for BCCs shall be calculated as follows: 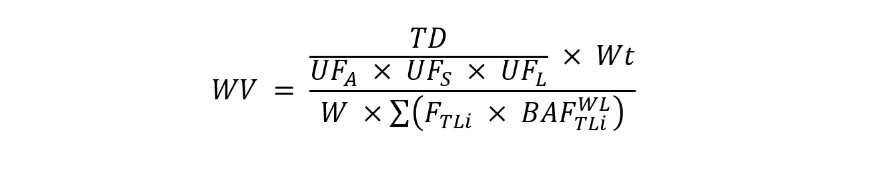 Where: WV = wildlife value in milligrams of substance per liter (mg/l). TD = test dose in milligrams of substance per kilograms per day (mg/kg-d) for the test species. This is either a NOAEL or a LOAEL. UFA = uncertainty factor for extrapolating toxicity data across species (unitless). A species-specific UF is selected and applied to each representative species, consistent with the equation. UFs = UF for extrapolating from subchronic to chronic exposures (unitless). UFL = UF for LOAEL to NOAEL extrapolations (unitless). Wt = average weight in kilograms (kg) for the representative species. W = average daily volume of water consumed in liters per day (l/d) by the representative species. FTLi = average daily amount of food consumed from trophic level I in kilograms per day (kg/d) by the representative species. BAFWLTLi = bioaccumulation factor for wildlife food in trophic level I in liters per kilogram (l/kg), developed using the BAF methodology contained in rule 3745-1-41 of the Administrative Code. For consumption of piscivorous birds by other birds (e.g., herring gull by eagles), the BAF shall be derived by multiplying the trophic level three BAF for fish by a biomagnification factor to account for the biomagnification from fish to the consumed birds. (2) Identification of representative species for protection. For bioaccumulative chemicals, piscivorous species are identified as the focus of concern for wildlife criteria development in the Great Lakes. Three avian species (eagle, kingfisher and herring gull) and two mammalian species (mink and otter) serve as representative species for protection. The TD obtained from toxicity data for each taxonomic class shall be used to calculate WVs for each of the five representative species. (3) Calculation of avian and mammalian wildlife values and tier I criterion derivation. The avian WV is the geometric mean of the WVs calculated for the three representative avian species. The mammalian WV is the geometric mean of the WVs calculated for the two representative mammalian species. The lower of the mammalian and avian WVs shall be selected as the tier I criterion. (C) Parameters of the effect component of the wildlife criteria methodology. (1) Definitions. The following definitions provide additional specificity and guidance in the evaluation of toxicity data and the application of this rule: (a) Acceptable endpoints. For the purpose of wildlife criteria derivation, acceptable subchronic and chronic endpoints are those which affect reproductive or developmental success, organismal viability or growth, or any other endpoint which is, or is directly related to, parameters that influence population dynamics. (b) Chronic effect. An adverse effect that is measured by assessing an acceptable endpoint and results from continual exposure over several generations, or at least over a significant part of the test species' projected life span or life stage. (c) Subchronic effect. An adverse effect, measured by assessing an acceptable endpoint, resulting from continual exposure for a period of time less than that deemed necessary for a chronic test. (2) Minimum toxicity database for tier I criteria development. A TD value is required for criterion calculation. To derive a tier I criterion for wildlife, the data set shall provide enough data to generate a subchronic or chronic dose-response curve for any given substance for both mammalian and avian species. In reviewing the toxicity data available which meet the minimum data requirements for each taxonomic class, the following order of preference shall be applied to select the appropriate TD to be used for calculation of individual WVs. Data from peer-reviewed field studies of wildlife species take precedence over other types of studies, where such studies are of adequate quality. An acceptable field study is of subchronic or chronic duration, provide a defensible, chemical-specific dose-response curve in which cause and effect are clearly established, and assess acceptable endpoints as defined in this document. When acceptable wildlife field studies are not available, or determined to be of inadequate quality, the needed toxicity information may come from peer-reviewed laboratory studies. When laboratory studies are used, preference shall be given to laboratory studies with wildlife species over traditional laboratory animals to reduce uncertainties in making interspecies extrapolations. All available laboratory data and field studies shall be reviewed to corroborate the final tier I criterion, to assess the reasonableness of the toxicity value used, and to assess the appropriateness of any UFs which are applied. When evaluating the studies from which a test dose is derived in general, the following requirements shall be met: (a) The mammalian data come from at least one well-conducted study of ninety days or greater designed to observe subchronic or chronic effects as defined in this document. (b) The avian data come from at least one well-conducted study of seventy days or greater designed to observe subchronic or chronic effects as defined in this rule. (c) In reviewing the studies from which a TD is derived for use in calculating a WV, studies involving exposure routes other than oral may be considered only when an equivalent oral daily dose can be estimated and technically justified because the criteria calculations are based on an oral route of exposure. (d) In assessing the studies which meet the minimum data requirements, preference is given to studies which assess effects on developmental or reproductive endpoints. (3) Selection of TD data. In selecting data to be used in the derivation of WVs, the evaluation of acceptable endpoints, as defined in paragraph (C)(1) of this rule, shall be the primary selection criterion. All data not part of the selected subset may be used to assess the reasonableness of the toxicity value and the appropriateness of the UFs which are applied. Use of such data shall be as follows: (a) If more than one TD value is available within a taxonomic class, based on different endpoints of toxicity, that TD which is likely to reflect best potential impacts to wildlife populations through resultant changes in mortality or fecundity rates is used for the calculation of WVs. (b) If more than one TD is available within a taxonomic class, based on the same endpoint of toxicity, the TD from the most sensitive species is used. (c) If more than one TD based on the same endpoint of toxicity is available for a given species, the TD for that species is calculated using the geometric mean of those TDs. (4) In those cases in which a TD is available in units other than milligrams of substance per kilograms per day (mg/kg/d), the following procedures shall be used to convert the TD to the appropriate units prior to calculating a WV. (a) If the TD is given in milligrams of toxicant per liter of water consumed by the test animals (mg/l), the TD is multiplied by the daily average volume of water consumed by the test animals in liters per day (l/d) and divided by the average weight of the test animals in kilograms (kg). (b) If the TD is given in milligrams of toxicant per kilogram of food consumed by the test animals (mg/kg), the TD is multiplied by