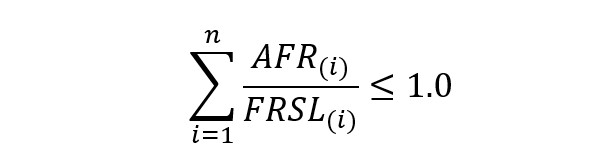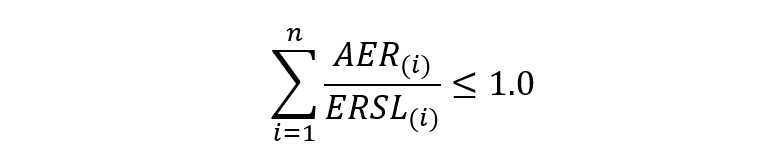(A) Purpose, scope, and
applicability.
(1) General.
(a) The purpose of this rule is to establish minimum standards
for owners and operators of "existing" boilers and industrial
furnaces that burn hazardous waste where such standards define the acceptable
management of hazardous waste until final administrative disposition of the
owner's or operator's permit application is made pursuant to section
3734.05 of the Revised Code. The standards of this rule apply to owners and
operators of existing facilities until either a permit is issued under
paragraph (D) of rule 3745-266-102 of the Administrative Code, or until closure
responsibilities identified in this rule are fulfilled. However, when the owner
and operator of an existing boiler or industrial furnace that burns hazardous
waste has obtained interim status or received a permit from U.S. EPA, the
director may apply this rule on a case-by-case basis.
(b) "Existing" or "in existence" means a
boiler or industrial furnace that on or before December 7, 2004, or the
effective date of any new, amended, or rescinded rule or statute that renders
the owner or operator of the boiler or industrial furnace subject to this rule,
was either in operation burning or processing hazardous waste or for which
construction (including the ancillary facilities to burn or to process the
hazardous waste) had commenced. A facility has commenced construction if the
owner or operator has obtained the federal, state, and local approvals or
permits necessary to begin physical construction; and either:
(i) A continuous on-site,
physical construction program has begun; or
(ii) The owner or
operator has entered into contractual obligations- which cannot be canceled or
modified without substantial loss- for physical construction of the facility to
be completed within a reasonable time.
(c) If a boiler or industrial furnace is located at a facility
that already has a permit or permit by rule, the owner or operator of the
facility shall comply with the applicable requirements for permit modifications
in rule 3745-50-51 of the Administrative Code.
(2) Exemptions. This rule
does not apply to hazardous waste and facilities exempt under rule 3745-266-108
or paragraph (B) of rule 3745-266-100 of the Administrative Code.
(3) Prohibition on
burning dioxin-listed wastes. The following hazardous waste listed for dioxin
and hazardous waste derived from any of these wastes may not be burned in a
boiler or industrial furnace operating under permit by rule: F020, F021, F022,
F023, F026, and F027.
(4) Applicability of
standards in Chapters 3745-65 to 3745-69 and 3745-256 of the Administrative
Code. Owners and operators of boilers and industrial furnaces that burn
hazardous waste and are operating under permit by rule are subject to the
following provisions of Chapters 3745-65 to 3745-69 and 3745-256 of the
Administrative Code, except as provided otherwise by this rule:
(a) [Reserved;]
(b) Rules 3745-65-11 to 3745-65-17 of the Administrative Code
(general facility standards);
(c) Rules 3745-65-31 to 3745-65-37 of the Administrative Code
(preparedness and prevention);
(d) Rules 3745-65-51 to 3745-65-56 of the Administrative Code
(contingency plan and emergency procedures);
(e) Rules 3745-65-71 to 3745-65-77 of the Administrative Code,
except that rules 3745-65-71, 3745-65-72, and 3745-65-76 of the Administrative
Code do not apply to owners and operators of on-site facilities that do not
receive any hazardous waste from off-site sources (manifest system,
recordkeeping, and reporting);
(f) Rules 3745-66-11 to 3745-66-21 of the Administrative Code
(closure and post-closure);
(g) Rules 3745-66-41, 3745-66-42, 3745-66-43, and 3745-66-47 to
3745-66-48 of the Administrative Code, except that states and the federal
government are exempt from rules 3745-66-40 to 3745-66-48 of the Administrative
Code (financial requirements); and
(h) Rules 3745-256-50 to 3745-256-64 of the Administrative Code
(air emission standards for equipment leaks), except as provided in paragraph
(A) of rule 3745-256-50 of the Administrative Code.
(5) Special requirements
for furnaces. The following controls apply during permit by rule to industrial
furnaces (e.g., kilns, cupolas) that feed hazardous waste for a purpose other
than solely as an ingredient [see paragraph (A)(5)(b) of this rule] at any
location other than the hot end where products are normally discharged or where
fuels are normally fired:
(a) Controls.
(i) The hazardous waste
shall be fed at a location where combustion gas temperatures are at least
eighteen hundred degrees Fahrenheit;
(ii) The owner or
operator shall determine that adequate oxygen is present in combustion gases to
combust organic constituents in the waste and shall retain documentation of
such determination in the facility record;
(iii) For cement kiln
systems, the hazardous waste shall be fed into the kiln; and
(iv) The hydrocarbon
controls in paragraph (C) of rule 3745-266-104 of the Administrative Code or
paragraph (C)(5) of this rule apply upon certification of compliance under
paragraph (C) of this rule irrespective of the carbon monoxide level achieved
during the compliance test.
(b) Burning hazardous waste solely as an ingredient. A hazardous
waste is burned for a purpose other than solely as an ingredient if the
hazardous waste meets either of the following criteria:
(i) The hazardous waste
has a total concentration of nonmetal compounds listed in the appendix to rule
3745-51-11 of the Administrative Code exceeding five hundred parts per million
(ppm) by weight, as-fired, and so is considered to be burned for destruction.
The concentration of nonmetal compounds in a waste as-generated may be reduced
to the five hundred ppm limit by bona fide treatment that removes or destroys
nonmetal constituents. Blending for dilution to meet the five hundred ppm limit
is prohibited, and documentation that the waste has not been impermissibly
diluted shall be retained in the facility record; or
(ii) The hazardous waste
has a heating value of five thousand British thermal units (Btu) per pound or
more, as-fired, and so is considered to be burned as fuel. The heating value of
a waste as-generated may be reduced to below the five thousand Btu per pound
limit by bona fide treatment that removes or destroys organic constituents.
Blending to augment the heating value to meet the five thousand Btu per pound
limit is prohibited, and documentation that the waste has not been
impermissibly blended shall be retained in the facility record.
