(A) Equine (horse)
(1) Acceptable euthanasia methods: penetrating captive bolt, gunshot, injectable euthanasia agents.
(2) Sites for physical methods:
(a) Frontal - the gun or penetrating captive bolt is directed at the point of the intersection of imaginary diagonal lines taken from the outer corner of the eye to the top of the opposite ear.


(b) Temporal (side) - the gun is directed at a ninety degree angle to the head at a point midway between the eye and the base of the ear.


(B) Poultry
Acceptable euthanasia methods:
(1) Poultry (laying hens, turkeys, chicks, poults, and broilers) - carbon dioxide (CO2), cervical dislocation, gunshot, blunt force trauma, decapitation, nonpenetrating captive bolt, electrocution, and injectable euthanasia agents.
(2) Maceration may be used for one day old chicks and poults, and for pipped and embryonated eggs. Delivery to the macerator must occur in a way and at a rate that prevents a backlog at the point of entry into the macerator; and without causing injury, suffocation, or avoidable distress before maceration.
(3) Blunt force trauma is acceptable only for turkeys weighing greater than or equal to fifteen pounds.
(4) Gunshot for free-range poultry only.
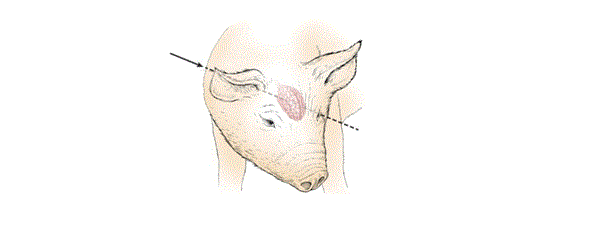
(C) Porcine (swine)
(1) Acceptable euthanasia methods:
(a) Pigs weighing more than seventy pounds: penetrating captive bolt, gunshot, and injectable euthanasia agents.
(b) Pigs weighing greater than twelve pounds and up to seventy pounds: penetrating captive bolt, gunshot, carbon dioxide (CO2), and injectable euthanasia agents.
(c) Pigs weighing less than or equal to twelve pounds: carbon dioxide (CO2), nonpenetrating captive bolt, blunt force trauma, injectable euthanasia agents.
(d) Pigs weighing equal to or greater than ten pounds: electrocution.
(2) Sites for the physical method:
(a) Frontal - the gun or penetrating captive bolt is directed at middle of the head and one inch above the level of the eyes aiming at the spine.


(b) Temporal (side) - the gun is directed at a ninety degree angle to the side of the head at a point midway between the eye and the base of the ear.


(c) Behind the ear the gun is directed from behind the ear diagonally toward the opposite eye.
(3) Electrocution
(a) For one-step electrocution, a minimum of one hundred ten volts that produces a minimum of 0.5 amps for pigs weighing equal to or greater than ten pounds and up to thirty five pounds is required. For pigs weighing greater than thirty five pounds, a minimum of two hundred twenty volts that produces a minimum of 1.3 amps is required.

(b) For two-step stunning and electrocution, the animal is first rendered unconscious by passing an alternating current across the head and followed immediately, in less than fifteen seconds, by passing the current from the head to the opposite side of the body behind the heart, or across the chest.
(D) Bovine (cattle)
(1) Acceptable euthanasia methods: penetrating captive bolt, gunshot, and injectable euthanasia agents.
(2) Sites for physical methods:
(a) Frontal - the gun or penetrating captive bolt is directed at the point of intersection of imaginary diagonal lines from the outside corner of the eye to the base of the opposite horn or to a point just above the opposite ear aiming at the spine.


(b) Temporal (side) - the gun is directed at a ninety degree angle to the side of the head at a point midway between the eye and the base of the ear.


(c) Poll method - the gun is directed at a point just behind the poll aiming at the muzzle.

(E) Caprine (goat) and ovine (sheep)
(1) Acceptable euthanasia methods: penetrating captive bolt, gunshot, carbon dioxide (CO2), and injectable euthanasia agents.
(2) Nonpenetrating captive bolt and blunt force trauma may be used on young animals less than twelve pounds.
(3) Sites for physical methods:
(a) Hornless and horned sheep - for the poll method the gun or penetrating captive bolt is directed at a point just behind the poll and aimed in the direction of the of the back of the throat.


(b) Hornless and hornded sheep and goats - for the frontal method the gun or penetrating captive bolt is directed at the middle of the forehead just above the level of the eyes and aiming at the spine.


(c) All goats - for the poll method the gunshot or penetrating captive bolt is directed at a point just behind the poll and aimed at the lower part of the chin.

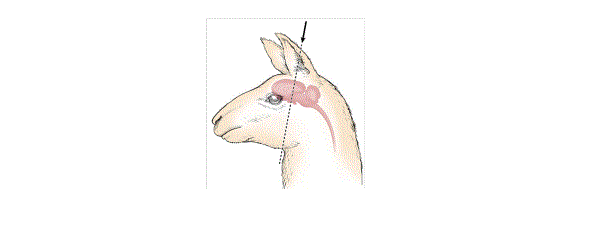
(F) Alpaca and llama
(1) Acceptable euthanasia methods: penetrating captive bolt, gunshot, and injectable euthanasia agents.
(2) Site for physical method:
(a) Frontal the gunshot or penetrating captive bolt is directed at the point of intersection of imaginary diagonal lines from the inside corner to the eye to the base of the opposite ear aiming at the spine.
(b) Poll method - the gunshot or penetrating captive bolt is directed at a point just behind the poll and aimed in the direction of the back of the throat.