the average amount of food in kilograms consumed daily by the test animals (kg/d) and divided by the average weight of the test animals in kilograms (kg). (5) Drinking and feeding rates. (a) When drinking and feeding rates and body weight are needed to express the TD in milligrams of substance per kilograms per day (mg/kg/d), they shall be obtained from the study from which the TD was derived. If not already determined, body weight, and drinking and feeding rates are converted to a wet weight basis. (b) If the study does not provide the needed values, the values shall be determined from appropriate scientific literature. For studies done with domestic laboratory animals, either the "Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances" or "Recommendations for and Documentation of Biological Values for Use in Risk Assessment" should be consulted. When these references do not contain exposure information for the species used in a given study, either the allometric equations in this rule or the exposure estimation methods presented in chapter 4 of "The Wildlife Exposure Factors Handbook" should be applied to approximate the needed feeding or drinking rates. The choice of the methods described in this paragraph is at the discretion of the director. (c) For mammalian species, the general allometric equations are as follows: (i) F = 0.0687 (Wt)0.82 Where: F = feeding rate of mammalian species in kilograms per day (kg/d) dry weight. Wt = average weight in kilograms (kg) of the test animals. (ii) W = 0.099 (Wt)0.90 Where: W = drinking rate of mammalian species in liters per day (l/d). Wt = average weight in kilograms (kg) of the test animals. (d) For avian species, the general allometric equations are: (i) F = 0.0582 (Wt)0.65 Where: F = feeding rate of avian species in kilograms per day (kg/d) dry weight. Wt = average weight in kilograms (kg) of the test animals. (ii) W = 0.059 (Wt)0.67 Where: W = drinking rate of avian species in liters per day (l/d). Wt = average weight in kilograms (kg) of the test animals. (6) LOAEL to NOAEL extrapolations (UFL). In those cases in which a NOAEL is unavailable as the TD and a LOAEL is available, the LOAEL may be used to estimate the NOAEL. If used, the LOAEL shall be divided by an UF to estimate a NOAEL for use in deriving WVs. The value of the UF shall not be less than one nor exceed ten, depending on the dose-response curve and any other available data, and is represented by UFL in the equation expressed in paragraph (B)(1) of this rule. (7) Subchronic to chronic extrapolations (UFs). In instances where only subchronic data are available, the TD may be derived from subchronic data. In such cases, the TD shall be divided by an UF to extrapolate from subchronic to chronic levels. The value of the UF shall not be less than one nor exceed ten, and is represented by UFs in the equation expressed in paragraph (B)(1) of this rule. This factor shall be used when assessing highly bioaccumulative substances where toxicokinetic considerations suggest that a bioassay of limited length underestimates chronic effects. (8) Selection and use of interspecies extrapolations (UFA) shall be as follows: (a) The selection of the UFA is based on the available toxicological data and on available data concerning the physicochemical, toxicokinetic, and toxicodynamic properties of the substance in question and the amount and quality of available data. This value is a UF that is intended to account for differences in toxicological sensitivity among species. (b) For the derivation of tier I criteria, a UFAshall not be less than one nor exceed one hundred, and applies to each of the five representative species, based on existing data and the director's best professional judgement. The value of UFAmay differ for each of the representative species. (c) For tier I wildlife criteria, the UFAis used only for extrapolating toxicity data across species within a taxonomic class, except as provided in this paragraph. The tier I UFA is not intended for interclass extrapolations because of the poorly defined comparative toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic parameters between mammals and birds. However, an interclass extrapolation employing a UFA may be used for a given chemical if it can be supported by a validated biologically-based dose-response model or by an analysis of interclass toxicological data, considering acceptable endpoints, for a chemical analog that acts under the same mode of toxic action. (D) Parameters of the exposure component of the wildlife criteria methodology. (1) Drinking and feeding rates of representative species. The body weights (Wt), feeding rates (FTLi), drinking rates (W), and trophic level dietary composition (as food ingestion rate and per cent in diet) for each of the five representative species are presented in table 43-1 of this rule. (2) BAFs. The methodology for development of bioaccumulation factors is in rule 3745-1-41 of the Administrative Code. Trophic level three and four BAFs are used to derive WVs because these are the trophic levels at which the representative species feed. (E) Application of criteria. The wildlife criterion shall be applied as a thirty-day average concentration outside the mixing zone. Table 43-1. Exposure parameters for the five representative species identified for protection. 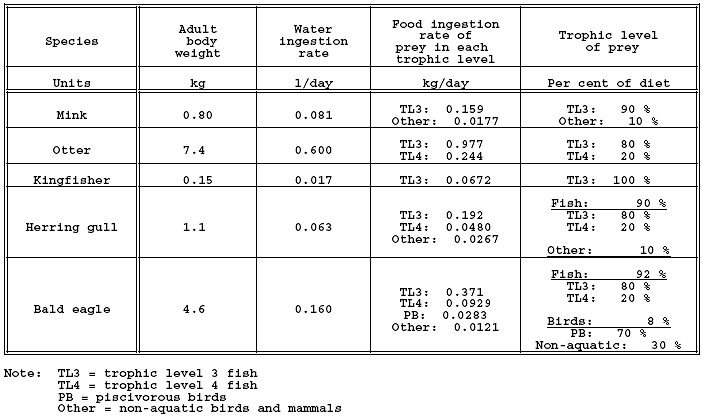
Last updated June 25, 2025 at 6:16 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-44 | Whole effluent toxicity provisions.
Effective:
March 20, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government
publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations,
federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see
rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] [Comment: See rule 3745-2-09 of the Administrative
Code for whole effluent toxicity water quality based effluent limit calculation
procedures.] (A) Protection of aquatic life - whole
effluent approach. (1) An acute toxicity
level of 0.3 acute units (TUa) applies
outside the mixing zone to limited resource water, warmwater, exceptional
warmwater, coldwater, seasonal salmonid, and modified warmwater habitat use
designations in accordance with this chapter and the following
equation: TUa =
100/LC50 Where: LC50 = the median lethal concentration as
defined in rule 3745-2-02 of the Administrative Code. (2) A chronic toxicity level of 1.0
chronic toxic units (TUc) applies
outside the mixing zone to warmwater, exceptional warmwater, coldwater,
seasonal salmonid, and modified warmwater habitat use designations,
where: TUc =
100/IC25 for all chronic endpoints,
except that: TUc = 100/(geometric mean of NOEC and LOEC) for
survival or mortality endpoints using daphnid species when this is more
restrictive than the TUc value
resulting from the definition based on IC25. (B) The chronic toxicity level does not apply to limited
resource water use designations. (C) For undesignated waters, an acute toxicity level of 0.3
TUa and a chronic toxicity level of
1.0 TUc applies outside of the mixing
zone. (D) Acute toxicity within the mixing zone is regulated by
paragraph (B) of 3745-33-07 of the Administrative Code.
Last updated March 25, 2024 at 10:07 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-50 | Wetland definitions and availability of documents.