(6) Restrictions on
burning hazardous waste that is not a fuel. Prior to certification of
compliance under paragraph (C) of this rule, owners and operators shall not
feed hazardous waste that has a heating value less than five thousand Btu per
pound, as-generated, (except that the heating value of a waste as-generated may
be increased to above the five thousand Btu per pound limit by bona fide
treatment; however, blending to augment the heating value to meet the five
thousand Btu per pound limit is prohibited, and records shall be kept to
document that impermissible blending has not occurred) in a boiler or
industrial furnace, except that:
(a) Hazardous waste may be burned solely as an ingredient;
or
(b) Hazardous waste may be burned for purposes of compliance
testing (or testing prior to compliance testing) for a total period of time not
to exceed seven hundred twenty hours; or
(c) Such waste may be burned if the director has documentation to
show that, prior to December 7, 2004, or prior to the effective date of any
new, amended, or rescinded rule or statute that renders the owner or operator
of the boiler or industrial furnace subject to this rule:
(i) The boiler or
industrial furnace is operating under the standards for incinerators in rules
3745-68-40 to 3745-68-52 of the Administrative Code, or the standards for
thermal treatment units provided by rules 3745-68-70 to 3745-68-83 of the
Administrative Code; and
(ii) The boiler or
industrial furnace met the permit by rule eligibility requirements under rule
3745-50-40 of the Administrative Code for rules 3745-68-40 to 3745-68-52 or
rules 3745-68-70 to 3745-68-83 of the Administrative Code; and
(iii) Hazardous waste
with a heating value less than five thousand Btu per pound was burned prior to
December 7, 2004, or prior to the effective date of any new, amended, or
rescinded rule or statute that renders the owner or operator of the boiler or
industrial furnace subject to this rule; or
(d) Such waste may be burned in a halogen acid furnace if the
waste was burned as an excluded ingredient under paragraph (E) of rule
3745-51-02 of the Administrative Code prior to December 7, 2004, or prior to
the effective date of any new, amended, or rescinded rule or statute that
renders the owner or operator of the boiler or industrial furnace subject to
this rule, and documentation is kept on file supporting this
claim.
(7) Direct transfer to
the burner. If hazardous waste is directly transferred from a transport vehicle
to a boiler or industrial furnace without the use of a storage unit, the owner
or operator shall comply with rule 3745-266-111 of the Administrative
Code.
(B) Certification of
precompliance.
(1) General. The owner or
operator shall provide complete and accurate information specified in paragraph
(B)(2) of this rule to the director within thirty days after December 7, 2004,
or within thirty days after the effective date of any new, amended, or
rescinded rule or statute that renders the owner or operator of the boiler or
industrial furnace subject to this rule, and shall establish limits for the
operating parameters specified in paragraph (B)(3) of this rule. Such
information is termed a "certification of precompliance" and
constitutes a certification that the owner or operator has determined that,
when the facility is operated within the limits specified in paragraph (B)(3)
of this rule, the owner or operator believes that, using best engineering
judgment, emissions of particulate matter, metals, hydrogen chloride, and
chlorine gas are not likely to exceed the limits in rules 3745-266-105,
3745-266-106, and 3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code. The facility may
burn hazardous waste only under the operating conditions that the owner or
operator establishes under paragraph (B)(3) of this rule until the owner or
operator submits a revised certification of precompliance under paragraph
(B)(8) of this rule or a certification of compliance under paragraph (C) of
this rule, or until a permit is issued.
(2) Information required.
The following information shall be submitted with the certification of
precompliance to support the determination that the limits established for the
operating parameters identified in paragraph (B)(3) of this rule are not likely
to result in an exceedance of the allowable emission rates for particulate
matter, metals, hydrogen chloride, and chlorine gas:
(a) General facility information:
(i) U.S. EPA
identification number;
(ii) Facility name,
contact person, telephone number, and address;
(iii) Description of
boilers and industrial furnaces burning hazardous waste, including type and
capacity of device;
(iv) A scaled plot plan
showing the entire facility and location of the boilers and industrial furnaces
burning hazardous waste; and
(v) A description of the
air pollution control system on each device burning hazardous waste, including
the temperature of the flue gas at the inlet to the particulate matter control
system.
(b) Except for facilities complying with the "Tier I"
or "Adjusted Tier I" feed rate screening limits for metals or total
chlorine and chloride in paragraph (B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 and
paragraph (B)(1) or (E) of rule 3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code,
respectively, the estimated uncontrolled (at the inlet to the air pollution
control system) emissions of particulate matter, each metal controlled by rule
3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code, hydrogen chloride, and chlorine, and
the following information to support such determinations:
(i) The feed rate (pounds
per hour) of ash, chlorine, antimony, arsenic, barium, beryllium, cadmium,
chromium, lead, mercury, silver, and thallium in each feedstream (hazardous
waste, other fuels, industrial furnace feedstocks).
(ii) The estimated partitioning factor to the combustion gas
for the materials identified in paragraph (B)(2)(b)(i) of this rule and the
basis for the estimate and an estimate of the partitioning to HCl and
Cl2 of total chloride and chlorine in
feed materials. To estimate the partitioning factor, the owner or operator
shall use either best engineering judgment or the procedures specified in the
appendix to this rule.
(iii) For industrial
furnaces that recycle collected particulate matter back into the furnace and
that will certify compliance with the metals emissions standards under
paragraph (C)(3)(b)(i) of this rule, the estimated enrichment factor for each
metal. To estimate the enrichment factor, the owner or operator shall use
either best engineering judgment or the procedures specified in
"Alternative Methodology for Implementing Metals Controls" in the
appendix to this rule.
(iv) If best engineering
judgment is used to estimate partitioning factors or enrichment factors under
paragraph (B)(2)(b)(ii) or (B)(2)(b)(iii) of this rule, respectively, the basis
for the judgment. When best engineering judgment is used to develop or evaluate
data or information and make determinations under this rule, the determinations
shall be made by a qualified professional engineer and a certification of such
engineer's determinations in accordance with paragraph (D) of rule
3745-50-42 of the Administrative Code shall be provided in the certification of
precompliance.
(c) For facilities complying with the "Tier I" or
"Adjusted Tier I" feed rate screening limits for metals or total
chlorine and chloride in paragraph (B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 and
paragraph (B)(1) or (E) of rule 3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code, the
feed rate (pounds per hour) of total chloride and chlorine, antimony, arsenic,
barium, beryllium, cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury, silver, and thallium in
each feedstream (hazardous waste, other fuels, industrial furnace
feedstocks).
(d) For facilities complying with the "Tier II" or
"Tier III" emission limits for metals or hydrogen chloride and
chlorine gas [under paragraph (C) or (D) of rule 3745-266-106 or paragraph
(B)(2) or (C) of rule 3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code], the estimated
controlled (outlet of the air pollution control system) emissions rates of
particulate matter, each metal controlled by rule 3745-266-106 of the
Administrative Code, hydrogen chloride, and chlorine gas, and the following
information to support such determinations:
(i) The estimated air
pollution control system removal efficiency for particulate matter, hydrogen
chloride, chlorine gas, antimony, arsenic, barium, beryllium, cadmium,
chromium, lead, mercury, silver, and thallium.
(ii) To estimate air
pollution control system removal efficiency, the owner or operator shall use
either best engineering judgment or the procedures prescribed in the appendix
to this rule.
(iii) If best engineering
judgment is used to estimate air pollution control system removal efficiency,
the basis for the judgment. Use of best engineering judgment shall be in
conformance with provisions of paragraph (B)(2)(b)(iv) of this
rule.
(e) Determination of allowable emissions rates for hydrogen
chloride, chlorine gas, antimony, arsenic, barium, beryllium, cadmium,
chromium, lead, mercury, silver, and thallium, and the following information to
support such determinations:
(i) For all
facilities:
(a) Physical stack
height;
(b) "Good
engineering practice stack height" as defined in 40 CFR
51.100(ii);
(c) Maximum flue gas flow
rate;
(d) Maximum flue gas
temperature;
(e) Attach a U.S.
geological service topographic map (or equivalent) showing the facility
location and surrounding land within five kilometers of the
facility;
(f) Identify terrain
type: complex or noncomplex; and
(g) Identify land use:
urban or rural.
(ii) For owners and
operators using "Tier III" site-specific dispersion modeling to
determine allowable levels under paragraph (D) of rule 3745-266-106 or
paragraph (C) of rule 3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code, or
"Adjusted Tier I" feed rate screening limits under paragraph (E) of
rule 3745-266-106 or paragraph (E) of rule 3745-266-107 of the Administrative
Code, by providing the following:
(a) Dispersion model and
version used;
(b) Source of
meteorological data;
(c) The dilution factor
in micrograms per cubic meter per gram per second of emissions for the maximum
annual average off-site (unless on-site is required) ground level concentration
(MEI location); and
(d) Indicate the MEI
location on the map required under paragraph (B)(2)(e)(i)(e) of this
rule.
(f) For facilities complying with the "Tier II" or
"Tier III" emissions rate controls for metals or hydrogen chloride
and chlorine gas, a comparison of the estimated controlled emissions rates
determined under paragraph (B)(2)(d) of this rule with the allowable emission
rates determined under paragraph (B)(2)(e) of this rule;
(g) For facilities complying with the "Tier I" (or
"Adjusted Tier I") feed rate screening limits for metals or total
chloride and chlorine, a comparison of actual feed rates of each metal and
total chlorine and chloride determined under paragraph (B)(2)(c) of this rule
to the "Tier I" allowable feed rates; and
(h) For industrial furnaces that feed hazardous waste for any
purpose other than solely as an ingredient [as determined by paragraph
(A)(5)(b) of this rule] at any location other than the product discharge end of
the device, documentation of compliance with paragraphs (A)(5)(a)(i),
(A)(5)(a)(ii), and (A)(5)(a)(iii) of this rule.
(i) For industrial furnaces that recycle collected particulate
matter back into the furnace and that will certify compliance with the metals
emissions standards under paragraph (C)(3)(b)(i) of this rule:
(i) The applicable
particulate matter standard in rule 3745-266-105 of the Administrative Code in
pounds per hour; and
(ii) The precompliance
limit on the concentration of each metal in collected particulate
matter.
(3) Limits on operating
conditions. The owner or operator shall establish limits on the following
parameters consistent with the determinations made under paragraph (B)(2) of
this rule and certify [under provisions of paragraph (B)(9) of this rule] to
the director that the facility will operate within these limits when there is
hazardous waste in the unit until revised certification of precompliance under
paragraph (B)(8) of this rule or certification of compliance under paragraph
(C) of this rule:
(a) Feed rate of total hazardous waste and [unless complying with
the "Tier I" or "Adjusted Tier I" metals feed rate
screening limits under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 of the
Administrative Code] pumpable hazardous waste;
(b) Feed rate of each metal in the following
feedstreams:
(i) Total feedstreams,
except that industrial furnaces that comply with the alternative metals
implementation approach under paragraph (B)(4) of this rule shall specify
limits on the concentration of each metal in collected particulate matter in
lieu of feed rate limits for total feedstreams;
(ii) Total hazardous
waste feed, unless complying with the "Tier I" or "Adjusted Tier
I" metals feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule
3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code; and
(iii) Total pumpable
hazardous waste feed, unless complying with the "Tier I" or
"Adjusted Tier I" metals feed rate screening limits under paragraph
(B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code;
(c) Total feed rate of chlorine and chloride in total
feedstreams;
(d) Total feed rate of ash in total feedstreams, except that the
ash feed rate for cement kilns and light-weight aggregate kilns is not limited;
and
(e) Maximum production rate of the device in appropriate units
when producing normal product, unless complying with the "Tier I" or
"Adjusted Tier I" feed rate screening limits for chlorine under rule
paragraph (B)(1) or (E) of rule 3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code and for
all metals under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 of the
Administrative Code, and the uncontrolled particulate emissions do not exceed
the standard under rule 3745-266-105 of the Administrative Code.
(4) Operating
requirements for furnaces that recycle particulate matter. Owners and operators
of furnaces that recycle collected particulate matter back into the furnace and
that will certify compliance with the metals emissions controls under paragraph
(C)(3)(b)(i) of this rule shall comply with the special operating requirements
in "Alternative Methodology for Implementing Metals Controls" in the
appendix to this rule.
(5) Measurement of feed
rates and production rate.
(a) General requirements. Limits on each of the parameters
specified in paragraph (B)(3) of this rule (except for limits on metals
concentrations in collected particulate matter for industrial furnaces that
recycle collected particulate matter) shall be established and continuously
monitored under either of the following methods:
(i) Instantaneous limits.
A limit for a parameter may be established and continuously monitored and
recorded on an instantaneous basis (i.e., the value that occurs at any time)
not to be exceeded at any time; or
(ii) Hourly rolling
average limits. A limit for a parameter may be established and
"continuously monitored" on an "hourly rolling average"
basis defined as follows:
(a) A "continuous
monitor" is one which continuously samples the regulated parameter without
interruption, and evaluates the detector response at least once each fifteen
seconds, and computes and records the average value at least every sixty
seconds.
(b) An "hourly
rolling average" is the arithmetic mean of the sixty most recent
one-minute average values recorded by the continuous monitoring
system.
(b) Rolling average limits for carcinogenic metals and lead. Feed
rate limits for the carcinogenic metals (arsenic, beryllium, cadmium, and
chromium) and lead may be established either on an hourly rolling average basis
as prescribed by paragraph (B)(5)(a)(ii) of this rule or on (up to) a
twenty-four hour rolling average basis. If the owner or operator elects to use
an averaging period from two to twenty-four hours:
(i) The feed rate of each
metal shall be limited at any time to ten times the feed rate that would be
allowed on an hourly rolling average basis;
(ii) The continuous
monitor shall meet the following specifications:
(a) A continuous monitor
is one which continuously samples the regulated parameter without interruption,
and evaluates the detector response at least once each fifteen seconds, and
computes and records the average value at least every sixty
seconds.
(b) The "rolling
average" for the selected averaging period is the arithmetic mean of one
hour block averages for the averaging period. A "one hour block
average" is the arithmetic mean of the one minute averages recorded during
the sixty-minute period beginning at one minute after the beginning of
preceding clock hour.
(c) Feed rate limits for metals, total chloride and chlorine, and
ash. Feed rate limits for metals, total chlorine and chloride, and ash are
established and monitored by knowing the concentration of the substance (i.e.,
metals, chloride or chlorine, and ash) in each feedstream and the flow rate of
the feedstream. To monitor the feed rate of these substances, the flow rate of
each feedstream shall be monitored under the continuous monitoring requirements
of paragraphs (B)(5)(a) and (B)(5)(b) of this rule.
(6) Public notice
requirements at precompliance. Within thirty days after December 7, 2004, or
within thirty days after the effective date of any new, amended, or rescinded
rule or statute that renders the owner or operator of the boiler or industrial
furnace subject to this rule, the owner or operator shall submit a notice with
the following information for publication in a major local newspaper of general
circulation and send a copy of the notice to the appropriate units of state and
local government. The owner or operator shall provide to the director with the
certification of precompliance evidence of submitting the notice for
publication.