Effective:
October 10, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government
publications, publications of recognized organizations, federal rules and
federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see paragraph (AA) of
this rule and rule 3745-1-03 of the Administrative Code.] In addition to the definitions in rules 3745-1-02
and 3745-32-01 of the Administrative Code technical words used in rules
3745-1-50 to 3745-1-54 of the Administrative Code are defined as
follows: (A) (1) "Alternatives analysis"
means a systematic review and evaluation of practicable alternatives including
avoidance, minimization and compensatory mitigation for impacts to a
wetland. (2) "Applicant" means any
person who submits an application to obtain a section 401 water quality
certification or isolated wetland permit from the Ohio environmental protection
agency (Ohio EPA). (3) "Areal cover" means the per
cent of vegetation covering any area of wetland. Areal measurements are those
made as if the wetland were being viewed from above. (4) "Avoidance" is the first
step in the alternatives analysis and means that the applicant demonstrates
that alternatives that fulfill the basic project purpose and have less or no
impacts to the wetland are not practicable, so long as the alternative does not
have other significant adverse environmental consequences. (B) (1) "Biodiversity" means the
number of community types, different species, and genetic variants of species
found in a given area. (2) "Bog" means a
peat-accumulating wetland that has no significant inflows or outflows and
supports acidophilic mosses. Characteristic indicator species may include, but
are not limited to Calla palustris, Carex atlantica var. capillacea, Carex
echinata, Carex oligosperma, Carex trisperma, Chamaedaphne calyculata, Decodon
verticillatus, Eriphorum virginicum, Ilex mucronata, Larix laricina,
Scheuchzeria palustris, Sphagnum spp., Vaccinium macrocarpon, Vaccinium
corymbosum, Vaccinium oxycoccos, Woodwardia virginica, and Xyris
difformis. (C) (1) "Compensatory mitigation"
refers to the final step in the alternatives analysis and means reestablishment
(restoration), establishment (creation), rehabilitation (enhancement) or, in
certain circumstances preservation of wetlands for the purpose of compensating
for unavoidable adverse impacts which remain after all appropriate and
practicable avoidance and minimization have been achieved. (2) "Critical habitat" means
the following: (a) The specific areas within the geographical area
currently occupied by a species, at the time it is listed in accordance with
the Endangered Species Act on which are found those physical or biological
features essential to the conservation of the species, and that may need
special management considerations or protection. (b) Specific areas outside the geographical area occupied
by a species at the time it is listed in accordance with the Endangered Species
Act, upon a determination by the secretary of the department of the interior,
that such areas are essential for the conservation of the species. (3) "Cumulative impacts" means
the impact on the environment which results from the incremental impact of the
action when added to other past, present, and reasonable foreseeable future
actions. Cumulative impacts can result from individually minor but collectively
significant actions taking place over a period of time. Cumulative impacts are
considered on a watershed basis. (D) (1) "Direct impacts" means
effects which are caused by the action and occur at the same time and
place. (2) "Dispersal corridor" means
an area that is used by organisms to move from one place of suitable habitat to
another. (E) (1) "Endangered species" means
a native Ohio plant species listed or designated by the Ohio department of
natural resources as endangered or extirpated pursuant to section 1518.01 of
the Revised Code, and animal species listed or designated as endangered or
extirpated by the Ohio department of natural resources pursuant to section
1531.25 of the Revised Code; or any plant or animal species that is native to
Ohio or that migrates or is otherwise reasonably likely to occur within the
state which has been listed as endangered pursuant to section 4 of the
Endangered Species Act. (2) "Establishment (creation)"
means the manipulation of the physical, chemical, or biological characteristics
present to establish a wetland where one did not formerly exist at an upland
site. (F) (1) "Fen" means a carbon
accumulating (peat, muck) wetland that is saturated, primarily by a discharge
of free flowing ground water during most of the year. Fens are rarely
inundated. Fens often have a sloped surface which prevents the accumulation of
stagnant or ponded water. The water of fens is usually mineral rich and has a
circumneutral pH (5.5-9.0). In calcareous fens, soil may be dominated by
deposits of calcium carbonate rich sediments (marl). Characteristic indicator
species may include, but are not limited to Cacalia plantaginea, Carex flava,
Carex sterilis, Carex stricta, Dasiphora fruticosa, Deschampsia caespitosa,
Eleocharis rostellata, Eriophorum viridicarinatum, Gentianopsis spp., Lobelia
kalmii, Oligoneuron ohioense, Parnassia glauca, Rhamnus alnifolia, Rhynchospora
capillacea, Salix candida, Salix myricoides, Salix serissima, Tofieldia
glutinosa, Triglochin maritimum, Triglochin palustre, and Zygadenus elegans
var. glaucus. (2) "Forested wetland" means a
wetland class characterized by woody vegetation that is twenty feet tall or
taller. (3) "Floodplain" means the
relatively level land next to a stream or river channel that is periodically
submerged by flood waters. It is composed of alluvium deposited by the present
stream or river when it floods. (4) "Function" means the
physical, chemical, and biological processes occurring in a wetland that
contribute to a larger ecological condition such as water quality improvement,
flood control or biodiversity maintenance. (G) (1) "Ground water discharge"
means water flowing out of a ground water zone. In regard to wetlands, ground
water discharge occurs when water flows from a ground water zone to a
wetland. (2) "Ground water recharge"
means water flow into a ground water zone. In regards to wetlands, ground water
recharge occurs when water flows from a wetland to a ground water
zone. (H) "Hydrologically isolated wetlands" means
those wetlands which: (1) Have no surface water
connection to a surface water of the state. (2) Are outside of, and
not contiguous to, any one hundred-year "floodplain" as that term is
defined in this rule. (3) Have no contiguous
hydric soil between the wetland and any surface water of the
state. (I) (1) "Indirect impacts" means
effects which are caused by the project and that occur farther removed in
distance from the project, but are still reasonably foreseeable. Indirect
impacts may include related effects on air and water and other natural systems,
including ecosystems, and other adverse environmental impacts that may be a
consequence of the project. (2) "In-kind" means a wetland
of a similar structural and functional type to the impacted
wetland. (3) "In-lieu fee program" means
a program that has been approved in accordance with 33 C.F.R. Part 332.8,
involving the reestablishment (restoration), establishment (creation),
rehabilitation (enhancement), or preservation of aquatic resources through
funds paid to a governmental or non-profit natural resources management entity
to satisfy compensatory mitigation requirements. (J) [Reserved.] (K) [Reserved.] (L) "Long term protection" means compensatory
mitigation that is protected with a legal instrument such as an environmental
covenant, conservation easement, or deed restriction. In the event a legal
instrument is not a viable option based on land ownership or lease agreements
where compensatory mitigation has occurred, the applicant should clearly
demonstrate operational control to sustain and preserve the compensatory
mitigation project after performance standards are met and monitoring
requirements have been fulfilled. (M) (1) "Minimization" refers to a
step in the alternatives analysis and means that unavoidable impacts are
reduced to the maximum extent practicable. (2) "Mitigation bank" means a
site that has been approved in accordance with 33 C.F.R. Part 332.8, where