(a) The notice, which shall be entitled "Notice of
Certification of Precompliance with Hazardous Waste Burning Requirements of
Paragraph (B) of Rule 3745-266-103 of the Administrative Code," shall
include:
(i) Name and address of
the owner and operator of the facility as well as the location of the device
burning hazardous waste;
(ii) Date that the
certification of precompliance is submitted to Ohio EPA;
(iii) Brief description
of the regulatory process required to comply with this rule including required
emissions testing to demonstrate conformance with emissions standards for
organic compounds, particulate matter, metals, hydrogen chloride, and chlorine
gas;
(iv) Types and quantities
of hazardous waste burned including, but not limited to, source, whether solids
or liquids, as well as an appropriate description of the waste;
(v) Type of devices in
which the hazardous waste is burned including a physical description and
maximum production rate of each device;
(vi) Types and quantities
of other fuels and industrial furnace feedstocks fed to each unit;
(vii) Brief description
of the basis for this certification of precompliance as specified in paragraph
(B)(2) of this rule;
(viii) Locations where
the record for the facility can be viewed and copied by interested
parties:
(a) The administrative
record kept by Ohio EPA where the supporting documentation was submitted or
another location designated by the director; and
(b) The boiler and
industrial furnace correspondence file kept at the facility site where the
device is located. The correspondence file shall include all correspondence
between the facility and the director, state and local regulatory officials,
including copies of all certifications and notifications, such as the
precomplicance certification, precompliance public notice, notice of compliance
testing, compliance test report, compliance certification, time extension
requests and approvals or denials, enforcement notifications of violations, and
copies of U.S. EPA and Ohio EPA site visit reports submitted to the owner or
operator.
(ix) Notification of the
establishment of a facility mailing list whereby interested parties may notify
Ohio EPA that such interested parties wish to be placed on the mailing list to
receive future information and notices about this facility; and
(x) Location (mailing
address) of the applicable Ohio EPA office, hazardous waste division, where
further information can be obtained on Ohio EPA regulation of hazardous waste
burning.
(b) At a minimum, these records and locations shall
include:
(i) The administrative
record kept by the Ohio EPA office where the supporting documentation was
submitted or another location designated by Ohio EPA; and
(ii) Files kept at the
facility site where the device is located. The files shall include all
correspondence between the facility and the U.S. EPA, state and local
regulatory officials, including copies of all certifications and notifications,
such as the precompliance certification, precompliance public notice, notice of
compliance testing, compliance test report, compliance certification, time
extension requests and approvals or denials, enforcement notifications of
violations, and copies of U.S. EPA and Ohio EPA site visit reports submitted to
the owner or operator.
(c) Notification of the establishment of a facility mailing list
whereby interested parties shall notify Ohio EPA that such interested parties
wish to be placed on the mailing list to receive future information and notices
about this facility.
(d) Location (mailing address) of the applicable U.S. EPA
regional office, hazardous waste division, where further information can be
obtained on regulation of hazardous waste burning.
(7) Monitoring other
operating parameters. When the monitoring systems for the operating parameters
listed in paragraphs (C)(1)(e) to (C)(1)(m) of this rule are installed and
operating in conformance with vendor specifications or (for carbon monoxide,
hydrocarbon, and oxygen) specifications in the appendix to this rule, as
appropriate, the parameters shall be continuously monitored and records shall
be maintained in the operating record.
(8) Revised certification
of precompliance. The owner or operator may revise at any time the information
and operating conditions documented under paragraphs (B)(2) and (B)(3) of this
rule in the certification of precompliance by submitting a revised
certification of precompliance under procedures in those
paragraphs.
(a) The public notice requirements of paragraph (B)(6) of this
rule do not apply to recertifications.
(b) The owner and operator shall operate the facility within the
limits established for the operating parameters under paragraph (B)(3) of this
rule until a revised certification is submitted under paragraph (B)(8) of this
rule or a certification of compliance is submitted under paragraph (C) of this
rule.
(9) Certification of
precompliance statement. The owner or operator shall include the following
signed statement with the certification of precompliance submitted to the
director:
"I certify under penalty of law that this
information was prepared under my direction or supervision in accordance with a
system designed to ensure that qualified personnel properly gathered and
evaluated the information and supporting documentation. Copies of all emissions
tests, dispersion modeling results and other information used to determine
conformance with the requirements of paragraphs (B)(3) and (B)(4) of rule
3745-266-103 of the Administrative Code are available at the facility and can
be obtained from the facility contact person listed above. Based on my inquiry
of the person or persons who manages the facility, or those persons directly
responsible for gathering the information, the information submitted is, to the
best of my knowledge and belief, true, accurate, and complete. I am aware that
there are significant penalties for submitting false information, including the
possibility of fine and imprisonment for knowing violations.
I also acknowledge that the operating limits
established in this certification pursuant to paragraphs (B)(3) and (B)(4) of
rule 3745-266-103 of the Administrative Code are enforceable limits at which
the facility can legally operate during interim status until a revised
certification of precompliance is submitted, a certification of compliance is
submitted, or an operating permit is issued."
(C) Certification of compliance. The
owner or operator shall conduct emissions testing to document compliance with
the emissions standards of rules 3745-266-105, 3745-266-106, 3745-266-107, and
paragraphs (B) to (E) of rule 3745-266-104 of the Administrative Code, and
paragraph (A)(5)(a)(iv) of this rule, under the procedures in paragraph (C) of
this rule, except under extensions of time in paragraph (C)(7) of this rule.
Based on the compliance test, the owner or operator shall submit to the
director within thirty days after December 7, 2004, or within thirty days after
the effective date of any new, amended, or rescinded rule or statute that
renders the owner or operator of the boiler or industrial furnace subject to
this rule, a complete and accurate "certification of compliance"
[under paragraph (C)(4) of this rule] with those emission standards
establishing limits on the operating parameters specified in paragraph (C)(1)
of this rule.
For purposes of compliance with this rule, all
owners and operators who have submitted a certification of compliance to U.S.
EPA, in accordance with 40 CFR 266.103(c), may submit a copy of the
certification of compliance to the director within thirty days after December
7, 2004, or within thirty days after the effective date of any new, amended, or
rescinded rule or statute that renders the owner or operator of the boiler or
industrial furnace subject to this rule. The copy of the certification of
compliance that is submitted to the director shall be submitted with the
"Part A" application required by rule 3745-50-40 of the
Administrative Code, and shall be considered part of such application.
(1) Limits on operating
conditions. The owner or operator shall establish limits on the following
parameters based on operations during the compliance test [under procedures
prescribed in paragraph (C)(4)(d) of this rule] or as otherwise specified and
include these limits with the certification of compliance. The boiler or
industrial furnace shall be operated in accordance with these operating limits
and the applicable emissions standards of rules 3745-266-105, 3745-266-106,
3745-266-107, and paragraphs (B) to (E) of rule 3745-266-104 of the
Administrative Code and paragraph (A)(5)(a)(iv) of this rule at all times when
there is hazardous waste in the unit.