aquatic resources have been reestablished (restored), established (created),
rehabilitated (enhanced) or preserved expressly for the purpose of providing
compensatory mitigation for authorized impacts. (3) "Mitigation ratio" means
the rate at which wetland units (e.g., acres) will be reestablished (restored),
established (created), rehabilitated (enhanced) or preserved to provide for
compensation of unavoidable wetland losses. (N) (1) "Native species" means a
species which, by scientific evidence, was present in Ohio just prior to
European exploration and settlement. (2) "Non-native species" means
a species which, by scientific evidence, was not present in Ohio just prior to
European exploration and settlement. (3) "Nuisance organisms" means
primarily vegetative organisms, that generally are non-native and have
opportunistic growth patterns that displace more diverse
assemblages. (O) "Old-growth forests" means forests
characterized by, but not limited to, the following characteristics: overstory
canopy trees of great age (exceeding at least fifty per cent of a projected
maximum attainable age for a species); little or no evidence of human-caused
understory disturbance during the past eighty to one hundred years; an all-aged
structure and multilayered canopies; aggregations of canopy trees interspersed
with canopy gaps; and significant numbers of standing dead snags and downed
logs. (P) (1) "Permittee" means any
person who has been issued a section 401 water quality certification or
isolated wetland permit by the Ohio EPA. (2) "Practicable" means
available and capable of being done after taking into consideration cost,
existing technology and logistics in light of overall and basic project
purposes. For the purposes of this definition: (a) "Available" means an alternative which is
obtainable for the purpose of the project. (b) "Basic project purpose" means the generic
function of the project. (c) "Overall project purpose" means the basic
project purpose plus consideration of costs and technical and logistical
feasibility. (3) "Preservation" means the
removal of a threat to, or preventing the decline of ecologically important
aquatic resources through the implementation of appropriate legal mechanisms to
prevent harm to the wetland. Preservation may include protection of adjacent
upland areas as necessary to ensure protection of the wetland. (4) "Public need" means an
activity or project that provides important tangible and intangible gains to
society, that satisfies the expressed or observed needs of the public where
accrued benefits significantly outweigh reasonably foreseeable
detriments. (Q) [Reserved.] (R) (1) "Reestablishment"
(restoration) means the manipulation of the physical, chemical, or biological
characteristics of a site with the goal of returning natural or historic
functions to a former or degraded aquatic resource. (2) "Rehabilitation
(enhancement)" means the manipulation of the physical, chemical, or
biological characteristics of existing wetlands to heighten, intensify, or
improve existing or historic natural functions of a wetland. (S) (1) "Service area" means the
geographic area within which impacts can be mitigated at a specific mitigation
bank or an in-lieu fee program, as designated in its instrument. (2) "Services" means the
benefits that human populations receive from functions that occur in
wetlands. (3) "Substrate" means solid
material, such as soil, on or within which organisms can live. (T) "Threatened species" means: a native Ohio
plant species listed or designated by the Ohio department of natural resources
as threatened with extirpation pursuant to section 1518.01 of the Revised Code;
or an animal species listed or designated as threatened with statewide
extinction by the Ohio department of natural resources pursuant to section
1531.25 of the Revised Code; or a species that appears on the threatened
species registry, as defined in rule 3745-1-05 of the Administrative Code; or
any plant or animal species that is native to Ohio or that migrates or is
otherwise reasonably likely to occur within the state and which has been listed
as threatened pursuant to section 4 of the Endangered Species Act. (U) "Upland buffer" means land surrounding the
jurisdictional edge of a wetland that consists of upland prairie, old field,
shrub, or forest vegetation that is maintained in a natural state through
passive or active management. This does not include lawns, mowed roadsides,
fields where crops are grown or animals pastured, and other similar land
uses. (V) "Vernal pools" means shallow, temporarily
flooded, depressional forested or forest edge wetlands, that are typically dry
for most of the summer and fall. These wetlands are generally inundated in the
late winter and spring when they are subject to a burst of biological activity,
including amphibian breeding. When flooded, vernal pools are often comprised of
areas of open water that are not densely vegetated. They also tend to
accumulate organic (woody) debris. (W) "Watershed" means a common surface drainage
area corresponding to one from the list of thirty-seven adapted from the
forty-four cataloging units as depicted on the hydrologic unit map of Ohio,
U.S. geological survey, 1988, and as described in paragraph (G) of rule
3745-1-54 of the Administrative Code or as otherwise shown on appendix 1 to
rule 3745-1-54 of the Administrative Code. Watersheds are limited to those
parts of the cataloging units that geographically lie within the borders of the
state of Ohio. (X) [Reserved.] (Y) [Reserved.] (Z) [Reserved.] (AA) Incorporation by
reference. This chapter includes references to certain matter or materials. The
text of the referenced materials is not included in the rules contained in this
chapter. Information on the availability of the referenced materials as well as
the date of, or the particular edition or version of the material is included
in this rule. For materials subject to change, only the specific versions
specified in this rule are referenced. Material is referenced as it exists on
the effective date of this rule. Except for subsequent annual publication of
existing (unmodified) Code of Federal Regulation compilations, any amendment or
revision to a referenced document is not applicable unless and until this rule
has been amended to specify the new dates. (1) Availability. The
materials incorporated by reference are available as follows: (a) "Code of Federal Regulations" (CFR).
Information and copies may be obtained by writing to: "U.S. government
printing office, P.O. Box 979050, St. Louis, MO 63197-9000." The full text
of the CFR is also available in electronic format at www.ecfr.gov/. The CFR
compilations are also available for inspection and use at most public libraries
and "The State Library of Ohio." (b) "Endangered Species Act." Information and
copies may be obtained by writing to: "U.S. Government Printing Office,
P.O. Box 979050, St. Louis, MO 63197-9000." The full text of the act is
also available in electronic format at
https://www.fws.gov/media/endangered-species-act. A copy of the act is also
available for inspection and use at most public libraries and "The State
Library of Ohio." (c) Other publications. The availability of these
documents is provided in paragraph (AA)(2) of this rule. However, many of the
documents are also available for inspection and copying at most public
libraries and "The State Library of Ohio." (2) Incorporated
materials. (a) 33 CFR; "Navigation and Navigable Waters" as
published in the July 1, 2023 Code of Federal Regulations. (b) 40 CFR; "Protection of Environment" as
published in the July 1, 2023 Code of Federal Regulations. (c) Endangered Species Act; contained in 16 U.S.C.
1531-1544; "Endangered Species"; as published in the 2018 edition of
the United States Code. (d) "Field Manual for the Amphibian Index of Biotic
Integrity for Wetlands" (Ohio EPA, 2011) is available on Ohio EPA's
website at:
https://epa.ohio.gov/static/Portals/35/wetlands/AmphIBI_Field_Manual.pdf. This
document may also be obtained by writing to: "Ohio EPA, Division of
Surface Water, PO Box 1049, Columbus, Ohio 43216-1049." (e) "Guidelines for Wetland Mitigation Banking and
In-lieu Fee Programs in Ohio," version 2.0 (September 2020) can be found
at
https://usace.contentdm.oclc.org/utils/getfile/collection/p16021coll11/id/6537.