(a) Feed rate of total hazardous waste and [unless complying with
the "Tier I" or "Adjusted Tier I" metals feed rate
screening limits under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 of the
Administrative Code], pumpable hazardous waste;
(b) Feed rate of each metal in the following
feedstreams:
(i) Total feedstreams,
except that:
(a) Facilities that
comply with "Tier I" or "Adjusted Tier I" metals feed rate
screening limits may set facility operating limits at the metals feed rate
screening limits determined under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 of
the Administrative Code; and
(b) Industrial furnaces
that shall comply with the alternative metals implementation approach under
paragraph (C)(3)(b) of this rule shall specify limits on the concentration of
each metal in the collected particulate matter in lieu of feed rate limits for
total feedstreams.
(ii) Total hazardous
waste feed [unless complying with the "Tier I" or "Adjusted Tier
I" metals feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule
3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code]; and
(iii) Total pumpable
hazardous waste feed [unless complying with the "Tier I" or
"Adjusted Tier I" metals feed rate screening limits under paragraph
(B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code];
(c) Total feed rate of chlorine and chloride in total
feedstreams, except that facilities that comply with "Tier I" or
"Adjusted Tier I" feed rate screening limits may set facility
operating limits at the total chlorine and chloride feed rate screening limits
determined under paragraph (B)(1) or (E) of rule 3745-266-107 of the
Administrative Code;
(d) Total feed rate of ash in total feedstreams, except that the
ash feed rate for cement kilns and light-weight aggregate kilns is not
limited;
(e) Carbon monoxide concentration, and where required,
hydrocarbon concentration in stack gas. When complying with the carbon monoxide
controls of paragraph (B) of rule 3745-266-104 of the Administrative Code, the
carbon monoxide limit is one hundred parts per million by volume (ppmv), and
when complying with the hydrocarbon controls of paragraph (C) of rule
3745-266-104 of the Administrative Code, the hydrocarbon limit is twenty ppmv.
When complying with the carbon monoxide controls of paragraph (C) rule
3745-266-104 of the Administrative Code, the carbon monoxide limit is
established based on the compliance test;
(f) Maximum production rate of the device in appropriate units
when producing normal product, unless complying with the "Tier I" or
"Adjusted Tier I" feed rate screening limits for chlorine under
paragraph (B)(1) or (E) of rule 3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code and for
all metals under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 of the
Administrative Code, and the uncontrolled particulate emissions do not exceed
the standard under rule 3745-266-105 of the Administrative Code;
(g) Maximum combustion chamber temperature where the temperature
measurement is as close to the combustion zone as possible and is upstream of
any quench water injection [unless complying with the "Tier I" or
"Adjusted Tier I" metals feed rate screening limits under paragraph
(B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code];
(h) Maximum flue gas temperature entering a particulate matter
control device [unless complying with "Tier I" or "Adjusted Tier
I" metals feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule
3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code and the total chlorine and chloride
feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-107 of
the Administrative Code];
(i) For systems using wet scrubbers, including wet ionizing
scrubbers [unless complying with "Tier I" or "Adjusted Tier
I" metals feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule
3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code and the total chlorine and chloride
feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B)(1) or (E) of rule 3745-266-107
of the Administrative Code], the following:
(i) Minimum liquid to
flue gas ratio;
(ii) Minimum scrubber
blowdown from the system or maximum suspended solids content of scrubber water;
and
(iii) Minimum pH level of
the scrubber water;
(j) For systems using venturi scrubbers, the minimum differential
gas pressure across the venturi [unless complying with the "Tier I"
or "Adjusted Tier I" metals feed rate screening limits under
paragraph (B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code and the
total chlorine and chloride feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B)(1)
or (E) of rule 3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code].
(k) For systems using dry scrubbers [unless complying with the
"Tier I" or "Adjusted Tier I" metals feed rate screening
limits under paragraph (B) or (E) of rule 3745-266-106 of the Administrative
Code and the total chlorine and chloride feed rate screening limits under
paragraph (B)(1) or (E) of rule 3745-266-107 of the Administrative
Code]:
(i) Minimum caustic feed
rate; and
(ii) Maximum flue gas
flow rate;
(l) For systems using wet ionizing scrubbers or electrostatic
precipitators [unless complying with the "Tier I" or "Adjusted
Tier I" metals feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B) or (E) of
rule 3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code and the total chlorine and
chloride feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B)(1) or (E) of rule
3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code]:
(i) Minimum electrical
power in kilovolt amperes (kVA) to the precipitator plates; and
(ii) Maximum flue gas
flow rate;
(m) For systems using fabric filters (baghouses), the minimum
pressure drop [unless complying with the "Tier I" or "Adjusted
Tier I" metal feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B) or (E) of
rule 3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code and the total chlorine and
chloride feed rate screening limits under paragraph (B)(1) or (E) of rule
3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code].
(2) Prior notice of
compliance testing. At least thirty days prior to the compliance testing
required by paragraph (C)(3) of this rule, the owner or operator shall notify
the director and submit the following information:
(a) General facility information including:
(i) U.S. EPA
identification number;
(ii) Facility name,
contact person, telephone number, and address;
(iii) Person responsible
for conducting compliance test, including company name, address, and telephone
number, and a statement of qualifications;
(iv) Planned date of the
compliance test;
(b) Specific information on each device to be tested
including:
(i) Description of boiler
or industrial furnace;
(ii) A scaled plot plan
showing the entire facility and location of the boiler or industrial
furnace;
(iii) A description of
the air pollution control system;
(iv) Identification of
the continuous emission monitors that are installed, including:
(a) Carbon monoxide
monitor;
(b) Oxygen
monitor;
(c) Hydrocarbon monitor,
specifying the minimum temperature of the system and, if the temperature is
less than one hundred fifty degrees Celsius, an explanation of why a heated
system is not used [see paragraph (C)(5) of this rule] and a brief description
of the sample gas conditioning system;
(v) Indication of whether
the stack is shared with another device that will be in operation during the
compliance test;
(vi) Other information
useful to an understanding of the system design or operation.
(c) Information on the testing planned, including a complete copy
of the test protocol and quality assurance or quality control plan, and a
summary description for each test providing, at a minimum, the following
information:
(i) Purpose of the test
(e.g., demonstrate compliance with emissions of particulate matter);
and
(ii) Planned operating
conditions, including levels for each pertinent parameter specified in
paragraph (C)(1) of this rule.
(3) Compliance
testing.
(a) General. Compliance testing shall be conducted under
conditions for which the owner or operator has submitted a certification of
precompliance under paragraph (B) of this rule and under conditions established
in the notification of compliance testing required by paragraph (C)(2) of this
rule. The owner or operator may seek approval on a case-by-case basis to use
compliance test data from one unit in lieu of testing a similar on-site unit.
To support the request, the owner or operator shall provide a comparison of the
hazardous waste burned and other feedstreams, and the design, operation, and
maintenance of both the tested unit and the similar unit. The director shall
provide a written approval to use compliance test data in lieu of testing a
similar unit if the director finds that the hazardous wastes, the devices, and
the operating conditions are sufficiently similar, and the data from the other
compliance test is adequate to meet the requirements of paragraph (C) of this
rule.