This document may also be obtained by writing to: "Huntington District,
U.S. Army Corps of Engineer, 502 Eighth Street Huntington, West Virginia
25701-2070." (f) "Ohio Rapid Assessment Method" (ORAM) version
5.0 (Ohio EPA, February 1, 2001) is available on Ohio EPA's website at:
https://epa.ohio.gov/divisions-and-offices/surface-water/reports-data/wetland-ecology.
This document may also be obtained by writing to: "Ohio EPA, Division of
Surface Water, PO Box 1049, Columbus, Ohio 43216-1049." (g) "Vegetation Index of Biotic Integrity for
Wetlands," version 1.5 (Ohio EPA, 2015) is available on Ohio EPA's
website at:
https://epa.ohio.gov/divisions-and-offices/surface-water/reports-data/wetland-ecology.
This document may also be obtained by writing to: "Ohio EPA, Division of
Surface Water, PO Box 1049, Columbus, Ohio 43216-1049."
Last updated October 10, 2024 at 8:39 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-51 | Wetland narrative criteria.
Effective:
October 10, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government
publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations,
federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see
rules 3745-1-03 and 3745-1-50 of the Administrative Code.] [Comment: To the extent the director has specific
authority under Chapter 6111. of the Revised Code, including sections 6111.03
and 6111.041 of the Revised Code, the criteria specified in this rule are
applicable to the maintenance or rehabilitation (enhancement) of wetland
functions. Such authority includes the issuance of certifications under section
401 of the Clean Water Act, 33 U.S.C. section 1341, and Chapter 3745-32 of the
Administrative Code, the issuance of NPDES permits under section 402 of the
Clean Water Act, 33 U.S.C. section 1342, and Chapter 3745-33 of the
Administrative Code, and the issuance of permits and plan approvals under
Chapter 3745-42 of the Administrative Code and sections 6111.44 and 6111.45 of
the Revised Code.] In addition to the criteria listed in rule
3745-1-04 of the Administrative Code, to every extent practicable and possible
as determined by the director, and except as authorized in accordance with rule
3745-1-54 of the Administrative Code, the following narrative criteria apply to
wetlands. (A) The hydrology necessary to support
the biological and physical characteristics naturally present in wetlands shall
be protected to prevent significant adverse impacts on any of the
following: (1) Water currents,
erosion or sedimentation patterns. (2) Natural water
temperature variations. (3) Chemical, nutrient
and dissolved oxygen regimes of the wetland. (4) The movement of
aquatic fauna. (5) The pH of the
wetland. (6) Water levels or
elevations, including those resulting from ground water recharge and
discharge. (7) The biological
integrity of natural floral and faunal communities. (B) Water quality necessary to support existing habitats, and the
populations of wetland flora and fauna shall be protected to prevent
significant adverse impacts on any of the following: (1) Food supplies for fish and
wildlife. (2) Reproductive and nursery
areas. (3) Dispersal corridors, as that term is
defined in rule 3745-1-50 of the Administrative Code. (4) Biodiversity. (5) Maturity level of woody
vegetation. (6) Water quality shall be protected to
prevent conditions conducive to the establishment or proliferation of nuisance
organisms, as that term is defined in rule 3745-1-50 of the Administrative
Code. (C) No person shall cause or contribute
to conditions that will have a significant adverse impact on the ability of the
wetland to be used for wetland-dependent recreational opportunities in or on
the water.
Last updated October 10, 2024 at 8:39 AM
|
Rule 3745-1-52 | Numeric chemical criteria for waste water discharges to wetlands.
Effective:
October 10, 2024
For the purposes of establishing waste water
discharge permit limits for waste water discharges to wetlands pursuant to
Chapter 6111. of the Revised Code, numeric chemical criteria associated with
the "warmwater aquatic life habitat" use designation, as specified in
this chapter of the Administrative Code, apply at the outfall prior to
discharge to the wetland. The applicant may submit a request, in writing, to
the director to use alternative criteria. The director may approve the request
if the use of alternative criteria is deemed not to be injurious to the
wetland's designated use and assigned category, as specified in rule
3745-1-54 of the Administrative Code.
Last updated June 25, 2025 at 6:16 PM
|
Rule 3745-1-53 | Wetland use designation.
Promulgated Under:
Ch 119.
All surface waters of the state of Ohio which meet the definition of
a wetland in rule 3745-1-02 of the Administrative Code are assigned the wetland
designated use.
Last updated September 25, 2025 at 1:05 PM
Supplemental Information
Authorized By:
–
Amplifies:
–
Five Year Review Date:
|
Rule 3745-1-54 | Wetland antidegradation.