(b) Special requirements for industrial furnaces that recycle
collected particulate matter. Owners and operators of industrial furnaces that
recycle back into the furnace particulate matter from the air pollution control
system shall comply with one of the following procedures for testing to
determine compliance with the metals standards of paragraph (C) or (D) of rule
3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code:
(i) The special testing
requirements prescribed in "Alternative Method for Implementing Metals
Controls" in the appendix to this rule; or
(ii) Stack emissions
testing for a minimum of six hours each day while hazardous waste is burned
during permit by rule. The testing shall be conducted when burning normal
hazardous waste for that day at normal feed rates for that day and when the air
pollution control system is operated under normal conditions. During permit by
rule, hazardous waste analysis for metals content shall be sufficient for the
owner or operator to determine if changes in metals content may affect the
ability of the facility to meet the metals emissions standards established
under paragraph (C) or (D) of rule 3745-266-106 of the Administrative Code.
Under this option, operating limits [under paragraph (C)(1) of this rule] shall
be established during compliance testing under paragraph (C)(3) of this rule on
the following parameters:
(a) Feed rate of total
hazardous waste;
(b) Total feed rate of
chlorine and chloride in total feedstreams;
(c) Total feed rate of
ash in total feedstreams, except that the ash feed rate for cement kilns and
light-weight aggregate kilns is not limited;
(d) Carbon monoxide
concentration, and where required, hydrocarbon concentration in stack
gas;
(e) Maximum production
rate of the device in appropriate units when producing normal product;
or
(iii) Conduct compliance
testing to determine compliance with the metals standards to establish limits
on the operating parameters of paragraph (C)(1) of this rule only after the
kiln system has been conditioned to enable the kiln system to reach equilibrium
with respect to metals fed into the system and metals emissions. During
conditioning, hazardous waste and raw materials having the same metals content
as will be fed during the compliance test shall be fed at the feed rates that
will be fed during the compliance test.
(c) Conduct of compliance testing.
(i) If compliance with
all applicable emissions standards of rules 3745-266-104 to 3745-266-107 of the
Administrative Code is not demonstrated simultaneously during a set of test
runs, the operating conditions of additional test runs required to demonstrate
compliance with remaining emissions standards shall be as close as possible to
the original operating conditions.
(ii) Prior to obtaining
test data for purposes of demonstrating compliance with the applicable
emissions standards of rules 3745-266-104 to 3745-266-107 of the Administrative
Code or establishing limits on operating parameters under this rule, the
facility shall operate under compliance test conditions for a sufficient period
to reach steady-state operations. However, industrial furnaces that recycle
collected particulate matter back into the furnace and that comply with
paragraph (C)(3)(b)(i) or (C)(3)(b)(ii) of this rule need not reach steady
state conditions with respect to the flow of metals in the system prior to
beginning compliance testing for metals.
(iii) Compliance test
data on the level of an operating parameter for which a limit shall be
established in the certification of compliance shall be obtained during
emissions sampling for the pollutants (i.e., metals, particulate matter,
hydrogen chloride or chlorine gas, organic compounds) for which the parameter
shall be established as specified by paragraph (C)(1) of this
rule.
(4) Certification of
compliance. Within ninety days after completing compliance testing, the owner
or operator shall certify to the director compliance with the emissions
standards of rules 3745-266-105, 3745-266-106, 3745-266-107, and paragraphs
(B), (C), and (E) of rule 3745-266-104 of the Administrative Code and paragraph
(A)(5)(a)(iv) of this rule. The certification of compliance shall include the
following information:
(a) General facility and testing information
including:
(i) U.S. EPA
identification number;
(ii) Facility name,
contact person, telephone number, and address;
(iii) Person responsible
for conducting compliance testing, including company name, address, and
telephone number, and a statement of qualifications;
(iv) Dates of each
compliance test;
(v) Description of boiler
or industrial furnace tested;
(vi) Person responsible
for quality assurance or quality control, title, and telephone number, and
statement that procedures prescribed in the quality assurance or quality
control plan submitted under paragraph (C)(2)(c) of this rule have been
followed, or a description of any changes and an explanation of why changes
were necessary;
(vii) Description of any
changes in the unit configuration prior to or during testing that would alter
any of the information submitted in the prior notice of compliance testing
under paragraph (C)(2) of this rule, and an explanation of why the changes were
necessary;
(viii) Description of any
changes in the planned test conditions prior to or during the testing that
alter any of the information submitted in the prior notice of compliance
testing under paragraph (C)(2) of this rule, and an explanation of why the
changes were necessary; and
(ix) The complete report
on results of emissions testing.
(b) Specific information on each test including:
(i) Purposes of test
(e.g., demonstrate conformance with the emissions limits for particulate
matter, metals, hydrogen chloride, chlorine gas, and carbon
monoxide).
(ii) Summary of test
results for each run and for each test including the following
information:
(a) Date of
run;
(b) Duration of
run;
(c) Time-weighted average
and highest hourly rolling average carbon monoxide level for each run and for
the test;
(d) Highest hourly
rolling average hydrocarbon level, if hydrocarbon monitoring is required for
each run and for the test;
(e) If dioxin and furan
testing is required under paragraph (E) of rule 3745-266-104 of the
Administrative Code, time-weighted average emissions for each run and for the
test of chlorinated dioxin and furan emissions, and the predicted maximum
annual average ground level concentration of the toxicity equivalency
factor;
(f) Time-weighted average
particulate matter emissions for each run and for the test;
(g) Time-weighted average
hydrogen chloride and chlorine gas emissions for each run and for the
test;
(h) Time-weighted average
emissions for the metals subject to regulation under rule 3745-266-106 of the
Administrative Code for each run and for the test;
(i) Quality assurance or
quality control results.
(c) Comparison of the actual emissions during each test with the
emissions limits prescribed by rules 3745-266-105, 3745-266-106, 3745-266-107,
and paragraphs (B), (C), and (E) of rule 3745-266-104 of the Administrative
Code and established for the facility in the certification of precompliance
under paragraph (B) of this rule.
(d) Determination of operating limits based on all valid runs of
the compliance test for each applicable parameter listed in paragraph (C)(1) of
this rule using any of the following procedures:
(i) Instantaneous limits.
A parameter may be measured and recorded on an instantaneous basis (i.e., the
value that occurs at any time) and the operating limit specified as the
time-weighted average during all runs of the compliance test; or
(ii) Hourly rolling
average basis.
(a) The limit for a
parameter may be established and "continuously monitored" on an
"hourly rolling average" basis defined as follows:
(i) A "continuous
monitor" is one which continuously samples the regulated parameter without
interruption, and evaluates the detector response at least once each fifteen
seconds, and computes and records the average value at least every sixty
seconds.
(ii) An "hourly
rolling average" is the arithmetic mean of the sixty most recent
one-minute average values recorded by the continuous monitoring
system.
(b) The operating limit
for the parameter shall be established based on compliance test data as the
average over all test runs of the highest hourly rolling average value for each
run.