Effective:
October 10, 2024
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations, federal rules and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see rules 3745-1-03 and 3745-1-50 of the Administrative Code.] [Comment: For definitions of terms used in this rule, see rules 3745-1-02 and 3745-1-50 of the Administrative Code.] (A) The provisions in this rule apply in addition to the provisions in rule 3745-1-05 of the Administrative Code. (B) Wetland antidegradation requirements. (1) The wetland designated use shall be maintained and protected such that degradation of surface waters through direct, indirect, or cumulative impacts does not result in the net loss of wetland acreage or functions or services in accordance with paragraphs (D), (E), and (F) of this rule. (2) Wetland categorization and function. (a) Each wetland is assigned a category by Ohio EPA for the purposes of reviews of projects pursuant to this rule. Wetland categories assigned by Ohio EPA for regulatory purposes are valid for a period of five years following assignment by Ohio EPA unless the wetland category assignment is adopted in a permit decision. If adopted in a permit decision, wetland categories assigned by Ohio EPA will remain valid as long as the permit remains valid. (i) A category will be assigned based on the wetland's relative functions and services, sensitivity to disturbance, rarity, and potential to be adequately compensated for by wetland mitigation. (ii) In assigning a wetland category, the director will consider the results of an appropriate wetland evaluation method acceptable to the director, including but not limited to the "Ohio Rapid Assessment Method (ORAM)" version 5.0, "Vegetation Index of Biotic Integrity for Wetlands (VIBI)" version 1.5, and "Amphibian Index of Biotic Integrity for Wetlands (AmphIBI)," and other information necessary in order to fully assess the wetland's functions and services. (iii) In assessing any reestablished (restored), established (created), or rehabilitated (enhanced) wetland for any purpose, the director will consider the results of VIBI or other appropriate wetland evaluation method acceptable to the director. ORAM is not an acceptable wetland evaluation method for reestablished (restored), established (created), or rehabilitated (enhanced) wetlands. (iv) Wetland antidegradation categories, and the requirements for an antidegradation review for wetlands in each category, are outlined in paragraphs (C) and (D) of this rule. (b) The functions and services of a wetland may include, but are not limited to, the following: (i) Ground water exchange, including the discharge and recharge of ground water. (ii) Nutrient removal or transformation. (iii) Sediment or contaminant retention. (iv) Water storage. (v) Sediment stabilization. (vi) Shoreline stabilization. (vii) Maintenance of biodiversity, as that term is defined in rule 3745-1-50 of the Administrative Code. (viii) Recreation. (ix) Education and research. (x) Habitat for threatened or endangered species. (3) The director may consider the regional significance of the functions and services a wetland performs (e.g., wetlands recognized as providing important hydrological functions in watershed management plans) when determining whether degradation of the wetland can be authorized. (4) Threatened or endangered species. (a) In making determinations regarding the lowering of water quality in wetlands which contain critical habitat for threatened or endangered species, or either the permanent or seasonal presence of a threatened or endangered species, the director considers the anticipated impact of the proposed lowering of water quality on the threatened or endangered species. (b) To assist the director in making this determination, an applicant shall provide Ohio EPA written comments from both the Ohio department of natural resources and the U.S. fish and wildlife service, regarding threatened and endangered species, including the presence or absence of critical habitat, for all wetlands under review, unless another entity has been designated by the aforementioned agencies to make this determination. In that case, the designated entity shall provide the necessary written comments. (5) Indirect impacts. In making determinations regarding the lowering of water quality in a wetland, the director may take into consideration other environmental impacts that may be a consequence of approving the request. (6) Wetlands impacted without prior authorization. (a) Where a wetland has been degraded or destroyed without prior authorization, the wetland will be considered a category 3 wetland, unless the applicant demonstrates that a lower category is appropriate based on other information including, but not limited to, adjacent wetland or vegetation, aerial photographs, U.S. fish and wildlife service national wetland inventory maps, Ohio wetland inventory maps, public information, on-site inspections, previous site descriptions, and soil maps. (b) The director may consider other information in determining whether a lower category is appropriate. (c) When reviewing applications for discharges to wetlands which have occurred without prior authorization, the fact that the discharge has already occurred has no bearing on the decision of whether to allow lower water quality. Ohio EPA reviews the impacts based on pre-discharge conditions. (d) The director may require compensatory mitigation, if approved in accordance with other provisions of this rule, at the same mitigation ratios as indicated for impacts to category 3 wetlands, as shown in table E-1 of this rule. (e) Nothing in paragraph (B)(6) of this rule relieves any person from liability for degrading or destroying a wetland without prior authorization or in violation of any applicable laws. (C) Wetland categories. (1) Wetlands assigned to category 1. (a) Wetlands assigned to category 1 support minimal habitat, and minimal hydrological and recreational functions as determined by an appropriate wetland evaluation methodology acceptable to the director. Wetlands assigned to category 1 do not provide critical habitat for threatened or endangered species or contain rare, threatened or endangered species. (b) Wetlands assigned to category 1 may be typified by some or all of the following characteristics: hydrologic isolation, low species diversity, a predominance of non-native species (greater than fifty per cent areal cover for vegetative species), no significant habitat or wildlife use, and limited potential to achieve beneficial wetland functions. (c) Wetlands assigned to category 1 may include, but are not limited to, wetlands that are acidic ponds created or excavated on mined lands without a connection to other surface waters throughout the year and that have little or no vegetation and wetlands that are hydrologically isolated and comprised of vegetation that is dominated (greater than eighty per cent areal cover) by Lythrum salicaria; Phalaris arundinacea; or Phragmites australis. (2) Wetlands assigned to category 2. (a) Wetlands assigned to category 2 support moderate habitat, or hydrological or recreational functions as determined by an appropriate wetland evaluation methodology acceptable to the director. (b) Wetlands assigned to category 2 may include, but are not limited to: wetlands dominated by native species but generally without the presence of, or habitat for, rare, threatened or endangered species; and wetlands which are degraded but have a reasonable potential for reestablishing lost wetland functions. (3) Wetlands assigned to category 3. (a) Wetlands assigned to category 3 support superior habitat, or hydrological or recreational functions as determined by an appropriate wetland evaluation methodology acceptable to the director. (b) Wetlands assigned to category 3 may be typified by some or all of the following characteristics: high levels of diversity, a high proportion of native species, or high functional values. (c) Wetlands assigned to category 3 may include, but are not limited to: wetlands which contain or provide habitat for threatened or endangered species; high quality forested wetlands, including old growth forested wetlands, mature forested riparian wetlands; vernal pools; and wetlands which are scarce regionally or statewide including, but not limited to, bogs and fens. (4) In addition to assigning a wetland a category pursuant to this rule, the director may designate a wetland which has national ecological or recreational significance as an outstanding national resource water pursuant to rule 3745-1-05 of the Administrative Code. Requests to undertake activities which will result in short-term disturbances to water quality in wetlands which are designated as outstanding national resource waters are evaluated in accordance with rule 3745-1-05 of the Administrative Code. (D) Wetland avoidance, minimization, and compensatory mitigation. (1) Alternatives analysis. (a) Category 1 wetlands. The wetland designated use shall be maintained and protected for wetlands assigned to category 1 unless the applicant demonstrates, to the satisfaction of the director, all of the following: (i) Avoidance. There is no practicable alternative which would have less or no adverse impact on the wetland