(iii) Rolling average
limits for carcinogenic metals and lead. Feed rate limits for the carcinogenic
metals (i.e., arsenic, beryllium, cadmium, and chromium) and lead may be
established either on an hourly rolling average basis as prescribed by
paragraph (C)(4)(d)(ii) of this rule or on (up to) a twenty-four hour rolling
average basis. If the owner or operator elects to use an averaging period from
two to twenty-four hours, the owner or operator shall include the following in
determining those limits:
(a) The feed rate of each
metal shall be limited at any time to ten times the feed rate that would be
allowed on an hourly rolling average basis;
(b) The continuous
monitor shall meet the following specifications:
(i) A continuous monitor
is one which continuously samples the regulated parameter without interruption,
and evaluates the detector response at least once each fifteen seconds, and
computes and records the average value at least every sixty
seconds.
(ii) The "rolling
average" for the selected averaging period is the arithmetic mean of one
hour block averages for the averaging period. A "one hour block
average" is the arithmetic mean of the one minute averages recorded during
the sixty-minute period beginning at one minute after the beginning of
preceding clock hour.
(c) The operating limit
for the feed rate of each metal shall be established based on compliance test
data as the average over all test runs of the highest hourly rolling average
feed rate for each run.
(iv) Feed rate limits for
metals, total chloride and chlorine, and ash. Feed rate limits for metals,
total chlorine and chloride, and ash are established and monitored by knowing
the concentration of the substance (i.e., metals, chloride or chlorine, and
ash) in each feedstream and the flow rate of the feedstream. To monitor the
feed rate of these substances, the flow rate of each feedstream shall be
monitored under the continuous monitoring requirements of paragraph (C)(4)(d)
of this rule.
(e) Certification of compliance statement. The following
statement shall accompany the certification of compliance:
"I certify under penalty of law that
this information was prepared under my direction or supervision in accordance
with a system designed to ensure that qualified personnel properly gathered and
evaluated the information and supporting documentation. Copies of all emissions
tests, dispersion modeling results and other information used to determine
conformance with the requirements of paragraph (C) of rule 3745-266-103 of the
Administrative Code are available at the facility and can be obtained from the
facility contact person listed above. Based on my inquiry of the person or
persons who manages the facility, or those persons directly responsible for
gathering the information, the information submitted is, to the best of my
knowledge and belief, true, accurate, and complete. I am aware that there are
significant penalties for submitting false information, including the
possibility of fine and imprisonment for knowing violations. I also acknowledge
that the operating conditions established in this certification pursuant to
paragraph (C)(4)(d) of rule 3745-266-103 of the Administrative Code are
enforceable limits at which the facility can legally operate during permit by
rule until a revised certification of compliance is submitted."
(5) Special requirements
for hydrocarbon monitoring systems. When an owner or operator is required to
comply with the hydrocarbon controls in paragraph (C) of rule 3745-266-104 of
the Administrative Code or paragraph (A)(5)(a)(iv) of this rule, a conditioned
gas monitoring system may be used in conformance with specifications in the
appendix to this rule provided that the owner or operator submits a
certification of compliance without using extensions of time in paragraph
(C)(7) of this rule.
(6) Special operating
requirements for industrial furnaces that recycle collected particulate matter.
Owners and operators of industrial furnaces that recycle back into the furnace
particulate matter from the air pollution control system shall:
(a) When complying with paragraph (C)(3)(b)(i) of this rule,
comply with the operating requirements prescribed in "Alternative Method
to Implement the Metals Controls" in the appendix to this rule;
and
(b) When complying with paragraph (C)(3)(b)(ii) of this rule,
comply with the operating requirements prescribed by paragraph (C)(3)(b)(ii) of
this rule.
(7) Extensions of
time.
(a) If the owner or operator does not submit a complete
certification of compliance for all of the applicable emissions standards of
rules 3745-266-104, 3745-266-105, 3745-266-106, and 3745-266-107 of the
Administrative Code on or before thirty days after December 7, 2004, or on or
before thirty days after the effective date of any new, amended, or rescinded
rule or statute that renders the owner or operator of the boiler or industrial
furnace subject to this rule, the owner or operator shall do any of the
following:
(i) Stop burning
hazardous waste and begin closure activities under paragraph (L) of this rule
for the hazardous waste portion of the facility; or
(ii) Limit hazardous
waste burning only for purposes of compliance testing (and pretesting to
prepare for compliance testing) for a total period of seven hundred twenty
hours for the period of time beginning on December 7, 2004, or on the effective
date of any new, amended, or rescinded rule or statute that renders the owner
or operator of the boiler or industrial furnace subject to this rule, submitted
a notification to the director by thirty days after December 7, 2004, or by
thirty days after the effective date of any new, amended, or rescinded rule or
statute that renders the owner or operator of the boiler or industrial furnace
subject to this rule, stating that the facility is operating under restricted
permit by rule and intends to resume burning hazardous waste, and submitted a
complete certification of compliance within two years of December 7, 2004, or
within two years after the effective date of any new, amended, or rescinded
rule or statute that renders the owner or operator of the boiler or industrial
furnace subject to this rule; or
(iii) Obtain a
case-by-case extension of time under paragraph (C)(7)(b) of this
rule.
(b) The owner or operator may request a case-by-case extension of
time to extend any time limit in paragraph (C) of this rule if compliance with
the time limit is not practicable for reasons beyond the control of the owner
or operator.
(i) In granting an
extension, the director may apply conditions as the facts warrant to ensure
timely compliance with this rule and that the facility operates in a manner
that does not pose a hazard to human health and the environment;
(ii) When an owner or
operator requests an extension of time to enable the facility to comply with
the alternative hydrocarbon provisions of paragraph (F) of rule 3745-266-104 of
the Administrative Code and obtain an installation and operation permit because
the facility cannot meet the hydrocarbon limit of paragraph (C) of rule
3745-266-104 of the Administrative Code:
(a) In considering
whether to grant the extension, the director shall both:
(i) Determine whether the
owner or operator has submitted in a timely manner a complete "Part
B" permit application that includes information required under paragraph
(C)(9)(b) of rule 3745-50-44 of the Administrative Code; and
(ii) Consider whether the
owner or operator has made a good faith effort to certify compliance with all
other emission controls, including the controls on dioxins and furans of
paragraph (E) of rule 3745-266-104 of the Administrative Code and the controls
on particulate matter, metals, and hydrogen chloride or chlorine
gas.
(b) If an extension is
granted, as a condition of the extension, the director shall require the
facility to operate under flue gas concentration limits on carbon monoxide and
hydrocarbon that, based on available information, including information in the
"Part B" permit application, are baseline carbon monoxide and
hydrocarbon levels as determined by paragraph (F) of rule 3745-266-104 of the
Administrative Code.
(8) Revised certification
of compliance. The owner or operator may submit at any time a revised
certification of compliance (recertification of compliance) under the following
procedures:
(a) Prior to submittal of a revised certification of compliance,
hazardous waste may not be burned for more than a total of seven hundred twenty
hours under operating conditions that exceed those established under a current
certification of compliance, and such burning may be conducted only for
purposes of determining whether the facility can operate under revised
conditions and continue to meet the applicable emissions standards of rules
3745-266-104, 3745-266-105, 3745-266-106, and 3745-266-107 of the
Administrative Code.