ecosystem. (ii) Minimization. Storm water and water quality controls will be installed in accordance with paragraph (D)(2) of this rule (iii) The impact would not result in significant degradation to the aquatic ecosystem, as determined consistent with 40 C.F.R Part 230.10(c). (iv) Compensatory mitigation. The designated use is replaced by a category 2 or category 3 wetland in accordance with table E-1 of this rule. (b) Category 2 wetlands. The wetland designated use shall be maintained and protected for wetlands assigned to category 2, and no lowering of water quality shall be allowed, unless the applicant demonstrates to the satisfaction of the director all of the following: (i) Avoidance. There is no practicable alternative, based on technical, social and economic criteria, which would have less or no adverse impact on the wetland ecosystem, so long as the alternative does not have other significant adverse environmental impacts as determined through an off-site and on-site alternatives analysis. Less damaging upland alternatives are presumed to be available for category 2 wetlands, unless clearly demonstrated otherwise. [Comment: Social considerations may include, but are not limited to, public safety.] (ii) Minimization. Appropriate and practicable steps have been taken to minimize potential adverse impacts on the wetland ecosystem. For category 2 wetlands, the applicant shall minimize all potential adverse impacts foreseeably caused by the project and each application shall include an evaluation of all of the following: (a) The spatial requirements of the project. (b) The location of existing structural or natural features that may dictate the placement or configuration of the proposed project. (c) The overall and basic purpose of the project and how the purpose relates to the placement, configuration or density of the project. (d) The sensitivity of the site design to the natural features of the site, including topography, hydrology, and existing flora and fauna. (e) Direct and indirect impacts. (iii) The lowering of water quality is necessary to accommodate important social or economic development in the area in which the water body is located. (iv) Storm water and water quality controls will be installed in accordance with paragraph (D)(2) of this rule. (v) Compensatory mitigation. The designated use is replaced by a category 2 wetland, of equal or higher quality, or a category 3 wetland in accordance with table E-1 of this rule. (c) Category 3 wetlands. The wetland designated use shall be maintained and protected in wetlands assigned to category 3, and no lowering of water quality shall be allowed, unless the applicant demonstrates to the satisfaction of the director all of the following: (i) Avoidance. There is no practicable alternative, based on technical, social and economic criteria, which would have less adverse impact on the wetland ecosystem, so long as the alternative does not have other significant adverse environmental impacts as determined through an off-site and on-site alternatives analysis. Less damaging upland alternatives are presumed to be available for category 3 wetlands, unless clearly demonstrated otherwise. (ii) Minimization. Appropriate and practicable steps have been taken to minimize potential adverse impacts on the wetland ecosystem. For category 3 wetlands, the applicant shall minimize all potential adverse impacts foreseeably caused by the project and each application shall include an evaluation of all of the following: (a) The spatial requirements of the project. (b) The location of existing structural or natural features that may dictate the placement or configuration of the proposed project. (c) The overall and basic purpose of the project and how the purpose relates to the placement, configuration or density of the project. (d) The sensitivity of the site design to the natural features of the site, including topography, hydrology, and existing flora and fauna. (e) Direct and in-direct impacts. (iii) The proposed activity is necessary to meet a demonstrated public need, as defined in rule 3745-1-50 of the Administrative Code and as determined by the director. [Comment: Additional information on the public need demonstration can be found on pages 6 to 7 of the ORAM manual, as cited in rule 3745-1-50 of the Administrative Code.] (iv) The lowering of water quality is necessary to accommodate important social or economic development in the area in which the water body is located. (v) Storm water and water quality controls will be installed in accordance with paragraph (D)(2) of this rule. (vi) The wetland is not scarce regionally or statewide, or if the wetland is scarce, the project will cause only a short-term disturbance of water quality that will not cause long-term detrimental effects. (vii) Compensatory mitigation. The designated use is replaced by a category 3 wetland, of equal or higher quality, in accordance with table E-1 of this rule. (2) Appropriate storm water control measures shall be installed to ensure that peak post-development rates of surface water runoff from the impacted wetland site do not exceed the peak pre-development rates of runoff from the on-site wetlands, for all categories of wetlands. Water quality improvement measures shall be incorporated into the design of the storm water control measures to the maximum extent practicable. Examples of these measures include, but are not limited to, incorporating vegetated areas in the storm water control plans. (E) Compensatory mitigation requirements. (1) The compensatory mitigation type and location shall be provided in the following preferred order: (a) At a mitigation bank, approved in accordance with 33 C.F.R. Part 332.8, with a service area including the same watershed as the location of the proposed wetland impacts that provides credits for the appropriate wetland category and type. (b) Through an in-lieu-fee program, approved in accordance with 33 C.F.R. Part 332.8, with a service area including the same watershed as the location of the proposed wetland impacts that provides credits for the appropriate wetland category and type. (c) At a permittee-responsible compensatory mitigation site located in accordance with 33 C.F.R. Part 332.3(b). (2) Deviations from the preferred order established in paragraph (E)(1) of this rule require a demonstration of all of the following: (a) Description of the available credits for each approved mitigation bank or in-lieu fee program with a service area including the same watershed as the location of the proposed wetland impacts. (b) Description of the costs associated with the proposed compensatory mitigation and each preceding option outlined in paragraph (E)(1) of this rule. (c) Discussion of how the proposed compensatory mitigation will provide a greater ecological benefit than each preceding option outlined in paragraph (E)(1) of this rule. (3) Compensatory mitigation shall be in-kind unless there is a compelling ecological reason that it should not be. The director may consider compensatory mitigation at a forested wetland mitigation location for impacts to a non-forested wetland site. (4) Compensatory mitigation ratios. | Category of wetland impacted | Wetland type | Minimum mitigation ratio | Wetland replacement category | | 1 | Non-forested | 1.5 : 1 | 2 or 3 | | Forested | 1.5 : 1 | | 2 | Non-forested | 2.0 : 1 | 2 or 3 | | Forested | 2.5 : 1 | | 3 | Non-forested | 2.5 : 1 | 3 | | Forested | 3.0 : 1 |
(5) For category 1 or 2 wetlands created by previous coal mining activities that are impacted as part of a remining coal operation, as defined in paragraph (PPPPP) of rule 1501:13-1-02 of the Administrative Code, or part of an "Abandoned Mine Land Reclamation" project, as defined in division (C)(1) of section 1513.37 of the Revised Code, and were not used as previous mitigation, the minimum compensatory mitigation ratio is one to one for all wetland categories and types. (F) Permittee-responsible compensatory mitigation. (1) Reestablishment (restoration) or establishment (creation) of wetlands as the sole component of compensatory mitigation shall be in accordance with the ratios and other provisions in paragraph (E) of this rule. (2) The applicant must demonstrate that the compensatory mitigation site will be protected long term and that appropriate management measures are, or will be, in place to restrict harmful activities that may jeopardize the compensatory mitigation wetland. (3) Compensatory mitigation shall be in the form of wetland reestablishment (restoration) unless it can be demonstrated by the applicant that wetland reestablishment (restoration) is impracticable. Alternative compensatory mitigation options include wetland establishment (creation) and wetland rehabilitation (enhancement). These and other alternative compensatory mitigation options, including preservation of high quality wetlands and upland buffers adjacent to wetlands assigned to category 2 or category 3 which have been avoided in accordance with other provisions of this rule, may be considered on a case-by-case basis. (4) Reestablishment (restoration) or establishment (creation) of wetlands as compensatory mitigation shall replace the impacted wetland with an equivalent or higher quality wetland. (5) Wetland rehabilitation (enhancement). (a) Wetland rehabilitation (enhancement) may be a component of acceptable compensatory mitigation. In determining the acceptability of wetlands rehabilitation (enhancement) as compensatory mitigation, the director considers the extent to which the rehabilitation (enhancement) activities will improve or repair the existing or natural functions and services of the wetland. (b) Wetland rehabilitation (enhancement) will be considered most favorably as a component of compensatory mitigation when it is located adjacent to a wetland reestablishment (restoration) project. (c) When wetland rehabilitation (enhancement) is a component of acceptable compensatory mitigation, wetlands reestablishment (restoration) or establishment (creation) must also be a component of the compensatory mitigation and shall result in at least one acre of reestablished (restored) or established (created) wetland for each acre of wetland that is impacted. Wetland rehabilitation (enhancement) must occur at a rate of at least two acres of wetland rehabilitation (enhancement) for every remaining acre of the compensatory wetland mitigation requirement. The wetland rehabilitation (enhancement) requirement can be calculated using the following equation: E = [(LMR x N) - RE] x 2, where: E = minimum number of acres of wetlands to be enhanced. LMR = left side of mitigation ratio, from the wetland mitigation table E-1of this rule. N = number of acres of impacted wetlands. RE = number of acres of proposed reestablishment (restoration) or establishment (creation) wetlands For example, if the mitigation ratio for compensatory mitigation of a category 3 forested wetland is 3:1 for an impact to two acres of wetland, an acceptable mitigation plan may include at least two acres of reestablished (restored) or established (created) wetlands and at least eight acres of rehabilitated (enhanced) wetlands. (6) Wetland preservation. (a) The director may, in exceptional circumstances, consider wetland preservation, as defined in rule 3745-1-50 of the Administrative Code, for compensatory mitigation if the applicant can demonstrate all of the following: (i) The wetland to be preserved is a category 3 wetland which will be preserved long term, or the wetland to be preserved is pivotal in protecting a category 3 wetland and both wetlands will be preserved long term, or the wetland is a high quality category 2 wetland with a reasonable potential to reestablish superior functions if preserved, as determined by the director, including, but not limited to, mature forested wetlands, vernal pools and wetlands important to protecting other water resources. (ii) The wetland to be preserved for compensatory mitigation purposes should have important habitat or water quality characteristics which are imminently threatened. (iii) The wetland to be preserved for compensatory mitigation purposes shall be deeded to a responsible party for management or rehabilitation (enhancement) in accordance with a plan approved by the director. (iv) Long term protection of the wetland to be preserved for compensatory mitigation purposes shall include upland buffers and generally occur prior to any filling of wetlands at the project site. At the director's discretion, it may be acceptable for compensatory mitigation to occur concurrently with the impacts at the project site. (b) When preservation is a component of acceptable compensatory mitigation, wetlands establishment (restoration) or establishment (creation) must also be a component of the compensatory mitigation and shall result in at least one acre of reestablished (restored) or established (created) wetland for each acre of wetland that is impacted to ensure no net loss of wetland acreage or function, unless the director determines that reestablishment (restoration) or establishment (creation) need not be a component of compensatory mitigation based on significant ecological reasons. Wetland preservation must occur at a rate of at least two acres of preservation for every remaining acre of the compensatory wetland mitigation requirement. The wetland preservation requirement can be calculated using the following equation: P = [(LMR x N) - RE] x 2, where: P = minimum number of acres of wetlands to be preserved. LMR = left side of mitigation ratio, from wetland mitigation table E-1 of this rule. N = number of acres of impacted wetlands. RE = number of acres of proposed reestablishment (restoration) or establishment (creation) wetlands. For example, if the mitigation ratio for compensatory mitigation of a category 3 forested wetland is 3:1 for an impact to two acres of wetland, an acceptable compensatory mitigation plan may include at least two acres of reestablished (restored) wetlands and at least eight acres of preserved wetlands. (7) Upland buffers which are adjacent to wetlands assigned to category 2 or category 3 and which are avoided in accordance with the requirements of paragraph (D)(1)(b)(i) or (D)(1)(c)(i) of this rule, may be a component of acceptable compensatory mitigation, if the applicant can demonstrate all of the following: (a) The average upland buffer width exceeds the minimum of fifty feet for category 2 wetlands and one hundred feet for category 3 wetlands. (b) The upland buffer and the wetland are preserved long term. (c) The upland buffer consists of native vegetation which is not maintained through mowing, application of herbicide or other means which would result in deleterious effects to either the upland buffer or the adjacent wetland. (d) When upland buffers are a component of acceptable compensatory mitigation, credit shall not exceed more than 0.5 units of the compensatory mitigation ratio, as identified in table E-1 of this rule. For example, upland buffers could be used to reduce the compensatory mitigation requirement for a category 2 non-forested wetland from 2.0:1 to 1.5:1. (8) Performance standards. The director may require the permittee to achieve performance standards to demonstrate the ecological success of the mitigation project in accordance with the "Guidelines for Wetland Mitigation Banking and In-Lieu Fee Programs in Ohio," version 2.0 or other performance standards acceptable to the director as determined during the review of the permit application. (9) Compensatory mitigation monitoring. The director requires the permittee to conduct ecological monitoring of the compensatory mitigation project and submit annual reports detailing the results of the ecological monitoring to demonstrate progress towards compliance with the performance standards. (a) The ecological monitoring may include, but is not limited to, collection of data on hydrologic characteristics, vegetation communities and soils at the compensatory mitigation site and conducting an assessment of the compensatory mitigation wetlands using an appropriate wetland evaluation method in accordance with paragraph (B)(2)(a)(iii) of this rule. (b) Ecological monitoring shall be conducted for a period of at least five years for non-forested wetlands and at least ten years for forested wetlands following construction of the compensatory mitigation. (i) Upon written request, the director may waive ecological monitoring requirements for the full five or ten years if it is demonstrated to the satisfaction of the director that the compensatory mitigation wetland is meeting the performance standards. (ii) Upon written request, the director may grant a maximum two year extension from the end of the five year or ten year monitoring period to complete outstanding compensatory mitigation obligations. Submittal of annual reports shall continue during the extension. (iii) At the end of five years or ten years, or seven years or twelve years if an extension is approved, compensatory mitigation that does not meet performance standards will be rectified through the purchase of mitigation credits at a wetland mitigation bank or through an in-lieu-fee program, when available, in accordance with paragraph (E) of this rule. When mitigation credits are not available, permittees may propose alternate compensatory mitigation to fulfill the permit requirements for the director to consider. The director may consider reductions in the compensatory mitigation based upon the ecological status of the original compensatory mitigation project. (G) The following thirty-seven groupings of cataloging units from the hydrologic unit map of Ohio, U.S. geological survey, 1988, are the watersheds for the purposes of location of compensatory mitigation : (04100001, 04100002, and 04100009 - combined); (0410003, 04100005 - combined); 04100004; 04100006; 04100007; 04100008; 04100010; 04100011; 04100012; 04110001; 04110002; (04110003 (minus the Chagrin river watershed) and 04110101 - combined); 04110003 (Chagrin river watershed only); 04110004; 05030101; 05030102; 05030103; 05030106; 05030201; 05030202; 05030204; 05040001; 05040002; 05040003; 05040004; 05040005; 05040006; 05060001; 05060002; 05060003; 05080001; (05080002, 05080003, and 05090203 - combined); 05090101; 05090103; 05090201; 05090202; and (05120101 and 05120103 - combined). This information is also depicted in appendix 1 to this rule.
View Appendix
Last updated October 10, 2024 at 8:40 AM
|