(b) At least thirty days prior to first burning hazardous waste
under operating conditions that exceed those established under a current
certification of compliance, the owner or operator shall notify the director
and submit the following information:
(i) U.S. EPA
identification number, and facility name, contact person, telephone number, and
address;
(ii) Operating conditions
that the owner or operator is seeking to revise and description of the changes
in facility design or operation that prompted the need to seek to revise the
operating conditions;
(iii) A determination
that when operating under the revised operating conditions, the applicable
emissions standards of rules 3745-266-104, 3745-266-105, 3745-266-106, and
3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code are not likely to be exceeded. To
document this determination, the owner or operator shall submit the applicable
information required under paragraph (B)(2) of this rule;
(iv) Complete emissions
testing protocol for any pretesting and for a new compliance test to determine
compliance with the applicable emissions standards of rules 3745-266-104,
3745-266-105, 3745-266-106, and 3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code when
operating under revised operating conditions. The protocol shall include a
schedule of pre-testing and compliance testing. If the owner or operator
revises the scheduled date for the compliance test, the owner or operator shall
notify the director in writing at least thirty days prior to the revised date
of the compliance test;
(c) Conduct a compliance test under the revised operating
conditions and the protocol submitted to the director to determine compliance
with the applicable emissions standards of rules 3745-266-104, 3745-266-105,
3745-266-106, and 3745-266-107 of the Administrative Code; and
(d) Submit a revised certification of compliance under paragraph
(C)(4) of this rule.
(D) Periodic recertifications. The owner
or operator shall conduct compliance testing and submit to the director a
recertification of compliance under provisions of paragraph (C) of this rule
within five years from submitting the previous certification or
recertification. If the owner or operator seeks to recertify compliance under
new operating conditions, the owner or operator shall comply with paragraph
(C)(8) of this rule.
(E) Noncompliance with certification
schedule. If the owner or operator does not comply with the compliance schedule
in paragraphs (B), (C), and (D) of this rule, hazardous waste burning shall
terminate on the date that the deadline is missed, closure activities shall
begin under paragraph (L) of this rule, and hazardous waste burning may not
resume except under an operating permit issued under rule 3745-50-66 of the
Administrative Code. For purposes of compliance with the closure provisions of
paragraph (L) of this rule, paragraph (D)(2) of rule 3745-66-12, and rule
3745-66-13 of the Administrative Code, the boiler or industrial furnace has
received "the known final volume of hazardous waste" on the date that
the deadline is missed.
(F) Start-up and shut-down. Hazardous
waste [except waste fed solely as an ingredient under the "Tier I"
(or "Adjusted Tier I") feed rate screening limits for metals and
chloride or chlorine] shall not be fed into the device during start-up and
shut-down of the boiler or industrial furnace, unless the device is operating
within the conditions of operation specified in the certification of
compliance.
(G) Automatic waste feed cutoff. During
the compliance test required by paragraph (C)(3) of this rule, and upon
certification of compliance under paragraph (C) of this rule, a boiler or
industrial furnace shall be operated with a functioning system that
automatically cuts off the hazardous waste feed when the applicable operating
conditions specified in paragraphs (C)(1)(a) and (C)(1)(e) to (C)(1)(m) of this
rule deviate from those established in the certification of compliance. In
addition, the boiler or industrial furnace shall be operated as
follows:
(1) To minimize emissions
of organic compounds, the minimum combustion chamber temperature (or the
indicator of combustion chamber temperature) that occurred during the
compliance test shall be maintained while hazardous waste or hazardous waste
residues remain in the combustion chamber, with the minimum temperature during
the compliance test determined to be either:
(a) If compliance with the combustion chamber temperature limit
is based on an hourly rolling average, the minimum temperature during the
compliance test is considered to be the average over all runs of the lowest
hourly rolling average for each run; or
(b) If compliance with the combustion chamber temperature limit
is based on an instantaneous temperature measurement, the minimum temperature
during the compliance test is considered to be the time-weighted average
temperature during all runs of the test; and
(2) Operating parameters
limited by the certification of compliance shall continue to be monitored
during the cutoff, and the hazardous waste feed shall not be restarted until
the levels of those parameters comply with the limits established in the
certification of compliance.
(H) Fugitive emissions. Fugitive
emissions shall be controlled by any of the following:
(1) Keeping the
combustion zone totally sealed against fugitive emissions; or
(2) Maintaining the
combustion zone pressure lower than atmospheric pressure; or
(3) An alternate means of
control that the owner or operator can demonstrate fugitive emissions control
equivalent to maintenance of combustion zone pressure lower than atmospheric
pressure. Support for such demonstration shall be included in the operating
record.
(I) Changes. A boiler or industrial
furnace shall cease burning hazardous waste when changes in combustion
properties, or feed rates of the hazardous waste, other fuels, or industrial
furnace feedstocks, or changes in the boiler or industrial furnace design or
operating conditions deviate from the limits specified in the certification of
compliance.
(J) Monitoring and
inspections.
(1) At a minimum, the
owner or operator shall monitor and record the following while burning
hazardous waste:
(a) Feed rates and composition of hazardous waste, other fuels,
and industrial furnace feedstocks, and feed rates of ash, metals, and total
chloride and chlorine as necessary to ensure conformance with the certification
of precompliance or certification of compliance;
(b) Carbon monoxide, oxygen, and if applicable, hydrocarbons, on
a continuous basis at a common point in the boiler or industrial furnace
downstream of the combustion zone and prior to release of stack gases to the
atmosphere in accordance with the operating limits specified in the
certification of compliance. Carbon monoxide, hydrocarbon, and oxygen monitors
shall be installed, operated, and maintained in accordance with methods
specified in the appendix to this rule.
(c) Upon the request of the director, sampling and analysis of
the hazardous waste (and other fuels and industrial furnace feedstocks as
appropriate) and the stack gas emissions shall be conducted to verify that the
operating conditions established in the certification of precompliance or
certification of compliance achieve the applicable standards of rules
3745-266-104, 3745-266-105, 3745-266-106, and 3745-266-107 of the
Administrative Code.
(2) The boiler or
industrial furnace and associated equipment (pumps, valves, pipes, fuel storage
tanks, etc.) shall be subjected to thorough visual inspection when such
equipment contains hazardous waste, at least daily for leaks, spills, fugitive
emissions, and signs of tampering.
(3) The automatic
hazardous waste feed cutoff system and associated alarms shall be tested at
least once every seven days when hazardous waste is burned to verify
operability, unless the owner or operator can demonstrate that weekly testing
will unduly restrict or upset operations and that less frequent inspections
will be adequate. Support for such demonstration shall be included in the
operating record. At a minimum, operational testing shall be conducted at least
once every thirty days.
(4) These monitoring and
inspection data shall be recorded and the records shall be placed in the
operating log.
(K) Recordkeeping. The owner or operator
shall keep in the operating record of the facility all information and data
required by this rule for five years.
(L) Closure. At closure, the owner or
operator shall remove all hazardous waste and hazardous waste residues
(including, but not limited to, ash, scrubber waters, and scrubber sludges)
from the boiler or industrial furnace and shall comply with rules 3745-66-11 to
3745-66-15 of the Administrative Code.
[Comment: For dates of non-regulatory government
publications, publications of recognized organizations and associations,
federal rules, and federal statutory provisions referenced in this rule, see
rule 3745-50-11 of the Administrative Code titled "Incorporated by
reference."]